![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Cortical Bone
|
The dense outer layer of bone, resists the passage of the xray beam and appears radiopaque on a dental image
|
|
Cancellous Bone
|
Soft, spongy bone located between 2 layers of dense cortical bone
|
|
Tuberosity
|
A rounded prominence of bone that extends posterior to the third molar region
|
|
Hamulus
|
A small hooklike projection of bone extending from the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone
|
|
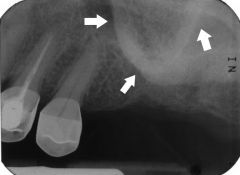
Zygomatic Process
|
The bony projection of the maxilla that articulates with the zygomar or malar bone composed of dense cortical bone
|
|
Saggital Plane
|
Is a vertical plane which passes from front to rear dividing the body into right and left halves
|
|
|
Horizontal Plane
|
Is an imaginary plane that dived the body into superior and inferior parts, it is perpendicular to the coronial and saggital planes
|
|
|
Frontol (Coronial) Plane
|
Is any vertical plane that divides the body into front and rear sections
|
|
|
Occlusal Plane
|
Refers to contact between teeth when the jaw is closed and stationary
|
|
|
Frankfurt plane
|
An imaginary line that passes from the highest point of the ear canal through to the lowest point of the eye socket
|
|
|
Enamel
|
The hard translucent substance covering the exposed portion of the tooth
|
|
|
Dentine
|
Hard portion of the root that surrounds the pulp and it covered by enamel on the crown and by the cementum of the root
|
|
|
Pulp Chamber
|
The natural cavity in the central portion of the tooth crown that is occupied by the dental pulp
|
|
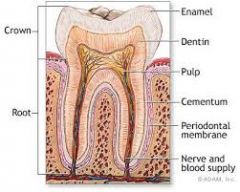
Cementum
|
Specialised calcified connective tissue that covers the atomic root of the tooth given attachment to the periodontal ligament
|
|
|
Periodontal ligament
|
The fibrous connective tissue that surrounds the root of a tooth separating it from an attachment to the alveloar bone and serving to hold the tooth in its socket
|
|
|
Anatomical crown
|
Portion of the tooth that is covered by enamel
|
|
|
Apical foramen
|
An opening at or near the apex of the root of the tooth given passage to surrounding structures supplying the pulp
|
|
|
Alveolar Bone
|
The thin layer of bone making up the bony processes of the maxilar and mandible surrounding and containing the teeth
|
|
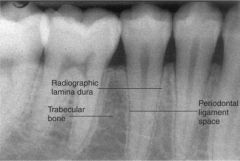
Lamina Dura
|
A sheet of compact alveolar bone that lies adjacent to the periodontal membrane, the lining of the alveolus
|
|
|
Gingiva
|
The mucous membrane (gum) with supporting fibrous tissue covering the tooth bearing border of the jaw
|
|
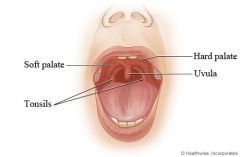
Hard palate
|
The anterior portion of the palate separating the oral and nasal cavities
|
|
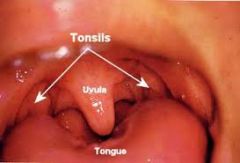
Tonsil
|
A small oral mass of lymphoid tissue especially either of two such masses embedded in the lateral walls of the opening between the mouth and the pharynx
|
|
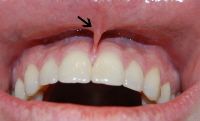
Upper labial frenum
|
The vertical band of oral mucosa connecting the lip of the residual alveolar ridge near the midline of the maxillary arch
|
|
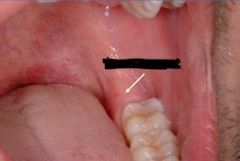
Retromolar pad
|
A cushioned mass of soft tissue located on the alveolar process of the mandible behind the area of the last natural molar tooth
|
|
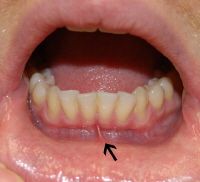
Lower labial frenum
|
The vertical band of oral mucose connecting the lip of the residual alveolar ridge near the midline of the mandible arch
|
|
|
Soft palate
|
The fleshy part of the palate extending from the posterior edge of the hard palate
|
|
|
Mandibular vestibule
|
Connecting passage. The space between the buccal and the labial aspect of the teeth and gingiva and the inner aspect of the teeth and lips.
|
|
|
Uvula
|
A small conical fleshy mass of tissue suspended from the centre of the soft palate
|
|
|
Orbital
|
Eye area that is covered by the eyelids
|
|
|
Zygomatic
|
Prominence of the cheek
|
|
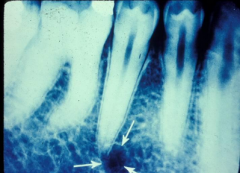
Foramen
|
An opening or hole in a bone that permits the passage of nerves and blood vessels
|
|
|
Fossa
|
A broad, shallow, scooped-out or depressed area of bone. An example is the submandibular fossa of the mandible.
|
|
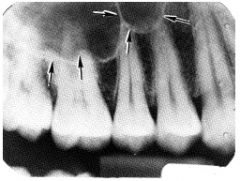
Sinus
|
A hollow space, cavity, or recess in bone. An example is the maxillary sinus.
|
|
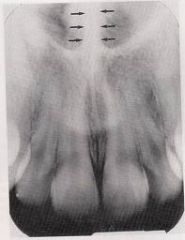
Septum
|
A bony wall or partition that divides two spaces or cavities. A septum may be present within the space of a fossa or sinus. A bony septum appears radiopaque, in contrast to a space or cavity, which appears radiolucent. An example is the nasal septum.
|
|
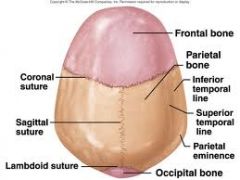
Suture
|
An immovable joint that represents a line of union between adjoining bones of the skull. Sutures are found only in the skull. On dental images, a suture appears as a think radiolucent line. An example is the median palatine suture of the maxilla.
|
|
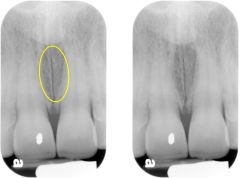
Incisive foramen
|
Also known as the nasopalatine foramen. Is an opening or hole in the bone located at the midline of the anterior portion of the hard palate directly posterior to maxillary central incisors.
|
|
|
The superior foramina of the incisive canal
|
Are the 2 tiny openings or holes in bone that are located on the floor of the nasal cavity. Foramina is the plural of foramen.
|
|
|
The median palatine suture
|
Is the immovable joint between the 2 palatine processes of the maxilla (the palatine processes of the maxilla form the major portion of the hard palate)
|
|
|
The lateral fossa
|
Also known as the canine fossa. Is a smooth depressed area of the maxilla located just inferior and medial to the infraorbital foramen between maxillary canine and lateral incisors.
|
|
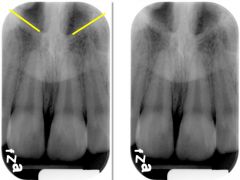
The nasal cavity
|
Also known as the nasal fossa, is a pear shaped compartment of bone located superior to the maxilla. The inferior portion, or floor, of the nasal cavity is formed by the palatal processes of the maxilla and the horizontal portions of palatine bones.
|
|
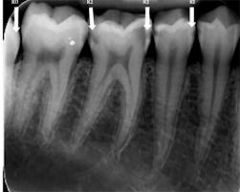
(DEJ) Dentino enamel junction
|
Is the junction between the dentine and enamel of the tooth. The DEJ appears as a line where the enamel (very radiopaque) meets the dentine (less radiopaque)
|

