![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
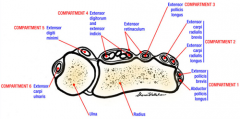
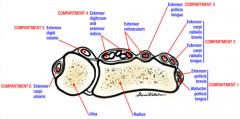
name the six compartments of the wrist? mnemonic
|
2-2-1-(Longus, short/Brevis)(Longus, short/Brvis,) (Longus)
(APL/EPB,ECRL/ECRB,EPL) 6-1-1 (EIP) (EDC) PIN-- Extensor digiti minimi (EDM)-- Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) |
|
what are the associated tendon pathology of each of 6 compartment, name the entity and name the tendon?
|
1--Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB)
Abductor pollicis longus (APL) De Quervain's tenosynovitis 2--Extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) Extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) Intersection syndrome 3--Extensor pollicis longus (EPL) Drummer's wrist, traumatic rupture w/ distal radius fx 4--Extensor indicis proprius (EIP) Extensor digitorum communis (EDC) Posterior interosseous nerve Extensor tenosynovitis 5--Extensor digiti minimi (EDM) Vaughn-Jackson Syndrome 6--Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) Snapping ECU |
|
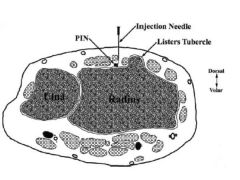
Which of the following dorsal wrist compartments is incorrectly paired with its contents? 1-Comprtmnt 6: ECU; 2- Comprtmnt->5: EDM; 3-Comprtmnt->4: EDC & PIN, 4-Comprtmnt->3: EPL & ECRL; 5-Comprtmnt->1: APL &EPB:::
|
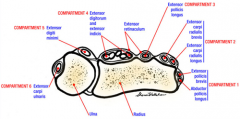
Compartment 1: Abductor pollicus longus, extensor pollicus brevis.
Compartment 2: Extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis Compartment 3: Extensor pollicus longus Compartment 4: Extensor digiti communis, extensor indicis propius, posterior interosseous nerve Compartment 5: Extensor digiti minimi Compartment 6: Extensor carpi ulnaris.Ans4 |
|
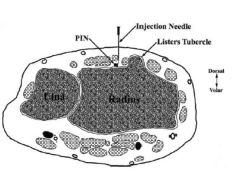
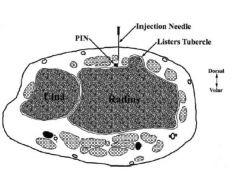
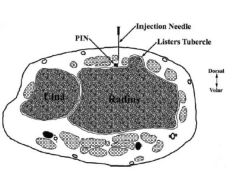
collegiate rower c/o dorsal wrst pn x 6 wks refractory: NSAIDs & brac'g. Max tendrnss: palpatd dorsoradial forearm approx 5 cm prox to wrist. Pn exacerbtd w/ resisted wrist exten. xrays= unrem, steroid in should be directed into comprtmnt contng which of the followg structures?
|
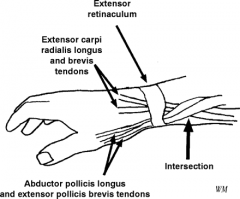
1-APL & EPB tendns; 2-ECRL & ECRB tendns; 3-EPL tendn; 4-APL & ECRB tendns; 5-Brachoradialis tendn::: Dx= intersection syndrm, a inflam response to overuse @ site 2nd dorsal comprtmnt X'ing under the 1st dorsal comprtmnt approx 5 cm prox to wrist.Ans2
|
|
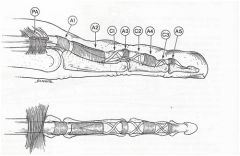
Which of the following flexor tendon annular pulleys originate from palmar plates overlying joints? 1-A1, A3, A5; 2-A2, A4; 3-A1, A2, A4; 4-A1, A2, A3; 5-A2, A4, A5
|
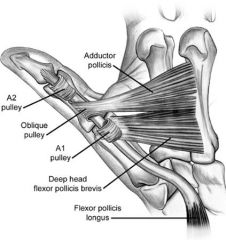
A2 & A4 arise from periosteum of prox 1/2 prox phalanx, & midportion middle phalanx.
A1, A3 A5 = jnt pulleys arising from palmar plates of the MP, PIP, DIP jnts C1, C2, C3 are thin, condensable, cruciate sections of the flexor sheath which permit the annular pulleys to approx each other durg flex.Ans1 |
|
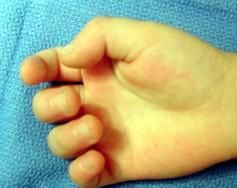
2yo child has a flex defrmty of the IP jnt ofthumb, Fig A. Surgical correction of this deformity places what structure most at risk as it crosses the surgical field? 1-Princeps pollicis A; 2-Ulnar digital N; 3-Oblique pulley; 4-Ulnar digital A; 5-Radial digital N
|
Surgical correction requires release of A1 pulley. Durg dissection, radial digital N crosses operative field & is @ risk. It must be id'd & protectd. trigger thumbs in children will resolve w/out tx in >60% of pts.Ans5
|
|
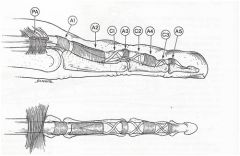
surgically tx'g a trigger finger in a child, what structr may need to be releasd in addition to A-1 pulley? 1-1 or both limbs of the sublimis tendn; 2-A-4 pulley; 3-Lumbrical origin; 4-Dorsal interosseous insertion; 5-Anomalous insertion of MCP jnt collateral lig:::
|
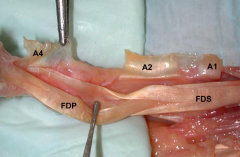
Unlike adults, release of A-1 pulley in a pedi trigger finger alone may NOT resolve triggerg sx's. all pediatric trigger fingrs should be tx'd w/ A-1 pulley release & resection of a single FDS tndn slip (aka sublimis T).Ans1
|
|
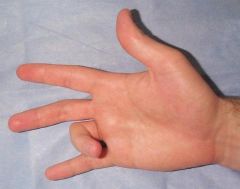
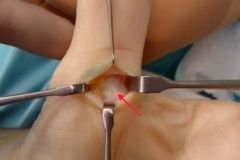
64yo DM F c/o sudden catchg & lockg of 4th fingr when trying to extend it. Attempts @ fingr exten are pnful, & notes tenderness in distal palm. Fig A. Which structures are implicated in the pathogenesis of this condition?
|
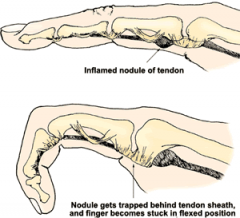
1- Extensor digitorum T; 2-Grayson's lig; 3-Oblique retinacular lig; 4-A1 pulley; 5-Transverse carpal lig:::MC'ly at the level of the 1st annular (A1) pulley, 2 corticosteroid injs given before surgery. DDx-collateral lig or volar plate tethers MC head/ Ophyte.Ans4
|
|

Chronic injury to what anatomic structure can lead to a boutonneire deformity of finger? 1-termnl extensr T;
2-sagittal band; 3-volar plate; 4-FDP T insertion; 5-central slip extensor T::: |
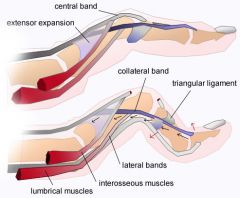
Rupture of the central slip of the extensor tendon & subsequent sublux of the lat bands grt boutonneire defrmty, which is PIP flex & DIP exten. rupture terminal extensor T= mallet fingr. Sagittal band inj= sublux exten tendn @ level MCP jnt. Chronic volar plate inj= swan neck deformts. Avulsion FDP insertn = jersey fingr.Ans5
|
|

54yo F c/o hand deformty. A surgical procedure is being considered that relocates lat bands dorsally to counteract the pathophysiology of defrmty. Which deformities does pt most likely have?
|
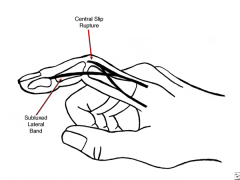
1-Boutonneire fingr defrmty; 2-Lumbrical plus fingr defrmty; 3-Mallet fingr defrmty; 4-Jersey fingr defrmty
5-Swan neck finger defmty::: PIP in flex & DIP in hyperextension, 2^ central slip rupture, Volar sublux lateral bands.Ans1 |

