![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the definition of FVC (forced vital capacity)?
|
total volume of air exhaled as fast as possible after maximal inhalation
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p194
|
|
|
What is the normal FEV1?
|
>80% of predicted normal value (based on gender, age, and height)
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p194
|
|
|
For best results when performing spirometry ...
|
Patient should:
loosen/remove restrictive clothing (ties, belts) wear nose clip to minimize air loss through nose sit/stand up straight completely fill and empty lungs There should be no: hesitation/false start coughing during first second early termination evidence of leak (mouth not tightly around mouthpiece) evidence of obstruction (glottic closure, tongue, false teeth) |
|
|
|
What are the indications for ordering PFTs?
|
diagnostic, evaluation and monitoring of respiratory disease
diagnosis of asthma and COPD monitoring after thoracic radiation, lung transplantation, drugs with potential lung toxicity |
|
|
|
How is air flow affected in obstructive diseases?
|
decrease flow of air but not volume
|
|
|
|
How is air flow affected in restrictive diseases?
|
decrease flow and volume of air
|
|
|
|
What is forced vital capacity (FVC)?
|
total volume of air exhaled as hard and fast as possible after maximal inhalation
|
|
|
|
What is forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)?
|
amount of air exhaled after 1 second
|
|
|
|
What is FEF(25-75)?
|
measures airflow rate during forced expiration from 25%-75% of vital capacity
25-75% is though to measure airflow in medium and small airways (bronchioles and terminal bronchioles) |
|
|
|
What is peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR)?
|
measure of maximum airflow rate (using peak flow meters)
|
|
|
|
What are the indications for peak flow meters (to measure peak expiratory flow rate)?
|
peak flow meters are useful indications of large airway function → monitor airway obstruction in asthmatics
|
|
|
|
What is body plethysmography?
|
method used to measure lung volume
patient sits in airtight box → told to inhale and exhale agaisnt a closed shutter → change in pressure measured during respiration → can calculate FRC, IC, RV, TLC |
|
|
|
What is residual volume (RV)?
|
volume of air remaining in lungs after forced expiration
|
|
|
|
What diseases have increased residual volume?
|
COPD
|
|
|
|
What is inspiratory capacity (IC)?
|
volume of air measured from beginning of inspiration to maximal inspiration
|
|
|
|
What diseases show increased/decreased functional residual volume (FRC)?
|
INCREASED:
hyperinflation → airway obstruction → obstructive lung diseases DECREASED: pneumonia restrictive lung diseases → pulmonary fibrosis |
|
|
|
What are the FEV1/FVC, FEV1, FVC, RV, and TLC results for obstructive and restrictive lung diseases?
|
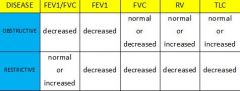
|
|

