![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mechnical Weathering |
Involves extremes of temperatures |
|
|
Chemical weathering |
Involves the decomposition of rock by the action of air, water and acid |
|
|
Exfoliation |
surface of rock heats up, cracks form and surface layers peel off |
|
|
Shattering |
homogenous structure shatters due to expansion and contraction |
|
|
Block seperation |
well jointed rock with prominent bedding planes - there are weaknesses so the rock breaks into blocks |
|
|
Crystal growth |
salt crystals expand in the heat and the rock falls apart |
|
|
Hydration |
salt minerals absorb water, swell and disintergrate |
|
|
Solution |
salty rock mineral are soluble in H2O so the rock dissolves |
|
|
Name the 4 types of mechanical weathering |
1. Exfoliation 2. Granular disintergration 3. Shattering 4. Block seperation |
|
|
Name the 3 types of chemical weathering |
1. Crystal growth 2. Hydration 3. Solutution
|
|
|
what are aeolian processes? |
processes that erode using the force of the wind |
|
|
define erosion |
the displacement of solids by agents of currents |
|
|
deflation? |
when wind erodes solids directly |
|
|
deflation hollows? |
a depression found in semi-/arid areas caused by wind erosion |
|
|
abrasion? |
physical weathering by air or wind on a surface |
|
|
yardangs? |

rock that is stream line due to being eroded by wind |
|
|
Rock pedestals? |

layers of soft and hard rock that are formed by abrasion and are usually top heavy |
|
|
Zeugens? |

landforms created by abrasion and have layers of soft hard rock meaning they have large cracks in them |
|
|
Suspension? |
particles or solids that are suspended in air or water |
|
|
saltation? |
transport or sediment is rolled along the surface by the wind |
|
|
deposition? |
the putting down of sediment or rock when the wind loses energy |
|
|
sand dunes |

hills and ridges of sand formed by the wind |
|
|
Barchans? |

sand dune in the shape of a crescent made by wind action in one direction |
|
|
name 3 desert landforms created by abrasion |
1. rock pedestals 2. yardangs 3. zuegens |
|
|
define erosion |
the displacement of solids by agents of currents - wind, water and ice |
|
|
name 3 formations caused by deflation |
1. desert pavements 2. deflation hollows 3. oases |
|
|
how is a desert pavement formed? |
DEFLATION wind removes loose surface material and carried it away leaving bigger rocks, causing a rock-strewn surface |
|
|
how are deflation hollows formed? |
DEFLATION wind removes vast amounts of surface material creating depression on rock surface which when cold air sinks at night becomes covered with dew speeding up weathering |
|
|
how are oases formed? |

DEFLATION when a deflation hollow gets so low it reaches the aquifer water seeps through the surface nad creates a pool |
|
|
how are rock pedestals formed? |
ABRASION eroding the softer lower layer of rock closer to the ground which creates a mushroom shaped or other strangely shaped rock |
|
|
how are yardangs formed? |
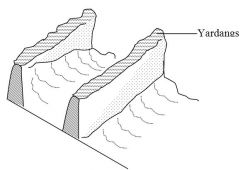
ABRASION bands of more and less resistant rock lie parallel to each other in the direction of the prevailing wind and abrasion wears away the less resistant rock |
|
|
how are zeugens formed? |
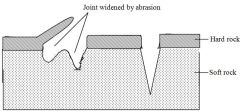
ABRASION bands of hard and soft rock lie in alternate horizontal layers and usually have a duricrust on top. the hard layer gets broken due to weathering and then the wond quickly wears down the soft rock underneath. the rock is continually undercut by wind and eventually collapse |
|
|
surface creep? |
coarse particles ( >0.25mm) are rolled along the ground and if others collide with them they are puched forward |
|
|
how are sand dunes formed? |

an obstacle or shrub gets in the way of the air flow which is carrying sand in suspension and the sand builds up behind the obstacle when it is depostited as the wind loses energy |
|
|
how do barchans move? |
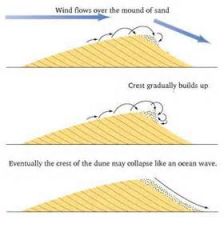
|
|
|
what are ephemeral rivers? and what can it lead to? |
rivers that flow when it rains or after it has rained. can lead to flooding |
|
|
what are endoreic rivers? |
rivers that terminate in inland lakes or salt lakes |
|
|
what are exogenous rivers? |
rivers that flow down from the mountains and ar involved in making canyons |
|
|
name 3 forms water erosion can produce |
braided channels mesas and buttes inselbergs |
|
|
name 3 forms water depostion can create |
alluvial fan bahada salt lakes |
|
|
define desertification |
land degradation in dry lands resulting from human actions |
|
|
what is carrying capacity? |
the number of cattle that can be grazed on an area of land successfully |
|
|
overgrazing?
|
when the herd exceed the carrying capacity |
|
|
overcultivation? |
too much is taken from the land |
|
|
deforestation? |
when forests are cut down |
|
|
irrigation? |
water supply systems that help control levels of it |
|
|
the sahel? |
the transistion between the sahara in the north and the savannah in the south |
|
|
name 4 human things that can lead to desertification |
overgrazing overcultivation deforestation irrigation
|
|
|
name 3 climatic/physical factors which contribute to desertification |
1. occurence of droughts 2. high temperatures ---> lead to high evapotranspiration rates and dry soils 3. infrequent and intense periods of rainfall
|
|
|
where is desertification taking place? |
1. on all continents bar Antarctica 2. usually occurs along tropics and either side of them 3. western side of continents 4. biggest areas are North Africa, Sahara and the middle of Asia |
|
|
what's a wadi? |

steep sided valley in the desert carved out by water |
|
|
what's a mesa? |

plateau like features with a flat top and steep sides leading to wadis or canyons |
|
|
what's a butte? |

like a mesa but smaller, small thin tower |
|
|
what's an insleberg? |

an isolated hill formed from crystalline rocks such as granite |
|
|
what's a pediment? |

a gentle sloping area of base rock and debris believed to be formed by water erosion` |
|
|
what's an alluvial fan? |

a deposit site where rivers deposit coarse material on one side and fine material on the other |
|
|
Define an arid area or desert
|
A desert id a region that receives less than or equal to 250mm of rainfall per year
|
|
|
Define a semi arid area
|
an area that receives 250–500mm of rainfall per year on the outskirts of arid areas
|
|
|
Where are deserts found?
|
Along the tropics – either side
Western side of continents |
|
|
What are ephemerals?
|
a plant that comes out when it rains and completes its cycle by germinating, flowering and dispersing in 3 weeks
|
|
|
What are xerophytes?
|
plants that have adapted to withstand droughts
|
|
|
Phreatophytes?
|
plants that avoid droughts by having long tap roots
|
|
|
Halophytes?
|
plants adapted to salty areas found in and around salty areas
|
|
|
Aridosol?
|
the different regions or layers of soil
|
|
|
Solentz?
|
a soil that forms in areas of sufficient rain to cause leaching but not enough to cause the minerals to be washed out
|
|
|
Solonchaks?
|
soils found in areas of high evaporation rates
|
|
|
Name the 4 ways deserts are formed?
|
Rainshadow effect
Continentality Cold currents Global circulation of air |
|
|
name the layers of soil
|
O = organic horizon
A = org/material mix B = nutrient layer C = parent material |
|
|
Describe global circulation of air?
|
1. the air at the equator is heated due to the sun's insolation being concentrated
2. the hot air rises and cools down as it does 3. the vapour condenses into droplets, clouds are formed and it rains 4. the rising air splits at the tropopause and travels north and south 5. the air cools and sinks so high pressure is created at the surface creating a Hadley cell |
|
|
Continentality?
|
maritime regions get higher rainfall than inland areas because the moist winds from oceans has travelled over 1000's km over land so lots of water vapour is lost, this means it is drier inland.
|
|
|
Cold currents?
|
1. global circulation of cold currents controlled by wind directions and rotation of air
2. the cold currents cool the air above it 3. moisture in air condenses into mist offshore 4. mist blown on–shore but burnt of by sun quickly 5. air over land is therefore dry as it has lost moisture over sea and warms up so no condensing into cloud |
|
|
Rainshadow? |
1. moist air from the sea travels up the windward side of the mountain |
|
|
what is a sheet flood? |

it is where water flows evenly over the land and is not confined to channels and it is thought material is deposited during this time
|
|
|
what's a pluvial? |

earlier wetter periods that occur before a sheet flood |
|
|
how are canyons formed? |
EROSION exogenous rivers erode the side of the river bank but, because erosion happens slower than in humid areas where the rivers energy is used to transport material, here it can be used to erode downwards |
|
|
how is a braided channel formed? |

EROSION sediment is deposited and the river has to wind its way around the piles of sediment creating channels, they change after each flood |
|
|
how are wadis formed? |

EROSION water erodes the rock away leaving a steep sided ravine |
|
|
how are mesas and buttes formed? |

EROSION weathering and water erosion of surrounding less resistant rock leave behind pillars of more resistant rock (differential erosion) |
|
|
how are inselbergs formed? |

EROSION rock surface gets weathered and the rainfall washes material away leaving a smooth surface
|
|
|
how are pluvials formed? |

DEPOSITION material gets washed down from uplands and deposited |
|
|
how are alluvial fans formed? |

deposition in a fan shape as the river spreads out from constricted area into small distributaries |
|
|
how is a bahada formed? |
alluvial fans may coalesce to form a large area |
|
|
what is a playa and how do they form? |
lowest part of a desert surface water evaporates quickly and leaving behind salt forming a think crust which has cracks in it |
|
|
what's a badland? |
an area that hosts all sorts of different desert landforms |
|
|
Mining in the SW USA? effects? [3] sustainable? |
effects on water resources: 1. removing water from naturally occurring springs means species are in danger 2. pollutes aquifers 3. increases water toxicity levels
sustainable: 1. removing water sources from animals and plants has lasting effects
|
|
|
National Parks in the SW USA? effects? [2] sustainable? [3] |
effects 1. 2.6 billion gallons of water are consumed in national parks each year 2. $44 million spent on energy costs each year
sustainable: 1. launched a green parks plan which has decreased fossil fuel and electricity by 13% 2. diverted 92% of construction and demolition waste 3. electric cars and shuttle buses used |
|
|
Tourism in Las Vegas? effects? [2] sustainable? |
effects: 1. 219 gallons of water per person per day 2. 152622 gallons of water used on golf courses each day
sustainability: 1. recycle sewage water for use on golf courses cutting it by 40% 2. south Nevada water authority's water smart landscape program has encouraged 30,000 southern nevadens to change 11 million sq m of lawn saving 25 billion litres of water each year |
|
|
retirement in SW USA? effects [2] sustainable [2] |
effects: 1. golf courses need to be kept green 2. houses need to be supplied with water
sustainability: 1. integrated water management system 2. Phoenix recycles 90% of its wastewater for use elsewhere |
|
|
domestic water supply in SW USA? effects [1] sustainability [2] |
effects: 1. lake mead has shrunk which supplies 90% of Las Vegas' water
sustainability: 1. desalination plant on coast of California 2. development of groundwater sources in snake country to extract and supply enough water for around 100,00 Las Vegas homes
|

