![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
93 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are carbohydrates? |

A molecule composed of carbon, hyrdrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. Are a quick source of energy for our bodies. |
|
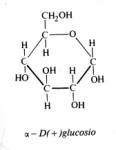
What is a single sugar unit called? |
A monosaccharide (ex. Glucose, fructose, and galactose) |
|
|
What is an isomer? |
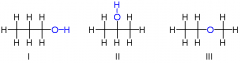
One of a group of chemicals that have the same chemical formula, but different chemical structure. |
|
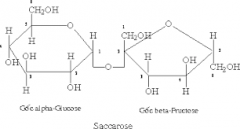
What is formed when two monosaccharides combine? |
A disaccharide (ex. sucrose, lactose, and maltose) |
|
|
What is the process of dehydration synthesis? |
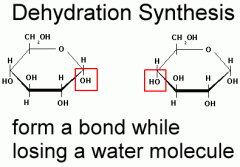
The process by which larger molecules are formed by the removal of water from two smaller molecules. |
|
|
What is the process by which larger molecules are split into smaller molecules by the addition of water called? (opposite of dehydration synthesis) |
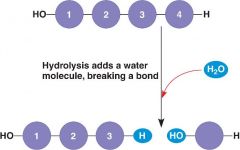
Hydrolysis |
|
|
What are polysaccharides? |
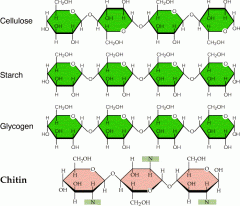
Carbohydrates composed of numerous single sugar units. (ex. cellulose, starch, and glycogen) |
|

What is a plant carbohydrate used to store energy? |
Starch |
|
|
What is glycogen? |
The form of carbohydrate storage in animals. In humans, it is stored in the liver, between the lungs, and between long muscles. |
|
|
What is a plant polysaccharide that makes up plant walls? (Hint: Humans can't digest it.) |

Cellulose |
|
|
What are triglycerides? |
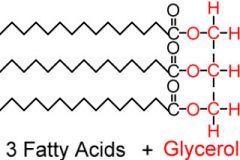
Lipids composed of a glycerol, and three fatty acids. |
|
|
Which lipid is solid at room temperature and contains saturated fatty acids? |

Fat (found mainly in food from animals) |
|

What are oils? (found mainly in food from plants). |
Lipids that are liquid at room temperature and contain unsaturated fatty acids. |
|
|
What is a chain of amino acids called? |

A protein. |
|
|
What is an amino acid? |
A chemical that contains nitrogen and can be linked together to form proteins. |
|
|
What is the bond that joins amino acids called? |
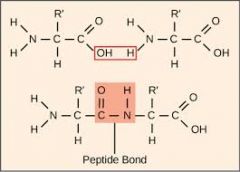
A peptide bond. |
|
|
What are polypeptides? |
A chain of three or more amino acids. |
|
|
What is the process that occurs when the bonds of a protein molecule are disrupted, causing a temporary change in shape? (also happens to enzymes when they are heated.) |
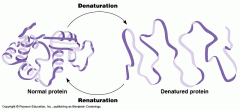
Denaturation. |
|

What is coagulation? |
The process that occurs when the bonds of a protein are disrupted, causing a permanent change in shape. |
|

What pH indicates an acidic solution? |
Any pH below 7. |
|

What pH indicates a neutral solution? |
7 |
|

What pH indicates a basic solution? |
Anything above 7. |
|
|
What functional groups do carbohydrates have? |
Aldehyde, Ketone, and Alcohol |
|
|
What functional groups do lipids have? |
Carboxyl, Alcohol, and Ester |
|
|
What functional groups do proteins have? |
Carboxyl, Alcohol, and Amino |
|
|
What is the aldehyde functional group composed of? |
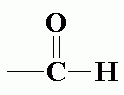
Carbon double bonded with oxygen, and bonded with hydrogen. |
|
|
What is the ketone functional group composed of? |
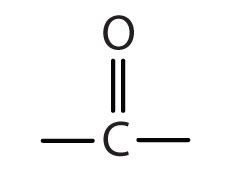
Carbon double bonded with oxygen. |
|
|
What is the carboxyl functional group composed of? |
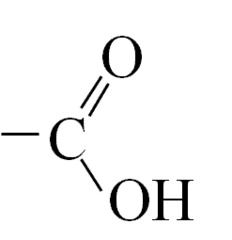
Carbon double bonded with oxygen, and bonded with hydroxide. |
|
|
What is the alcohol functional group composed of? |
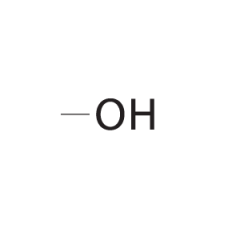
Bond with hydroxide. |
|
|
What is the amino functional group composed of? |
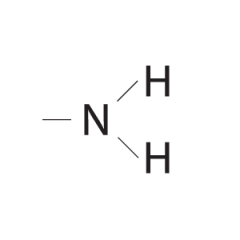
Nitrogen bonded with two hydrogens. |
|
|
What is the ester functional group composed of? |
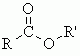
Carbon double bonded wtih oxygen, and bonded with oxygen. ('R' stands for carbon chain) |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that maintains the pH of the environment. |
|
|
What does Benedict's solution test identify, and what does a positive result look like? |
It tests for monosaccharides (reducing sugars), and a positive test turns from blue to yellow). |
|
|
What does the Iodine solution test identify, and what does a positive result look like? |
It tests for complex carbohydrates, and a positive test turns from brown to black or purple. |
|
|
What does the brown paper/transluscense test identify, and what does a positive result look like? |
It tests for lipids, and a positive test makes the brown paper turn transluscent, or slightly see through. |
|
|
What does the biuret test identify, and what does a positive result look like? |
It tests for proteins, and a positve test turns purple. The darker the purple, the more protein there is. |
|
|
What are nucleic acids made up of? |
Nucleotides |
|
|
What are nucleotides composed of? |
One sugar, one phosphate, and one nitrogen base. |
|
|
What are the only four possible nitrogen bases in nucleotides? |
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine. |
|
|
What are catalysts? |
A chemical that increases the rate of chemical reactions without altering the products or being altered itself. |
|
|
What is a protein catalyst that permits chemical reactions to proceed at low temperatures called? |
An enzyme. |
|
|
What is a substrate? |
A molecule on which an enzyme works. |
|
|
What is the area of an enzyme that combines with the substrate called? |
Active Site. |
|
|
What is a cofactor? |
An inorganic ion that helps an enzyme combine with a substrate molecule. |
|
|
What is an organic molecule synthesized from a vitamin that helps an enzyme to combine with a substrate molecule? (natural version of a cofactor) |
A coenzyme. |
|
|
What is a competitive inhibitor? |
A molecule with a shape complimentary to a specific enzyme that compets with the substrate for access to the active site of the enzyme. Is responsible for blocking chemical reactions. |
|
|
What is the inhibition of an enzyme in a metabolic pathway by the final product of that pathway called? |
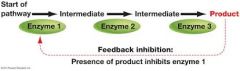
Feedback inhibition. |
|
|
What is alpha amylase? |
The enzyme found in the mouth produced by the salivary glands that breaks down complex carbohydrates. Works in a slightly acidic environment (6-7). |
|
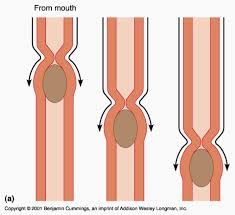
What is the rhythmic, wavelike contractions of muscle that move food along the digestive tract called? |
Peristalsis. |
|
|
What is a sphincter? |
A constrictor muscle that regulates the opening and closing of a tubelike structure. |
|
|
What is a protective and lubricative substance that is composed mostly of protein? |
Mucus |
|
|
What is pepsin? |
Pepsin is the protein-digesting enzyme produced in the stomach. In it's inactive form, it is called pepsinogen. |
|
|
What are the segments of the small intestine called? |
The duodenum, jejunum, and the ileum. |
|
|
What are villi? |
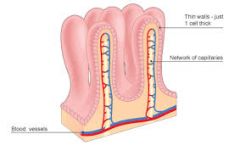
Small, fingerlike projections that extend into the small intestine to increase surface area and absorption. |
|
|
What cover the villi and increase the surface area and absortption of the small intestine even further? |
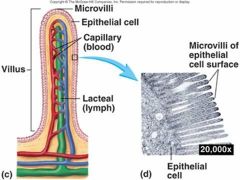
Microvilli. |
|
|
What is a capillary? |
A blood vessel that connects arteries and veins; the site of fluid and gas exchange. A vessel supplied to each villus along with a lymph vessel called a lacteal that transports materials. |
|
|
What is another protein digesting enzyme released from the pancreas called? |
Trypsin. |
|
|
What is lipase? |
A lipid-digesting enzyme released by the pancreas. |
|
|
What is the substance that is produced in the liver, stored in the gall bladder, and whose job is to emulsify large fat globules into smaller fat globules making them easier to absorb called? |
Bile. |
|
|
What is cholecystokinin? |
A hormone secreted by the small intestine that stimulates the release of pancreatic enzymes, and the release of bile. |
|
|
What are the segments of the large intestine? |
The cecum, the colon, and the rectum. |
|
|
What is gastrin? |
A hormone secreated by the stomach that stimulates the release of HCl. |
|
|
What is another name for the digestive tract? |
The alimentary canal. |
|
|
What are the major components of the digestion process? |
Injestion, digestion, absorption, and ejestion. |
|
|
What is injestion? |

The taking in of nutrients. |
|
|
What is digestion? |
The breakdown of organic molecules into smaller complexes. |
|
|
What is absorption? |
The transport of digested nutrietns to tissues of the body. |
|
|
What is ejestion? |
The removal of waste materials that can't be used by the body. |
|

How are the teeth used in digestion? |
They are involved in the mechanical digestion of food within the mouth. They breakdown, and increase the surface area of the food, making it easier for the rest of the digestive system to digest and absorb the food. Canines are used for tearing, incisors for biting, and molars for grinding. |
|
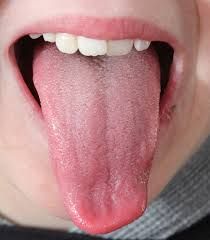
What is the tongue used for in digestion? |
It positions the food for chewing and swallowing, and it mixes the food with saliva forming it into a soft ball called a bolus. |
|
|
What's the difference between exocrine and endocrine glands? |
Exocrine glands are not a part of the blood stream (so they instead use ducts), whereas endocrine glands are. |
|
|
What is the pharynx? |
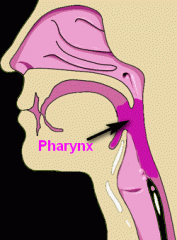
Where the mouth and the nose join. |
|
|
What is the flap that closes the opening to the trachea when swalling so that food goes down the esophagus called? |
The epiglottis. |
|
|
What helps the bolus (other than peristalsis) move from the mouth to the stomach within the esophagus? |
Mucin secreted from glands lubricating the esophogus. |
|
|
Why does the stomach need to have an acidic environment? |
An acidic environment within the stomach kills bacteria and activates the enzyme pepsinogen turning it into pepsin (the enzyme in charge of breaking down proteins). |
|
|
What other enzyme is present in the stomach in order to break down milk proteins? |
Rennin. |
|
|
What is the sphincter going into the stomach, and what is the sphincter going out of the stomach? |
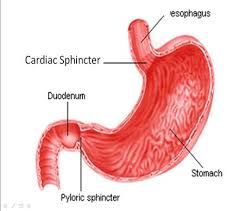
The cardiac spincter allows food to enter the stomach, the pyloric sphinter allows food to leave the stomach. |
|
|
What is chyme? |
The name for the semi-liquid state that food leaves the stomach in. |
|
|
What connective tissue holds the small intestine in place? |
Messentary. |
|
|
What occurs in the different parts of the small intestine? |
Digestion occurs in the duodenum (digests all three food types - protein, lipid, and carbohydrate), while absorption occurs in the jejunum and the ileum. |
|
|
What hormone from the small intestine causes the pancrease to release a buffer known as sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3)? |
Secretin. |
|
|
What does sodium bicarbonate do in the duodenum? |
Raises the pH of the environment, bringing it to a more basic level. This helps deactivate certain enzymes, and activate others. |
|
|
What is Beta Amylase? |
Amylase that is found in the small intestine secreted from the pancreas. Works in a more basic environment, and continues to break starch down. |
|
|
What does insulin do? |
Excreted by the pancreas, it decreases levels of glucose in the blood and maintains blood sugar levels. |
|
|
What does glucagon do? |
Produced by the pancreas, it raises the level of sugar in the blood. |
|
|
What is the liver? |
The largest organ gland in the body. Performs vital function such as: -producing and storing important chemicals. -converting glycogen into sugar. -producing bile. -deaminating amino acids to form urea. -metabolizing toxic substance (such as alcohol) |
|
|
What is the appendix? |
A vestigal organ in humans, however in herbivores is used to digest cellulose. Attatched to the cecum. |
|
|
What is the sphincter in between the ileum and the cecum called? |
The ileocaecal sphincter. |
|
|
What is the large intestine's job? |
To absorb water. |
|
|
What is the final sphincter in the digestive system? |
The anal sphincter. |
|
|
What are hormones? |
Chemicals carried in the blood which help regulate body functions. |
|
|
If glucose concentration in the liver is high, what is it converted into? |
Glycogen |
|
|
What are the two control mechanisms of the digestive system? |
The sympathetic and the parasympethetic nervous system. |

