![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the pterygomaxillary notch also referred to as?
|
The hamular notch
|
|
|
Where are the fovea palatinae located?
|
Near the middle of the palate. They are always in soft tissue, which makes them an ideal guide for the location of the posterior border of the denture
|
|
|
What type of material is alginate?
|
Alginate is an irreversible hydrocolloid
|
|
|
What is the vibrating line?
|
The vibrating line is an imaginary line drawn across the palate that marks the beginning of motion in the soft palate when an individual says “ah.” It extends from one hamular notch to the other. At the midline, it usually passes about 2 mm in front of the fovea palatinae.
|
|
|
What type of gypsum is used to pour preliminary models?
|
Type II gypsum
|
|
|
Should you flip your model upside down on its base immediately after pouring it?
|
No the initial pour might break in the tray
|
|
|
What is the setting time for fast set alginate?
|
1-2 minutes
|
|
|
What provides the main support for the lower denture?
|
The buccal shelf
|
|
|
What type of material do we use to make the preliminary impressions?
|
Irreversible hydrocolloid (alginate)
|
|
|
What is impression compound?
|
Impression compound is a thermoplastic material with a high viscosity
|
|
|
Why is wax placed over the preliminary cast before the tray is made?
|
It creates space for the impression material
|
|
|
Why are we so picky about the handle on the custom impression tray?
|
To avoid distending the lips because it would distort the impression
|
|
|
What do we use for border molding material?
|
Thermoplastic material called stick compound
|
|
|
What does thermoplastic mean?
|
Heat softens and cold hardens
|
|
|
The border molding material should not extend over the intaglio (inside) surface of the impression tray except in one area. That area is:
|
Posterior palatal area
|
|
|
After making the final impression, the master cast is made. Before pouring it, it is recommended to bead and box the impression. What is the reason for doing this?
|
To create a land area for the final cast and to ensure an adequate base
|
|
|
Before making the final impression, your custom tray is border molded. What is the purpose for doing this?
|
To capture the depth of the vestibule of both max & mand
also the sulcus of the mandibular impression |
|
|
What type of gypsum product should you use to pour your final impression?
|
Type III gypsum (microstone)
|
|
|
When border molding the impression tray, the border molding material should not be allowed to stay on the intaglio (inside) surface except in one area. That area is:
|
The posterior palatal seal area
|
|
|
One of the most important areas to capture in the upper impression is the posterior palatal seal area. What is the p.p.s.?
|
It is the area on the posterior part of the maxillary denture that has a positive shape onto the palate and looks like a cupids bow
|
|
|
What are 3 functions of the posterior palatal seal?
|
1. Decrease atmospheric pressure
2. Increase Retention 3. Keeps food from entering the denture |
|
|
The extent of the PPS is defined by the type of throat form. Three types have been described. Which is the most favorable for us to work with?
|
Type I
because the throat goes back allowing for the posterior vibrating line to 4.5 mm beyond the fovea palatinae |
|
|
The posterior extent of the PPS is defined by:
|
posterior vibrating line from hamular notch to hamular notch
|
|
|
One guideline as to the location of the PPS is the fovea palitinae. This landmark is found on the:
|
Soft palate
|
|
|
What is an impression?
|
A negative of the original
|
|
|
What is the setting time for slow set alginate?
|
3-4.5 minutes
|
|
|
What is a disadvantage of alginate?
|
Tears easily
|
|
|
What are 3 defects that can be seen in an alginate impression?
|
1. air pockets
2. fissures 3. pits |
|
|
Where are the foveae palatinae located?
|
Posterior section of maxilla near palatine seal, mid-sagitally located
|
|
|
What are 3/4 of the stages in the set of dental gypsum?
|
a. plastic
b. friable c. fluid |
|
|
Where would we want a thicker layer of impression material?
|
Non-load bearing areas
|
|
|
What is the primary bearing area on the maxilla?
|
Hard palate
|
|
|
Name three of the requirements for custom tray fabrication at CWRU
|
a. No undercuts, tray is easily placed and removed
b. Accurate reproduction of tissue structure c. Handles must not interfere with lips |
|
|
T/F Undercuts on the primary cast should be relieved prior to fabrication of the custom trays
|
True
|
|
|
What is the primary bearing area on the mandibular edentulous arch?
|
Buccal Shelf
|
|
|
What is diagnosis defined as?
|
Collection of clinical data
|
|
|
What is the least favorable throat form?
|
Class III
|
|
|
What are the % ingredients of each border molding compound in stick form?
|
40% resin
50% filler 7% wax 3% organic acid |
|
|
What is different about a heavy bodied impression material like polyether for border molding?
|
Placed all at one time & inserted & manipulated
|
|
|
What are 2 different methods of muscle manipulation in border molding?
|
Physiologic manipulation
Manual manipulation |
|
|
In border molding the lower custom tray, when you have your patient extend their tongue and move it from side to side, what muscle does this activate?
|
Mylohyoid muscle
|
|
|
What is the purpose of border molding?
|
Border molding is the process by which the shape of the border of the tray is made to conform accurately to the contours of the buccal and labial vestibules.
|
|
|
Name an area that needs to be relieved or carved as the border is molded?
|
Retromolar pad to prevent soft tissue irritation
|
|
|
The dental stick compound flows when it is applied and becomes solid when cooled. What is this quality of material known as?
|
Themoplastic
|
|
|
When the junction of the hard and soft palates are seen from a lateral cross section view, it is divided into three classes. Describe each class
|
Class I mostly flat junction
Class II Intermediate angle forms the junction between the hard & soft palate Class III Angle between the hard and soft palate is sharp |
|
|
What is the purpose of border molding?
|
To capture the depth of the vestibule in the max and mand
The sulcus of the mand impression |
|
|
What is the difference between an arcon and non-arcon articulator?
|
Arcon has the TMJ fossa element laid as part of the upper apparatus
(An articulator with the equivalent condylar guides fixed to the upper member and the hinge axis to the lower member, an instrument that maintains a constant relationship between the occlusal plane and the arcon guides at any position of the upper member, thereby making possible more accurate reproductions of mandibular movements) Non-Arcon has the TMJ fossa element as part of the lower apparatus |
|
|
The exteer
|
The external auditory meatus & the nasion in reference to the maxillary dentition (in a horizontal plane of reference)
|
|
|
In making the final impression of the maxilla, several areas that are difficult to obtain, but are important is the denture will be successful. What are these spots?
|
Coranoid Contour
Maxillary tuberosity Pterygomaxillary seal in the area of the hamular notch |
|
|
In the mandibular impression there are also several areas that are often either missed or the impression is insufficient. These are also very important to the success of the lower denture. What are these?
|
Retromolar fossa
Lingual Flange Buccal shelf |
|
|
T/F When teeth are removed the bone resorbs. It resorbs faster in the maxilla than the mandible.
|
False the mandible resorbs faster than the maxilla
|
|
|
We emphasize capturing the retromolar pad in the impression, and yet in practice much of the time dentists pay little attention to this landmark. They evidently do not remember that this little pad helps share the vertical force w/the alveolar bone and _________________
|
Look this one up and put answer here
|
|
|
In the mandible, _________ bounded medially by the crest of the residual ridge, laterally by the external oblique ridge, and distally by the retromolar pad.
|
Buccal Shelf
|
|
|
What is the intaglio?
|
The area on the tissue side (inner part) of the denture
|
|
|
What is the cameo?
|
The area on the labial side (outer part) of the denture
(the viewable portion of a removable denture prosthesis; the portion of the surface of a denture that extends in an occlusal direction from the border of the denture and includes the facial, lingual, and palatal surface. It is the part of the denture base that is usually polished, and includes the buccal and lingual surfaces of the teeth) |
|
|
What muscle dictates to a great deal the depth of the vestibule (mucobuccal turn, peripheral turn) of the denture (both maxillary and mandibular dentures)
|
Buccinator
|
|
|
We have now arrived at the third appt w/our patient. You have made your record bases and the wax occlusal rims. What are two things that you will look for when contouring the WORs for your patient and fitting it?
|
Look to see if the angulation is correct by the lip position
Check the verticle dimensions of the WORs |
|
|
Your maxillary WOR is 22 mm in length from the peripheral turn to the edge of the WOR in the lateral/canine region. It is to be 18 mm in length from the peripheral turn to the incisal edge in the lateral/canine region on the lower WOR. Why do we use these dimensions as a starting point for the vertical dimension?
|
We use these because most people have a verticle dimension of 40 mm + or - a few mm, unless they are an unusual case
|
|
|
One of the things we are doing at this third appt is obtaining the vertical dimension of the lower 1/3 of the face. The first thing we will do is obtain the verticle dimension of rest. What are the 2 methods of obtaining this V.D.R.?
|
???
|
|
|
How do you define the physiological rest position?
|
It is the position where the teeth and jaw rest when the individual is relaxed. The position is 2mm below the verticle dimension of occlusion
|
|
|
After we obtain the V.D. of rest we want to then create the V.D. of occlusion. This difference will create a space between the occlusal and incisive surfaces of the WOR and hence the teeth. This space is called __________
|
Interocclusal space
|
|
|
T/F CR is determined by the TMJ structures and not the dentition.
|
True
|
|
|
T/F Centric occlusion is the occlusion of opposing teeth when the mandible is in CR.
|
True
|
|
|
Centric relation is the vertical reference position of the mandible that can routinely be assumed by edentulous patients under the direction of the dentist/
|
False
Centric relation is a HORIZONTAL reference position |
|
|
There is a difference in dimension between vertical dimension of rest and vertical dimension of occlusion. This dimension is:
|
2-4 mm
|
|
|
Several tests are used to establish the vertical dimension of occlusion by means of wax occlusal rims. They are: a) judgment of overall facial support; b) visual observation of the space between the rims when the jaws are at rest; c) measurement between dots on the face when the jaws are at rest and when the occlusion rims are in contact; d) Observations when the "s" sound is enunciated accurately and repeatedly - the average "speaking space"
This speaking space is not the same as the vertical dimension of rest. It is 1.5-3 mm on average with Class I jaw relationship. It is usually greater in Class II patients and less in Class III patients |
True
|
|
|
When establishing the occlusal plane on the upper wax occlusal rim with a patient there are 2 lines that can aid in this exercise:
|
1. Interpupillary line
2. Ala-tragus line |
|
|
On the typodonts we have given arbitrary dimensions for the upper and lower WOR. The upper rim in humans will vary in vertical length and are used to help determine the incisal edge length. This length will usually be _____ the lip line of a patient 60 years of age.
|
Above
|
|
|
A facebow is used to locate the __________ hinge axis of the mandible.
|
Arbitrary
|
|
|
When obtaining the CR interocclusal records, the posterior portion of the lower WOR is relieved so as not to touch the upper rim. This is done so as not to create pressure on the posterior region. Allow essentially 3 points of contact the two condyles seated in the glenoid fossa and the anterior "stop" of the WORs
|
True
|
|
|
What are the 2 reasons for boxing a final impression?
|
To get a thick enough base
Prevent inverting cast |
|
|
What is the desired depth of the sulcus from the future landing area in the final cast?
|
2-3 mm
|
|
|
What should the thickness of the base of your final impression cast be?
|
15 mm
|
|
|
What should the dimensions of your land area be?
|
1-2 mm deep
3-4 mm wide |
|
|
What is the most common reason for having to repeat an impression due to?
|
incorrect positioning of the tray
|
|
|
What muscle should the custom tray accomodate when the floor of the mouth is raised?
|
Mylohyoid
|
|
|
What is the proper shape of the 3 grooves placed in your model prior to mounting?
|
V shape
Wide and deep enough No undercuts |
|
|
When making your triad base where should you cut off the excess?
|
at the border of the peripheral turn (edge of land area)
|
|

What is the dimension for the WOR from peripheral turn to incisal edge in lateral region?
|

22 mm
|
|
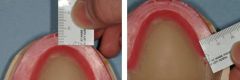
What should the anterior and posterior dimensions when shaping the occlusal surface of the WOR?
|
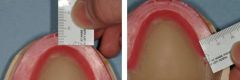
Anterior 6-8 mm wide
Posterior 8-10 mm wide (don't make too wide) |
|

When shaping the mandibular WOR, what is the labial dimension from peripheral turn to lateral incisor region?
|

18 mm
|
|

Where should you place your mark for the retromolar pad height?
|

1/2 - 2/3 from base of retromolar pad
|
|
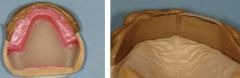
After your WOR is complete you should make a removable index. What is this?
|
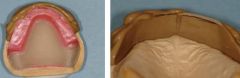
Removable index can serve as a check when you are setting the teeth, so as to maintain the desired position
|
|

What are the 2 methods for mounting the casts?
|

The face bow transfer
The Stratus Horizontal guide |
|

How should the horizontal guide be placed on your model?
|

Set anterior gauge to 18 mm, so the fork straddles labial frenum area.
Posterior arm position on 2/3 mark (of retromolar pad) The retromolar pad should be marked at the base and 2/3 up |
|

Where should the horizontal guide be attached to?
|

Attached to the instrument carrier and secured to the UPPER member of the articulator
|
|
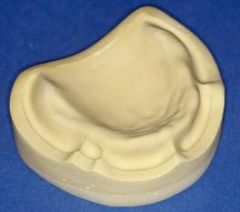
What are the requirements for your master cast?
|
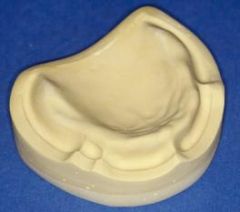
a. The full palate extending posterior to the posterior vibrating line
b. The entire activated muccobuccal fold to a depth of 1-2 mm c. the full hamular notch d. The entire alveolar ridge e. The activated frena attachments f. There must be no scratches on the anatomy of the master cast g. There must be no voids or positive bubbles on the master cast |
|
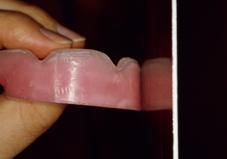
What are the requirements for Lip Support?
|
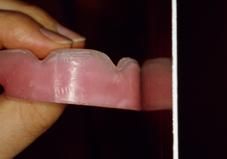
Contour the labial inclination of the WOR so that the lip seems supported according to the patient's profile.
Filtrum should be 90 deg to the columnella of the nose |
|
|
What mark extends the estimated incisal edge of the anterior teeth?
|
Parallel to the interpupillary line: Extend the mark horizontally to parallel the interpupillary line.
(I think interpupillary means in the midline between the eyes {maybe your philtrum is a good reference}) |
|
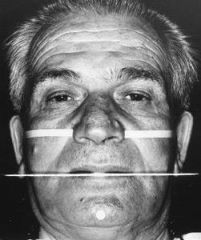
What is demonstrated in this picture and how is it applicable to contouring your wax occlusal rim?
|
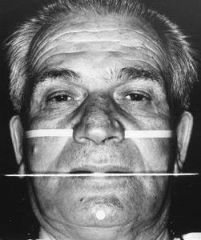
Ala-tragus line
Mark the upper wax occlusion rim posteriorly so that the occlusal plane will be basically parallel with a line from the ala of the nose to the tragus of the ear. |
|
|
Once you have made your Interpupillary line and your Ala-Tragus line, what should you do next?
|
Reduce the upper wax occlusion rim to the marks with the hotplate
|
|
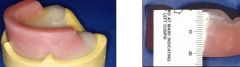
What should the height of the Maxillary WOR be?
|
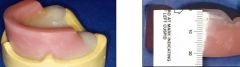
22 mm
|
|
|
What should the facial contour on the Maxillary WOR from cuspid to cuspid be?
|
Proclined 10-degrees
|
|
|
What should the buccal contours on the Maxillary WOR be?
|
Buccal contours converge slightly (3-4 mm distance inside the peripheral border of the record base)
|
|
|
What is significant regarding the posterior wax rim on a Maxillary WOR?
|
Posterior wax rim trimmed at a 45 degree angle so it extends anterior to the maxillary tuberosity
|
|
|
How much inclination is on the Anterior rim of a Mandibular WOR?
|
Anterior rim 0 degree inclination
|
|
|
How much inclination is on the Posterior rim of a Mandibular WOR?
|
Posterior rim 10-15 degree inclination
|
|
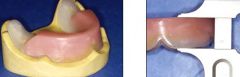
Where is the posterior wax rim height on a Mandibular WOR?
|
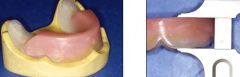
Level with a line drawn from anterior portion (18 mm height) to a point 1/2 to 2/3 up the retromolar pad.
|

