![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the parts of the alimentary canal, in order.
|
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine.
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is in the esophagus?
|
Stratified squamous nonkeratinized.
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is in the mouth?
|
Stratified squamous.
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is in the pharynx?
|
Stratified squamous.
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is in the stomach?
|
simple columnar
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is in the small intestine?
|
simple columnar
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is in the large intestine?
|
Simple columnar
|
|
|
What type of cells are found along with the epithelium in the small intestine?
|
Paneth cells, goblet cells, enterocytes, and enteroendocrine cells.
|
|
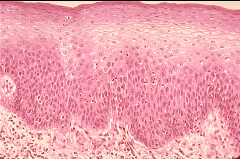
What part of the alimentary canal is this?
|
Mouth.
Simple stratified. |
|
What part of the alimentary canal is this?
|
Stomach.
|
|
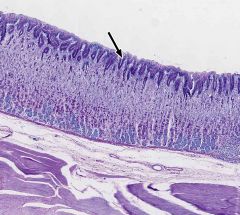
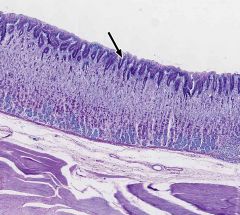
What part of the alimentary canal is this?
|
Esophagus.
Stratified squamous nonkeratinized. |
|
What part of the alimentary canal is this?
|
Stomach.
simple columnar |
|
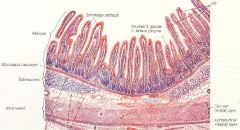
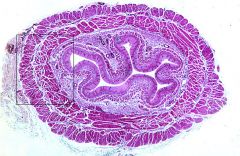
What part of the alimentary canal is this?
|
Small intestine.
Simple columnar |
|
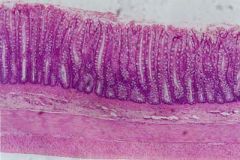
What part of the alimentary canal is this?
|
Large intestine.
Simple columnar |
|
|
Where are parietal cells located, and what do they do?
|
They are located in the stomach epithelium, and they secrete HCl.
|
|
|
What type of muscle is in the alimentary canal?
|
Smooth muscle.
Both circular and longitudinal. * The intestines have 'oblique' muscles that run at a slant to the canal. |
|
|
What are the muscles in the alimentary canal used for?
|
Moving food along (peristalsis), mixing food.
|
|
|
What do the circular muscles in the alimentary canal do?
|
Contract and relax.
(Like the tightening of a girdle) |
|
|
What do the longitudinal muscles in the alimentary canal do?
|
Contract and relax.
Shortens the height of the tube, making the canal wider. |
|
|
What are they layers of the alimentary canal?
|
There are four basic layers: starting at the innermost (closes to the food) there's the mucosa, then submucosa, then muscularis, then serosa.
|
|
|
What is the muscularis made up of?
|
The muscularis layer is made up of two distinct, concentric muscular layers, the *inner circular and the *outer longitudinal (named for the general direction of their muscle fibers).
|
|
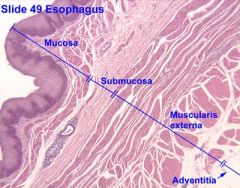
What do each of these parts do?
|
Mucosa:
- epithelium - lamina propria - muscularis mucosa Submucosa: - meissner's (submucosal) plexus Muscularis propria: - circular muscle (inner) - longitudinal muscle (outer) Serosa (or adventitia) |
|
|
The purpose of the villi in the intestine.
|
Absorption and increase surface area.
|
|
|
Function of amylase.
|
Break down carbs into sugars.
|
|
|
Name some of the glands associated with the digestive system.
|
Salivary glands, the liver secretes bile, the pancrease secretes an isosmotic fluid which helps buffer many enzymes into the small intestine.
|
|
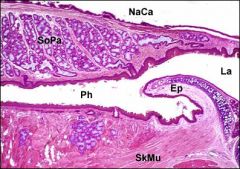
What part of the alimentary canal is this?
|
Pharynx.
|

