![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Endocrine glands release their hormones _____________________.
(Differentiate from exocrine) |
directly into the blood.
|
|
|
Exocrine glands relase their hormones _____________________.
(Differentiate from endocrine) |
into ducts.
|
|
|
Hormones that can pass through cell membranes and reach receptors inside target cells are
|
steroid hormones.
(Broader spectrum) |
|
|
Hormones that bind only to specific receptors on the outside of target cells are
|
protein hormones.
(More specific targets, uses cyclic AMP as messenger inside the cell) |
|
|
The two main systems that are responsible for maintaining homeostasis are
|
the nervous system and the endocrine system.
|
|
|
The ________ pituitary stores and releases hormones that are produced in the hypothalamus.
|
posterior
|
|
|
The ________ pituitary produces 5 main hormones that help control the other or endocrine glands and one broad spectrum hormone.
|
anterior
|
|
|
The hormone responsible for utirine contractions or the "let down" of milk for breastfeeding is
|
oxytocin
|
|
|
The action of ADH (antidiuretic hormone) is
|
to increase the re absorption of water by the kidney and therefore decrease urine output.
|
|
|
Diabetes Insipitus is characterized by
|
too little ADH and therefore very urine volume.
|
|
|
The hormone that stimulates growth and cellular reproduction in humans is
|
HGH or human growth hormone.
|
|
|
The hormone that stimulates the mammary glands to produce milk is
|
prolactin.
|
|
|
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) in females is responsible for
|
the maturation of follicle cells and eggs in the ovaries.
|
|
|
The hormone responsible for stimulating sertoli cells in males and therefore increasing sperm production is
|
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone).
|
|
|
The hormone most directly responsible for ovulation in females is
|
LH (Luteinizing hormone).
|
|
|
LH (luteinizing hormone) in males is responsible for stimulating
|
testosterone production from lydig cells (interstitial cells) in the testicles.
|
|
|
The hormone that targets the thyroid is
|
TSH (Thyroid stimulating hormone)
|
|
|
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) targets the
|
cortex of the arenal glands.
|
|
|
Give three human problems that result from improper levels of HGH.
|
Too little in children leads to dwarfism.
Too much in children leads to giantism. Too much as an adult leads to acromegaly. |
|
|
The main hormone responsible for regulating metabolism is
|
thyroxine (T4).
|
|
|
Too little idoine in the blood will cause
|
too little thyroxine to be created and will lead to goiter (swollen thyroid gland).
|
|
|
This hormone will cause calicum to be removed from the blood and stored in bone tissue
|
calcitonin.
(Created in the thyroid gland). |
|
|
Too little thyroxine in the blood will cause the _______ gland to release ________ which will target the _________ gland to release more thyroxine.
|
pituitary
TSH Thyroid |
|
|
PTH (parathormone) is released by the parathyroid glands and causes
|
calcium to be released into the blood system (from bones, and also increase absoption in kidneys or food.)
|
|
|
Symptoms of hypothyroidism include
|
Fatigue
Weight gain Coarse, dry hair Cold intolerance Decreased libido |
|
|
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include
|
Nervousness
Heat intolerance Weight loss Warm moist skin (myxedema) Staring gaze |
|
|
Goiter has virtually been eliminated from developed countries by
|
iodizing salt.
|
|
|
Which part of the pancreas secretes insulin?
|
The Islets of Langerhans (beta cells)
|
|
|
Which part of the pancreas secretes glucagon?
|
The Islets of Langerhans (alpha cells)
|
|
|
Which hormone is released as a result of increased blood sugar levels?
|
Insulin.
|
|
|
Glucose is stored as ___________ in the liver.
|
glycogen.
|
|
|
When blood sugar levels drop below normal levels this hormone is released.
|
Glucagon.
|
|
|
Diabetes Mellitus is
|
too little insulin production.
|
|
|
Type 1 diabetes can be managed by
|
blood sugar monitoring and insulin injections.
|
|
|
Type 2 diabetes can be managed by
|
diet and oral medication.
|
|
|
Common symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus include
|
Short term effects :
High urine volume Increased thirst Fatigue Long term effects: eye, kidney, heart problems trouble with ulcers and feeling in your extremities glucose in urine acetone breath |
|
|
Hypoglycaemia is
|
too little blood sugar.
|
|
|
Other treatments for Type 1 diabetes other than insulin injections include
|
The pump or Islet transplants.
|
|
|
In times of stress, which endocrine gland is targeted by both the NS system and the endocrine system?
|
The adrenal gland.
|
|
|
The cotex of the adrenal gland when targeted by _______, will release ___________.
|
ACTH
Cortisol, and Aldosterone. |
|
|
When released during times of stress, cortisol in the blood
|
increases blood pressure and blood sugar levels and suppresses the immune system.
|
|
|
When aldosterone is released into the blood it
|
increases Na+ re-absorption in the kidney, and therefore water follows Na+ back into blood and
keeps blood fluid high. |
|
|
epinephrin or adrenalin when released into the blood
|
increases heart rate and stroke volume, dilates the pupils, and constricts arterioles in the skin and gut while dilating arterioles in leg muscles.
Generally gets the body ready for a fight or fligh response. |
|
|
pituitary gland
|
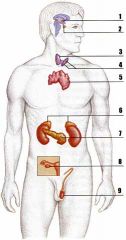
The gland labeled "2" is the
|
|
|
Diabetes Mellitus.
|
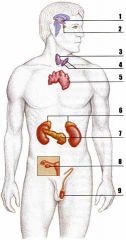
If gland "7" was removed or impaired, what condition would result?
|
|
|
Glands 3 (thyroid) and 4 (Parathyroid)
|
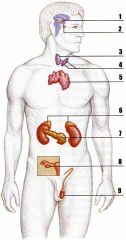
Which glands are most involved in blood calcium balance?
|
|
|
side 1, the side that regulates hypothalamus secretions.
|
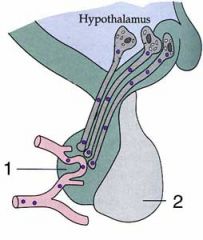
The posterior pituitary is labeled here as
|

