![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Labial |
Side towards lips (incisor, canine) |
|
|
Buccal |
Side towards the cheek (premolar, molar) |
|
|
Lingual |
Lower, side towards the tongue |
|
|
Palatal |
Upper, side towards the palate |
|
|
Mesial |
Surface towards the median line (front) |
|
|
Distal |
Surface away from the medial line (back) |
|
|
Occusal |
Biting surface |
|
|
Crown |
above the gum and covered by enamel |
|
|
Root |
below the crown and neck, enclosed in socket and covered by cementum |
|
|
Neck |
portion below the crown. Area known as CEJ (cemento-enamel juntion) |
|
|
Primary Teeth |
10:10 Dicidious. Average range is 6 months to 51/2 years Enamel is thinner (approx 1mm), root is smaller, slender shape Mammeleons NOT present 2 Incisors, 1 canine, 2 molars |
|
|
Secondary Teeth |
(16:16) Permanent. Average range6½+ years. Enamel is thicker (2-3mm), root islarger, bulbous shape Mammeleons present 2 incisors, canine, 2 premolars, 3molars |
|
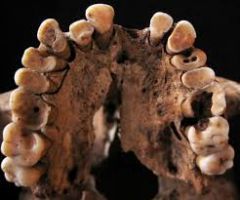
What is this dental disease? |
DENTAL CARIES Tooth decay from acid/sugar thatcauses bacterial breakdown Most common cause of oral pain andtooth lossStarts as white/brown spot onenamel, then destroys enamel to form a cavity Usually more frequent in molars Can cause abscesses |
|
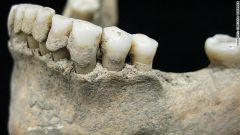
What is this dental disease? |
DENTAL CALCULUS - Mineralized plaque - Result of poor hygiene and high carbohydrates(and protein) intake - Greyish-white deposit on teeth o Supra-gingival (above gum line) o Sub-gingival (below gum line) |
|
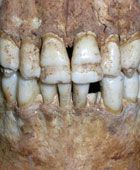
What is this dental disease? |
ENAMEL HYPOPLASIA Tooth defect, defective formation of the organicenamel matrix Enamel is hard but thin, enamel is deficient inamount o Result of Vitamin D deficiency Pitting in the tooth (hole) |
|
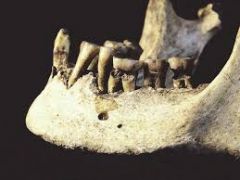
What is this dental disease? |
PERIODONTITIS Form of periodontal disease Gingivitis: infection/ inflammation of gums dueto plaque o Can lead to periodontitis Exposure of roots, resorption and remodeling ofalveolar bone around the cervical margin Can lead to anti-mortem tooth loss Recognized as a recession of alveolar margin |
|
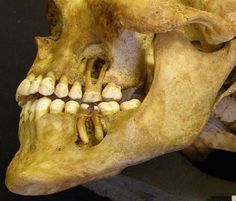
What is this dental disease? |
PERIAPICAL CAVITY Cavity at the apex of the tooth o Associated with caries Identified by a perforating fistula in aspecific alveolar locations Three types: cysts, granulomas, abscesses Infection of the dental pulp |
|
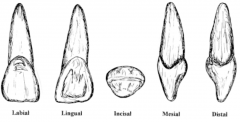
Why type of tooth is this? |
INCISORS (central and lateral) Front teeth Have a total of 8 Pointed and flat top |
|
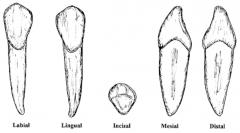
What type of tooth is this? |
CANINES (total of 4) One Root (longer/thicker than incisors) Crown is convex on labial side. Long and pointed Larger and stronger than incisors Long roots w/upper root is usually longer. |
|
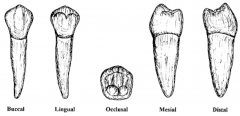
What type of tooth is this? |
PREMOLARS (total of 8) Two Roots (1-2) Have at lease two cusps Smaller than molars |
|
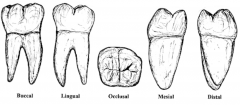
What type of tooth is this? |
MOLARS (total of 12) Three roots (3-4) Round, flat Have 4-5 cusps |
|
|
What are the 3 types of Dental Wear? |
Trauma Attrition Abrasion |
|
|
What is abrasion wear? |
Wear caused by foreign objects in the mouth Due to food, occupational and habitual activity |
|
|
What is attrition wear? |
Caused by teeth grinding against one another and results in wear facets Due to food, occupation, and habitual activity Results in the formation of secondary dentine |
|
|
What is trauma wear? |
chipping or fractures |
|
|
What is the composition of teeth? |
3 types of hard tissue: enamel, dentine, cementum Enamel is more crystalline where dentine is similar to bone - enamel is a harder material than bone - great proportion of mineral than bone |
|
|
What are different types of dental variation? |
Supernumerary teeth Congental absences Ectopic teeth Interchange of positions Migration of impact teeth Shape, crown and root features |

