![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diffusion |
As the net movement of particles from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration down a concentration gradient, as a result of their random movement. The energy for diffusion comes fromthe kinetic energy of random movement ofmolecules and ions. |
|
|
Examples of diffusion down concentration gradients |
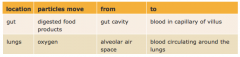
Substances move into and out of cells by diffusion through the cell membrane |
|
|
Factors that influencediffusion |
Surface Area-with a larger surface area, molecules have more surfaces through which to diffuse, this increases the rate of moment Temperature-Increased temperature means increased kinetic energy- means molecules collide with the cell membrane more often making movement through it more likely. Concentration Gradients- the difference between the concentration inside and outside of the cell. The bigger the difference is the more opportunity molecules have of diffusing. Distance-The rate of diffusion is increased when the distance is decreased as molecules have to travel less |
|
|
Brownian Motion |
Theory that says that particles move in random directions constantly.When it bumps into another particle,it changes direction. |

