![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Current |
I= q/ t
|
|
|
Ohm' Law |
V= IR |
|
|
Resistance |
R= r (L/A) r= resistance |
|
|
Resistors in Series |
Req= R1+R2+R3+R4+R5.....
|
|
|
Resistors in Parallel |
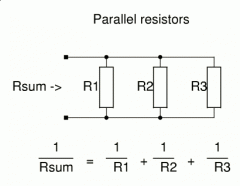
When you add more Resistors in Parallel you Decrease Resistance and Increase Current. RIP- not cool. |
|
|
Electric Power |
Power= Watts= Energy/ time (J/sec) P=IV=(I^2)R
|
|
|
Capacitance |
The ability to store charge over time. |
|
|
Potential Energy |
Storage Charge can be release at: |
|
|
Capacitors in Series |
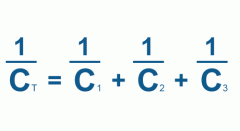
|
|
|
Capacitors in Parallel |
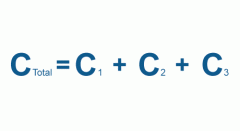
|
|
|
Dielectrics |
Cnew= kCold |
|
|
Kirchoff's 2nd Rule: |
|
|
|
Resistors SERIES |
IR1= V1 IR2= V2 |
|
|
Resistors PARALLEL |
|
|
|
Capacitor PARALLEL |
Ctota=C1+C2+C3+C4.. |
|
|
Capacitor SERIES |
1/Cs= 1/C1+1/C2+1/C3
|
|
|
Dielectrics |
Lowering the voltage across, the charged-up capacitor has made "more" room for more charge! Cnew=k(dielectric constant)Cold |
|
|
AC (Alternating Current) |
Current- (Same for Voltage). Irms= Imax/ sqr(2) or (Irms)sqr(2)= Imax |
|
|
The Capacitance |
The Capacitance of a capacitor is defined as the ratio of charge stored to the potential difference across the capacitor. |
|
|
Resistance (R) |
Can be thought of as the opposition to the flow of an electric current that occurs within a conductor. |
|
|
Kirchhoff 1st Law: Current |
States that any junction in a circuit is the sum of current directed into that point equals the sum of currents directed away from that point. |

