![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
116 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Starts mechanical breakdown of food through chewing activity. Salivary glands produce aqueous fluid containing digestive enzymes.
|
Oral Cavity
|
|
|
Begins breakdown of carbohydrates in the oral cavity.
|
Salivary Amylase
|
|
|
Wall contains skeletal muscle. Neuro or muscular disorders of this region cause dyspahgia.
|
Pharynx
|
|
|
This nerve controls vocals and swallowing.
|
Vagus
|
|
|
Food passes from the pharynx to here. It lies posterior to larynx/trachea. Upper 2/3 are lined with skeletal muscle. Lower 1/3 is lined with smooth muscle.
|
Esophagus
|
|
|
Digestive juices are secreted here and nutrient breakdown continues.
|
Stomach
|
|
|
Digested food products once they leave the stomach.
|
Chyme
|
|
|
1st section of the intestine. Plays an important role while the vast majority of its length absorbs digested nutrients.
|
Small intestine
|
|
|
Extracts a few more nutrients to form fecal material.
|
Large intestine
|
|
|
Stores and eliminates fecal material.
|
Anus
|
|
|
Innermost lining of the digestive tract. Made of simple columnar epithelium (secretory) and loose connective tissue (vascular).
|
Tunica Mucosa
|
|
|
Second layer of the digestive tract. Contains larger blood vessels and some nerve plexes.
|
Tunica Submucosa
|
|
|
Third and Fourth layers of the digestive tract. Includes smooth muscle in a circular and longitudinal layer.
|
Tunica Muscularis
|
|
|
Fifth layer of the digestive tract, also known as the visceral peritoneum. Made of simple squamous epithelium.
|
Tunica Serosa
|
|
|
Tasks of the digestive system.
(SPAMD) |
Secretion
Peristalsis. Absorption Motility Digestion |
|
|
Nerve beds that lie between tunics and connect with PNS and SNS innervation.
|
Enteric Plexus
|
|
|
Structures of the GI tract innervated by PNS.
|
Smooth muscle in wall of gut.
Digestive glands. |
|
|
Effect of PNS innervation on smooth muscle in wall of gut.
|
Increased peristalsis
|
|
|
Effect of PNS innervation on digestive glands.
|
Stimulates release of digestive secretions.
|
|
|
PNS Nerve pathways
|
Vagus nerve and Sacral Parasympathetic Splanchnic Nerves
|
|
|
Nerve that innervates foregut to midgut (esophagus to transverse colon).
|
Vagus
|
|
|
Nerves that originate from S2-S4 and innervate the descending colon to the rectum, bladder, and pelvic organs.
|
Sacral Parasympathetic Splanchnic Nerves.
|
|
|
Digestive structures innervated by the SNS.
|
Arteries, arterioles, and digestive sphincters.
|
|
|
Effects of SNS stimulation on digestive arteries/arterioles.
|
alpha-1 receptors shunt blood away from the GI tract during fight or flight response.
|
|
|
Effects of SNS stimulation on digestive sphincters.
|
alpha-1 receptors cause sphincters to constrict, stopping food from progressing through system.
|
|
|
Nerves that innervate branches of the celiac trunk, superior and inferior mesenteric arteries.
|
Sympathetic Splanchnic Nerves
|
|
|
Inferior portion of the esophagus that joins with the stomach. When food enters the stomach, stomach releases enzymes and acid, this closes to prevent reflux.
|
Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES), Gastroesophageal or Cardiac Sphincter.
|
|
|
This sphincter lies between the stomach and the 1st part of the small intestine. It's a thick band of smooth muscle and only relaxes when contents of the stomach have been digested and are ready to move forward.
|
Pyloric Sphincter
|
|
|
Folds within the stomach wall
|
Gastrin Rugae
|
|
|
These cells secrete hydrochloric acid into the gastric pits of the stomach.
|
Parietal Cells
|
|
|
These cells secrete pepsinogen into the gastric pits of the stomach.
|
Chief Cells
|
|
|
These cells secrete mucous that coats the inner lining of the stomach.
|
Mucus neck cells and surface epithelial cells.
|
|
|
Coordinated persitalsis of the 3 layers of smooth muscle in the tunica muscularis mixes ingested food with gastric secretions to form chyme.
|
Gastric Mixing
|
|
|
Molecules absorbed in the stomach
|
Alcohol
Aspirin Caffeine Very small amounts of water and electrolytes. |
|
|
A digestive enzyme secreted in inactive form.
|
Proenzyme
|
|
|
When pepsinogen is exposed to the acidic environment of the gastric contents it is convereted to it's active form known as....
|
Pepsin
|
|
|
Function of pepsin
|
Digests proteins into small chain fatty acids.
|
|
|
Functions of Hydrochloride
|
Activates pepsinogen (by keeping pH between 1-3)
Kills microorganisms Digests large proteins |
|
|
Mechanism for HCl secretion
|
CO2 from plasma (or generated in parietal cells) combines with H2O to make HCO3 + H.
H is pumped into gastric lumen via active transport. HCO3 is diffused out at the same time Cl from the plasma is pumped thru to the gastric lumen. |
|
|
Parasympathetic stimulation of enteric plexes via vagal stimulation.
|
Increased HCl + pepsinogen secretion, Release of gastrin
|
|
|
Secreted by G cells in stomach and duodenum in response to the presence of food.
|
Gastrin
|
|
|
Function of Gastrin
|
Stimulates HCl and pepsinogen secretion
|
|
|
Chemical released by Mast cells during inflammation
|
Histamine
|
|
|
Effect of histamine on H2 receptors in gastric epithelium
|
Enhances HCl secretion by enhancing the effects of ACh and gastrin.
Makes the environment less hospitable to ingested microorganisms. |
|
|
Function of mucus in the GI tract
|
Protects lining against mechanical injury.
Forms physical barrier between luminal contents and lining. |
|
|
Regulation of mucus secretion
|
Irritation = increased mucus
Prostaglandins = increased mucus |
|
|
Effect of NSAIDs on mucus
|
NSAIDS inhibit prostaglandins, thus inhibiting mucus sections, causing ulcer disease.
|
|
|
Secreted by pareital cells.
Required for vitamin B12 absorption |
Intrinsic Factor
|
|
|
Divisions of the small intestine
|
Duodenum
Jejunum Ileum |
|
|
6 inch section that forms a c-shaped loop from the stomach to the main part of the small intestine.
|
Duodenum
|
|
|
Function of the duodenum
|
Absorption of lipids
Some absorption of proteins and sugars Absorption of iron and calcium |
|
|
Function of the jejunum and ileum
|
Absorption of digested nutrients (sugars/proteins)
Vitamin and minteral absorption Sodium and water absorption *Deep circular folds and microvilli allow for increased absorption* |
|
|
1st segment of Large Intestine, collects chyme from the ileum. A pouch that hangs down below the point where the large and small intestine join.
|
Caecum
|
|
|
Valve that prevents chyme from refluxing into the small intestine.
|
Ileocecal valve
|
|
|
Small appendage to caecum (RLQ). Has small lumen that can trap chyme or bacteria.
|
Appendix
|
|
|
Parts of the colon
|
Ascending Colon
Transverse Colon Descending Colon Sigmoid Colon |
|
|
Terminal section of digestive tract. Forms straight tube that descends into pelvis.
|
Rectum
|
|
|
Function of the large intestine
|
Water and electrolyte absorption (Na and Cl)
Bicarbonate secretion Absorption of vitamins produced by intestinal flora. |
|
|
For every molecule of Cl absorbed, the tunica mucosa secretes one molecule of this. Its alkalinity neutralizes acid produced by GI bacteria.
|
Bicarbonate
|
|
|
These bacteria produce vitamins that must be absorbed because our daily intake is not enough.
|
Natural Flora
|
|
|
Located in the upper quadrant of the abdomen, just behind the stomach.
|
Pancreas
|
|
|
Small secretory sacs that are embedded in the body of the pancreas
|
Acini (Acinar sacs)
|
|
|
Pancreatic secretions produced in the acini flow into a central conduit called...
Delivers secretions to the duodenum. |
Pancreatic Duct
|
|
|
Smooth muscle sphincter that sits at the opening of the common duct shared by the pancreatic and common bile ducts.
Is a valve-like organ that contracts to prevent flow of bile and pancreatic secretions into the duodenum when no food is present. |
Sphincter of Oddi
|
|
|
Cells in the pancreatic duct that secrete sodium bicarbonate
|
Duct Cells
|
|
|
Cells in the pancreatic duct that secrete digestive enzymes
|
Acinar Cells
|
|
|
Secreted as proenzymes into the acini.
Responsible for the digestion of protein in our diet. |
Proteases
|
|
|
Activation of proenzymes from the pancreas occurs here.
Proenzymes enter the pancreatic duct and are secreted into THIS through the sphincter of Oddi. |
Duodenum
|
|
|
Proenzymes (Proteases)
|
Trypsinogen
Chymotrypsinogen Procarboxypeptidase |
|
|
Activated by enzymes present in the cells that line the duodenum.
Can activate surrounding proenzyme. Inhibitor required to prevent accidental activation while still inside pancreas. |
Trypsinogen (Trypsin)
|
|
|
Activated in the duodenum by Trypsin
|
Chymotrypsinogen (Chymotrypsin)
Procarboxypeptidase (carboxypeptidase) |
|
|
Responsible for carbohydrate digestion.
Breaks down polysaccharides into disaccharides that can be absorbed in intestine. Secreted in active form. |
Pancreatic Amylase
|
|
|
Secreted by acinar cells that are responsible for lipid digestion.
Breaks down TAGs into absorbable fatty acids. Secreted in active form. |
Pancreatic Lipase
*safe to secrete in active form because pancreas is all protein* |
|
|
Alkaline fluid secreted with the pancreatic enzymes (1-2L/day)
|
Sodium Bicarbonate
|
|
|
Function of Sodium Bicarbonate (Alkaline)
|
Prevents inactivation of pancreatic enzymes in the duodenum.
|
|
|
Stimulates release of sodium bicarbonate.
Secreted from duodenal mucosal cells. |
Secretin (exocrine)
|
|
|
Stimulates release of pancreatic enzymes, in response to fat in the duodenum
|
Cholecystokinin (CKK)
|
|
|
How secretin works
|
Acid in duodenum > secretin release from duodenal mucosa > secretin transported in blood > pancreatic duct cells secrete aqueous Sodium Bicarbonate solution into duodenal lumen.
|
|
|
How CCK works
|
Fat (and protein) in duodenal lumen > CCK release from duodenal mucosa > CCK transported in blood > Acinar cells secrete pancreatic enzymes into duodenal lumen.
|
|
|
Number of liver lobes
|
4
|
|
|
Duct that drains bile that is produced by liver
|
Hepatic duct
|
|
|
Duct that carries bile from the hepatic/cystic ducts toward the duodenum
|
Common bile duct
|
|
|
Stores bile until sphincter of Oddi relaxes
|
Gall bladder
|
|
|
Duct that comes from the gallbladder and joins the hepatic duct
|
Cystic Duct
|
|
|
Stimulates the gallbladder to contract and relaxes the sphincter of Oddi
|
Cholecystokinin
|
|
|
System of veins that drains blood from digestive organs to liver
|
Hepatic Portal System
|
|
|
Hepatic Portal System drains into large vein that enters the liver
|
Hepatic Portal Vein
|
|
|
Another name for hepatic capillaries
|
hepatic sinusoids
|
|
|
Once blood is filtered in the liver it drains into this.
|
Hepatic Veins
|
|
|
Hepatic veins drain into this.
|
Inferior vena cava.
|
|
|
Hepatic sinusoids are fed by the hepatic portal vein and are mode of these cells
|
Endothelial Cells
|
|
|
Resident macrophages of the liver.
Line sinusoids, waiting for bacteria/Old RBCs to phagocytose. |
Kupffer cells
|
|
|
Carry venous blood from digestive system.
Nutrients and other molecules can diffuse into hepatocytes through these. |
Vascular Channels
|
|
|
Some of the absorbed substances from the blood are converted into bile that is then secreted through theses channels.
Run in opposite direction of Vascular Channels. Eventuall converge to form hepatic duct. |
Biliary Channels.
|
|
|
Functions of the Liver
|
Carbohydrate Metabolism Protein Metabolism
Lipid Metabolism Formation of Plasma Proteins Detoxificatino of body waste products, hormones, and other foreign compounds Storage of Vitamins Activation of Vitamin D Storage of Iron as Ferritin Removal of bacteria and old RBCs Excretion of cholesterol in bile Excretion of bilirubin in bile |
|
|
Carbohydrate metabolism in the liver
|
Stores glycogen
Gluconeogenesis |
|
|
Protein Metabolism in the liver
|
Deamination of amino acids
Formation of urea from ammonia Forms lipoproteins (HDL, LDL, VLDL) |
|
|
Lipid Metabolism in the liver
|
Oxidation of fatty acids
Synthesis of TAGs from carbohydrates and proteins Synthesis of cholesterol and phospholipids |
|
|
Formation of plasma proteins in the liver
|
Albumin
Clotting proteins/factors Inflammatory proteins (complement and kinin) |
|
|
Detoxification in the liver
|
Liver metabolizes some drugs. Byproducts are either excreted into the bile or back into the blood to be removed by kindeys.
Heavy metals can't be metabolized and are stored in hepatocytes. |
|
|
Storage of Vitamins in the liver
|
A, D, B12
|
|
|
Activation of vitamin D in the liver
|
Necessary for calcium absorption in the intestine.
Promotes calcium deposition in the bones |
|
|
Removal of bacteria and old RBCs in the liver
|
Liver assists spleen in the removal of bacteria that have invaded the blood stream as well as old an injured RBCs.
Kupffer cells are responsible. |
|
|
Excretion of cholesterol in the bile
|
Excess cholesterol is taken up by hepatocytes and secreted in the biliary channels as a constituent of bile
|
|
|
Excretion of bilirubin in bile
|
Unconjugated bilirubin is water soluble and cannot be secreted into the bile.
Converted by hepatocytes to conjugated bilirubin through action of glucoronic acid. |
|
|
Greenish-yellow secretion from hepatocytes
Serves as medium for excreting some plasma substances Plays a role in digestion |
Bile
|
|
|
Constituents of Bile
|
Sodium Bicarbonate
Bile salts Cholesterol Lecithin Bilirubin |
|
|
Complex molecule formed of different lipids and phosphoric acid. Has positive charge that prevents the fat droplets from aggregating back into larger particles.
|
Lecithin
|
|
|
Pigment released from the hemoglobin that is later removed from the body by the liver.
|
Bilirubin
|
|
|
Function of bile salts
|
Lipid emulsification
Micelle formation |
|
|
The act of breaking up large globules of fat into smaller droplets.
Necessary precursor to fat digestion because pancreatic lipase can only work on the outer surface of the fat droplet |
Lipid Emulsification
|
|
|
Complexes of bile salts and other nutrient molecules.
Make nutrient molecules more readily absorbable. Bile salt + lecithin...absorbable through intestinal lining. |
Micelles
|
|
|
Formed from cholesterol.
Have water soluble portion and a lipid soluble portion. |
Bile Salts
|
|
|
Excreted in bile.
Can aggregate and form gallstones. |
Cholesterol
|
|
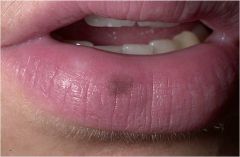
Simply a change in skin color 1 cm or less, without any elevation or depression in relation to the adjacent skin (Freckles, tattoos, hyperpigmentation, purpura)
|
Macule
|
|
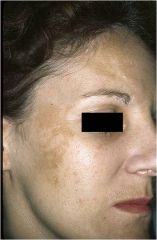
Large macules greater than 1 cm in size, without any elevation or depression in relation to the adjacent skin
(Vilitigo, vascular nevus (“salmon patch”), nevus flammeus) |
Patch
|

