![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Charle's Law
|
At a constant pressure, the volume of a gas varies directly with the absolute temperature, and at a constant volume, the pressure of a gas varies directly the absolute temperature.
|
|
|
Define Boyle's Law
|
The volume of a gas varies inversely with the absolute pressure, provided the temperature remains constant.
|
|
|
Define compressive stress.
|
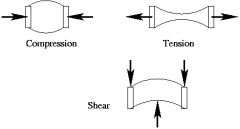
When two forces act from opposite directions, pushing toward the center of an object.
Fire tubes in a fire tube boiler are subjected to compressive stress. |
|
|
Define Shear Stress
|
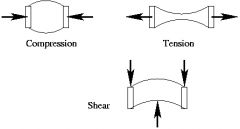
When two forces act in parallel to each other but in opposite directions
|
|
|
Define Tensile Stress
|
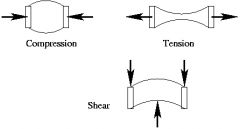
When two forces act on an object, pulling in opposite directions.
Affects boiler plates and staybolts. |
|
|
Define: Lever
|
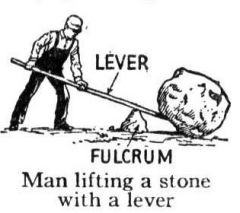
A rigid bar that pivots about one point (the fulcrum) and that is used to move an object at a second point by a force applied at a third.
|
|
|
Define: torque
|
A twisting force that tends to cause rotation.
|
|
|
Define: saturated steam
|
Steam at the temperature of the boiling point which corresponds to its pressure.
|
|
|
Define: sensible heat
|
Heat that causes a change in temperature.
|
|
|
Define: latent heat
|
Heat energy that is absorbed or rejected when a substance is changing state and there is no change in temperature.
|
|
|
Define: enthalpy
|
The total heat in the steam. (from a reference point of a given starting temperature)
|
|
|
Formula: Area of a rectangle
|
Area = w × h
w = width h = height |
|
|
Formula: Area of a circle
|
Area = πr^2
r = radius |
|
|
Formula: Circumference of a circle
|
Circumference = 2πr
r = radius |
|
|
Formula: Area of a cylinder
|
Area = 2(πr^2) + (2πr)h
r = radius h = height |
|
|
Formula: Volume of a cylinder
|
Volume = πr^2h
r = radius h = height |
|
|
Formula: °F to °C
|
°C = 5/9 (°F - 32)
|
|
|
Formula: °C to °F
|
°F = 9/5°C + 32
|
|
|
Formula: °F to Rankine
|
°R = °F + 460
|
|
|
Formula: °C to Kelvin
|
°K = °C + 273
|
|
|
Formula: Btu to Ft-lb
|
Ft-lb = Btu x 778
|

