![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the definition of a ruminant?
|
An animal with 4 complete stomach compartments that regurgitates undigested food from the rumen and masticates it at rest
|
|
|
What are the 3 forestomachs?
|
Rumen
Reticulum Omasum |
|
|
What is the true glandular stomach?
|
Abomasum
|
|
|
What does the process of rumination involve?
|
Regurgitation
Mastication Ensalivation Reswallowing |
|
|
Why does a ruminant need to ruminate?
|
The plant material it ingests has low digestibility (high in fibre) which cannot effectively be broken down by animal itself
|
|
|
What is the rumen capacity of an adult dairy cow?
|
>80 litres
|
|
|
Where does the rumen extend to cranially and caudally?
|
Cranially - 8th rib at cardia
Caudally - pelvic brim |
|
|
What is the structure and function of the internal rumen?
|
Covered in papilla, "carpet-like"
Increases surface area for fermentation and some absorption Also storage and mechanical breakdown of food |
|
|
What type of epithelium is found in the rumen?
|
Stratified squamous
|
|
|
Where is the reticulum found?
|
Cranial to rumen, caudal to diaphragm
Between 6-9th intercostal space |
|
|
What is traumatic reticulitis?
|
Pieces of wire/objects are stuck near reticular wall causing abscesses near diaphragm, heat, pericardium (pericarditis)
|
|
|
What is the structure and function of the internal reticulum?
|
Covered in honeycomb papillae
Sorts food for further mastication or digestion |
|
|
What type of epithelium is found in the reticulum?
|
Stratified squamous
- protection and absorption |
|
|
Is the omasum firmly attached to anything?
|
Yes:
rumen, reticulum and abomasum |
|
|
On which side of the abdomen is the omasum found?
|
RHS
|
|
|
What is the structure and function of the omasum?
|
Internal laminae "bible pages"
Absorption of water, fatty acids, electrolytes, fermentation, regulation of flow into abomasum |
|
|
What type of epithelium is found in the omasum?
|
Stratified squamous
with muscular mucosa for squeezing water and electrolytes |
|
|
Where is the abomasum located in the body?
|
Ventral, slightly on RHS
|
|
|
What is the pH of the abomasum in ruminants?
|
2-3
|
|
|
What is the structure and function of the internal abomasum?
|
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Simple branched tubular glands Enzymatic digestion of proteins |
|
|
What is the gastric groove divided into in the ruminant?
|
Reticular groove
Omasal groove Abomasal groove |
|
|
Which side of the reticulum does the reticular groove travel down?
|
RHS
|
|
|
What is contraction of the reticular groove stimulated by?
|
Suckling reflex
Presentation of milk Chemicals in adults (e.g. copper sulphate) |
|
|
By what age is the rumen larger than the abomasum?
|
2 months
|
|
|
When is the rumen fully developed?
|
6-12 months
|
|
|
What happens if milk in unweaned animals stays in the rumen instead of the abomasum?
|
It curdles and goes off
|
|
|
What happens if you stomach tube a ruminant too far?
|
You will go past the reticular groove, thereby not stimulating it to contract and milk will go into the rumen instead of the abomasum
|
|
|
What is the jejunum suspended from the roof of the abdomen by?
|
Common dorsal mesentery
|
|
|
Which part of the duodenum is connected to the small colon and by what is it connected?
|
Ascending duodenum
Duodenocolic fold |
|
|
How is the ileum connected to the caecum?
|
Ileocaecal fold
|
|
|
Which way do the centripetal and centrifugal coils go?
|
Centripetal - towards centre
Centrifugal - away from centre |
|
|
Where does the lesser omentum go to and from?
|
From liver
To omasum and lesser curvature of abomasum |
|
|
Where does the greater omentum go to and from?
|
Deep - right longitudinal groove to duodenum
Superficial - greater curvature of abomasum and duodenum to left longitudinal wall |
|
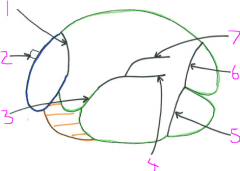
Left lateral view of exterior rumen
|
1 - rumenoreticular groove
2 - oesophagus 3 - cranial groove 4 - left longitudinal groove 5 - left ventral coronary groove 6 - left dorsal coronary groove 7 - left accessory groove |
|
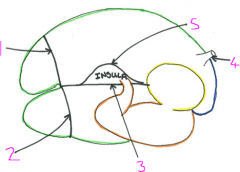
Right lateral view of exterior rumen
|
1 - right dorsal coronary groove
2 - right ventral coronary groove 3 - right longitudinal groove 4 - oesophagus 5 - right accessory groove |
|
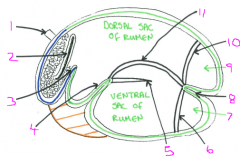
Left lateral view of internal rumen
|
1 - oesophagus
2 - reticular groove 3 - rumenoreticular fold 4 - cranial pillar 5 - right longitudinal pillar 6 - right ventral coronary pillar 7 - caudoventral blind sac 8 - caudal pillar 9 - caudodorsal blind sac 10 - right dorsal coronary pillar |
|
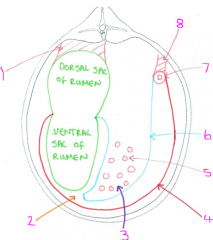
Greater omentum
|
1 - peritoneum of dorsal sac
2 - omental bursa 3 - omental recess 4 - superficial part of greater omentum 5 - jejunum 6 - deep part of greater omentum 7 - duodenum 8 - mesoduodenum |

