![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
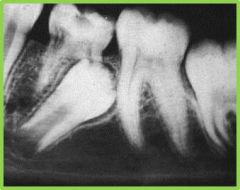
|
Ectopic Eruption |
|
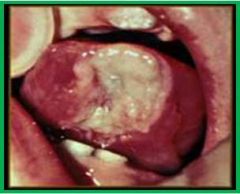
|
Riga-Fede Apathe: a small ulceration on the under-surface of the tongue in infants with natal or neonatal teeth. Frequently observed in children affected by whopping cough or diptheria |
|
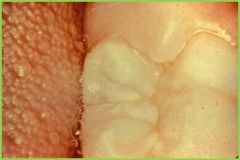
|
Operculum flap of tissue over an uneruped or partially erupted tooth |
|
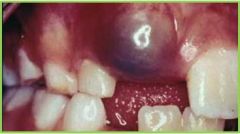
|
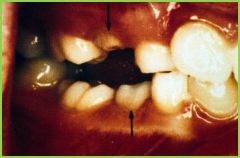
Eruption Hematoma |
|
|
Ankylosis: fusion of the root to the bone, resorption doesnt occur. Most often in deciduous molars |
|
|
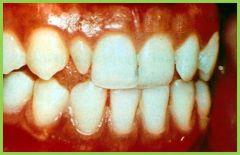
Microdontia/Isolated smaller than normal size perm teeth; often bilateral "peg lateral" |
|
|
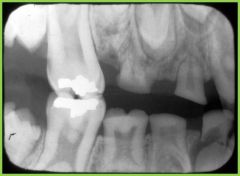
Taurodontism unusually large pulp chamber that may extend into the root area. normal size tooth "Bull" or "Prism" |
|
|
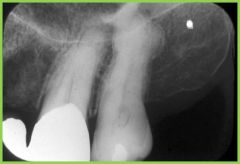
Hypyercementosis: excessive cementum on root |
|
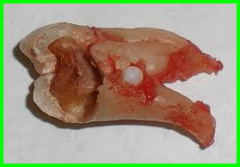
|
Enamel Pearl |
|
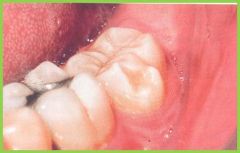
|
Accessory cusp |
|
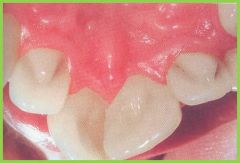
|
Talon cusps |
|
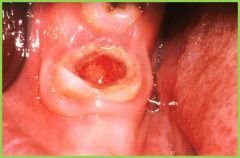
|
Pulp polyps: clinically soft, red, non-painful. Vital>nonvital |
|
|
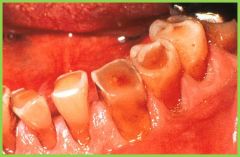
Attrition |
|
|
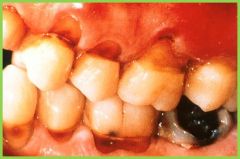
Abrasion: |
|
|
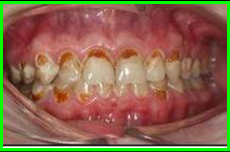
Erosion: |
|
|
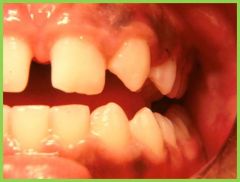
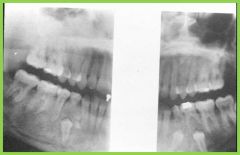
Hypodontia: congenital absence of one or a few teeth |
|
|
Hypodontia: |
|
|
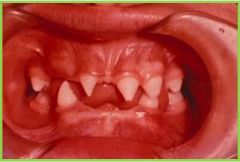
Ectodermal Dysplasia: syndromes in which there are abnormalities of two or more ectodermal structures, such as hair, teeth, nails ect. (note abnormal # of teeth and shape) |
|
|
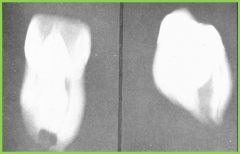
Dens in Dente: "Tooth within a tooth" |
|
|
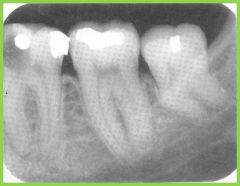
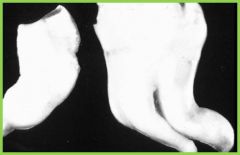
Dilaceration: crown and root are not in a linear relationship |
|
|
Felxion: ONLY root structure is distorted |
|
|
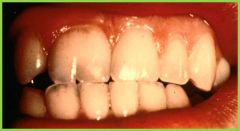
Gemination: incompletely divided crown, single root, common pulp cavity |
|
|
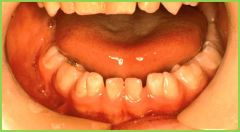
Fusion: union of two adjacent teeth. TWO roots, TWO pulp cavities |
|
|
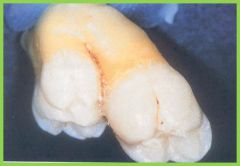
Concresence: two or more teeth joined through cementum only |
|
|
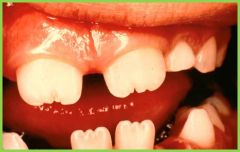
Hutchinson's teeth: due to prenatal syphilis |
|
|
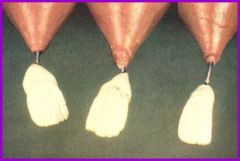
Dwarfed Root: normal sized crowns, abnormally short roots |
|
|
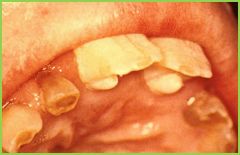
Accessory Cusps: aka tubercles |
|
|
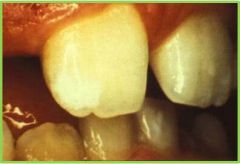
Hypocalcification: due to traumatic injury to primary teeth |
|
|
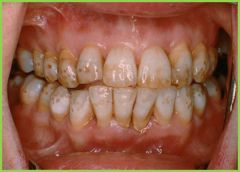
Dental fluorosis: excessive fluoride intake |
|
|
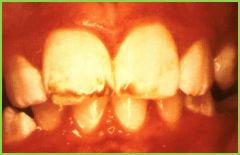
Amelogenesis imperfecta: ranges from almost complete absence of enamel to enamel that never fully matured |
|
|
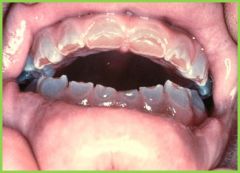
Dentinogenesis imperfecta: crown of tooth exhibits an opalescence or bluish-brown color |
|
|
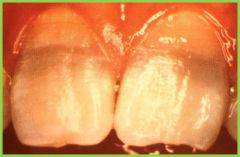
Tetracycline Staining |
|
|
Nasmyth's membrane |
the enamel cuticle or keratin membrane that covers an erupting tooth |
|
|
Macrodontia |
abnormally large teeth; may affect one, several or all |
|
|
Anodontia |
Complete absence of teeth, however, this is extremely rare |
|
|
Olgodontia |
numerous (more than 4) congentially missing teeth |
|
|
Hyperdontia |
aka. supernumerary teeth |
|
|
Enamel Dysplasia |
abnormal enamel formation |
|
|
Turner's tooth |
enamel hypoplasia of a permanent tooth |
|
|
Dental dysplasia |
abnormal dentin formation |

