![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What drugs do you use to treat dermatologic viral diseases? Drug list... |
Acyclovir Cidofovir Famciclovir Foscarnet Ganciclovir Valacyclovir Valganciclovir |
|
|
What is acyclovir used to treat? |
Varicella zoster Varicella chicken pox |
|
|
What is cidofovir used to treat? |
Pox family virus, HHV-6, HHV-7, HHV-8 |
|
|
What is famciclovir used to treat? |
Varicella zoster, HHV-8 |
|
|
What is foscarnet used to treat? |
HHV-6 |
|
|
What is ganciclovir used to treat? |
HHV-6, HHV-8, HHV-8 infection |
|
|
What is valacyclovir used to treat? |
Varicella zoster, varicella chicken pox, HHV-8 |
|
|
What is valganciclovir used to treat? |
HHV-6, HHV-8 infection |
|
|
What are valacyclovir and valgancyclovir metabolized to?
What famciclovir metabolized to? Which can be used to treat what? |
Valacyclovir and valgancyclovir => respective active drugs (acyclovir and ganciclovir respectively)
Famciclovir => penciclovir = metabolite not marketed as a drug in its own right to treat recurrent herpes labialis |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of acyclovir, vidarabine, foscarnet, and ganciclovir (all the same)? What types of viruses do these work in? |
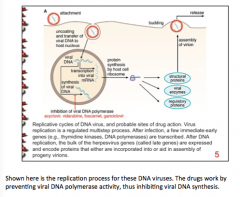
Inhibition of viral DNA polymerase |
|
|
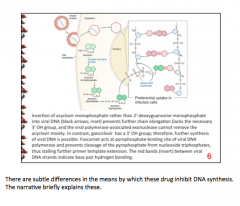
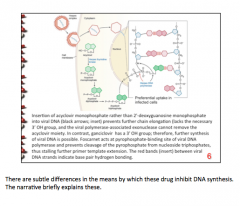
What is the specific mechanism of acyclovir? |
Inserts acyclovir monophosphate rather than 2'-deoxyguanosine monophosphate into DNA --> prevents further chain elongation (lacks the 3'-OH group) and viral polymerase-associated exonuclease cannot remove the acyclovir moiety. |
|
|
How is the specific mechanism of ganciclovir different from the specific mechanism of acyclovir? |
Ganciclovir has a 3'-OH group => further synthesis of viral DNA is possible |
|
|
How is this different from foscarnet? |
Foscarnet acts at the pyrophosphate-binding site of viral DNA polymerase and prevents cleavage of the pyrophosphate from nucleoside triphosphates = > stalls further primer template extension |
|
|
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of acyclovir, famciclovir, ganciclovir, valacyclovir, and valganciclovir? |
Competitively inhibits viral DNA polymerase; competes with deoxyguanosine triphosphate for incorporation into viral DNA. |
|
|
What is the mechanism of cidofovir? |
Competitively inhibits viral DNA polymerase; competes with deoxycytosine triphosphate for incorporation into viral DNA |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of foscarnet? |
Selectively inhibits the viral-specific DNA polymerases and reverse transcriptases at pyrophosphate-binding sites; blocks chain elongation. |
|
|
What drugs require sequential phosphorlyation to the triphosphate form that is the active product? Which virus types would be inherently resistant? Do they have cross hypersensitivity? |
Cidofovir and foscarnet Kinase deficient viral strains inherently resistant
No cross hypersensitivity (no similarity in structure that would cause hypersensitivity in other drugs)
|
|
|
Do all the viral drugs require dose adjustment in renal failure? Why? |
Yes! These drugs predominantly undergo renal elimination |
|
|
Which drugs do you have to worry about cross-hypersensitity in? |
Acyclovir, famciclovir, ganciclovir, valacyclovir, valganciclovir (all but cidofovir and foscarnet) |
|
|
Toxicity of acyclovir and valacyclovir? |
Neurotoxicity including seizures |
|
|
Toxicity of cidofovir? Monitor? |
Neurotoxicity (monitor creatinine and urinary protein) Probenecid hypersensitivity
|
|
|
Toxicity of famciclovir? |
None |
|
|
Toxicity of foscarnet? |
Electrolyte imbalance = chelates Ca2+ ions |
|
|
Toxicity of ganciclovir and valgancyclovir? |
Anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, pancytopenia, and thrombocytopenia (teratogen)!
"ENIAS" |

