![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
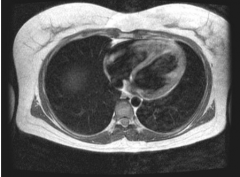
Does the above axial MRI sections through the thorax show contents of the superior or the inferior mediastinum?
|
Inferior mediastinum.
|
|
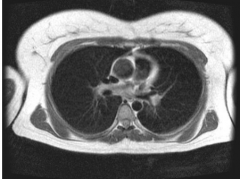
Does the above axial MRI sections through the thorax show contents of the superior or the inferior mediastinum?
|
Inferior mediastinum.
|
|
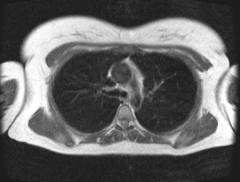
Does the above axial MRI sections through the thorax show contents of the superior or the inferior mediastinum?
|
Superior mediastinum.
|
|
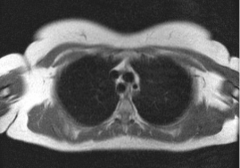
Does the above axial MRI sections through the thorax show contents of the superior or the inferior mediastinum?
|
Superior mediastinum.
|
|
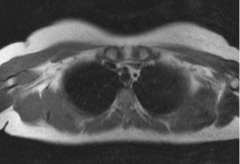
Does the above axial MRI sections through the thorax show contents of the superior or the inferior mediastinum?
|
Superior mediastinum.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements best applies to the diaphragm?
Select one: A. The left dome of the diaphragm rises to the level of T5 during deep inspiration. B. The left phrenic nerve passes through it closely applied to the inferior vena cava. C. It becomes tendinous towards its periphery. D. The inferior vena cava passes through it at the level of T10. E. Its central region is fused to the fibrous pericardium. |
E. Its central region is fused to the fibrous pericardium.
|
|
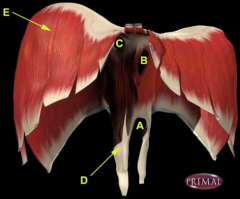
Identify the labelled structures A-E seen on the anterior view of the diaphragm above.
|
E – Right costal part of the diaphragm.
B – Oesophageal aperture. C – Vena cava aperture. A – Aortic aperture. D – Right crus. |
|
|
Which one of the following statements best applies to the mediastinum?
Select one: A. The contents of the superior mediastinum include the right auricular appendage. B. The descending aorta is positioned left of the oesophagus. C. The thoracic duct is on the right of the azygos vein. D. The trachea lies partly within the posterior mediastinum. E. The visceral pleural cavities are often continuous behind the sternum. |
B. The descending aorta is positioned left of the oesophagus.
|
|
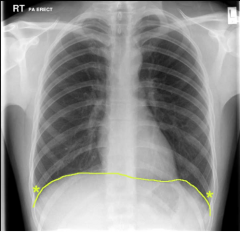
Which one of the following applies to the structure marked with asterisks (*) on the AP chest radiograph above? Note: The diaphragm is marked by the yellow line.
Select one: A. During expiration, it contains lung tissue. B. It extends supero-inferiorly from the 4th to the 7th rib. C. This is a dangerous place to perform a thoracocentesis (pleural tab) because the risk of pneumothorax (and lung puncture) is high. D. In standing position, pleural effusions can collect here in standing position. E. The amount of lung protruding into this space in quiet inspiration is considerable. |
D. In standing position, pleural effusions can collect here in standing position.
The asterisks denote the costophrenic anlge, a potential space between the costal and diaphragmatic pleurae. It usually shows as a dark sharp angled space between the chest wall and the diaphragm. Fluids from plural effusion can build up in this space due to gravity. Resulting deplaced lungs (upward) influence the costophrenic angle; on radiographs, it can appear fuzzy and obtuse. Obtuse angulation is a sign of disease. |

