![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
At long term follow-up, a M who sustains multiple traumatic injuries vs a premenopausal F, who sustained similar polytrauma, is most likely to have? 1-Higher quality-of-life scores than females; 2- > rates of complex regional pain synd; 3-Require >psychiatric counseling and pharmacologic managt than females
4-Take more absentee days at work as a result of illness than females; 5-Decreased incidence of lower extremity amputation |
Ten or more years after severe polytrauma, premenopausal women, compared to men, demonstrate a higher incidence of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and take more sick leave time from work, females had lower quality-of-life scores and were significantly more likely to develop early combined depression.Ans1
|
|
A pt sustains a severe LE injury. What can be said about his outcome @ 2 yrs if he chooses recon over amputation? 1-He has a higher risk of rehospitalization; 2-He has a higher chance of RTW
3-He will have a higher overall SIP (Sickness Impact Profile) score; 4-His psychosocial SIP score will improve with time; 5-He will have a better SIP score if he did not complete high school |
Severe LE injury pts undergoing reconstruction have a > rate of rehospitalization @ 2 yrs, LEAP study group; RTW = younger age, higher education, higher income, the presence of strong social support, and employment in a white-collar job that was not physically demanding, Risk factors for poorer SIP score were=rehospitalization for a major complication, a low educational level, nonwhite race, poverty, lack of private health insurance, poor social-support network, low self-efficacy (the patient's confidence in being able to resume life activities), smoking, and involvement in disability-compensation litigation.Ans1
|
|
Hx: child in a MVA GCS of 14. His injuries have been graded as severe but not life-threatening injury to the chest (3 pts), moderate injury to the abdomen (2 pts), and severe injuries but with probable survival injury to the the face or neck (4 pts) using (MISS). There are no injuries to extremities/pelvis . Based on this information, what is the child’s total MISS score?
|
The total score for the MISS, like the Injury Severity Score (ISS), is the sum of the squares for the highest injury score grades in the three most severely injured body regions. Therefore, in this case: chest (3x3) + abdomen (2x2) + face/neck (4x4) = 9+4+16 = 29. The Glasgow coma scale would be 1, which is less than the scores of 3 of the other areas so it is excluded.
|
|
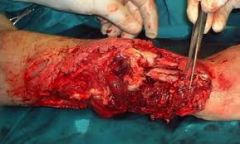
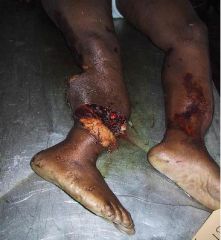
The mangled extremity severity score (MESS) utilizes all of the following variables EXCEPT: 1-Limb ischemia; 2-Shock; 3-Pt age; 4-Skeletal and soft tissue injury; 5-Time from admission to surgery
|
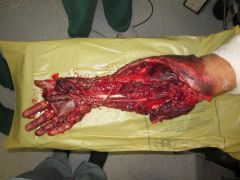
MESS is a tool utilized to help predict limb salvage success vs primary amputation at the time of presentation
1. Skeletal / soft-tissue injury: Low energy = 1; Medium energy = 2; High energy = 3; very high energy = 4; 2. Limb ischemia: Pulse reduced or absent but perfusion normal = 1; Pulseless = 2; Cool, paralyzed, insensate = 3; 3. Shock: normotensive = 0; transient hypotension = 1; persistent hypotension = 2; 4. Age: < 30 = 0; 30-50 = 1; >50 = 2. 4S-I-6=3*2-S2-A-30-50=1-heaven kiss good by your limb Limb category scores are doubled for ischemia > 6 hours. The system's original designers reported a cutoff of 7 as predicting amputation, none of the scoring systems predict functional outcomes at 6 or 24 months. |

