![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acetyl CoEnzyme A |
Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate enters the mitochondria where it is converted into acetyl CoA Acetyl CoA is the fuel for the citric Acid Cycle (CAC), which processes the 2 carbon acetly unit to 2 molecules of CO2 while generating high-energy electrons that can be used to form ATP |
|
|
How do sugars and lipids connect? |
acetyl CoA |
|
|
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex |
a mitochondrial matrix enzyme, oxidatively decarboxylates pyruvate to form acetyl CoA 3 enzymes make up the complex |
|
|
What does the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex catalyze |
1 decarboxylates pyruvate 2 oxidation 3 attachment of coenzyme A Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA involves the production of high energy molecules-->2 e |
|
|
Fates of Acetyl CoA |
Metabolism by CAC Incorporation into fatty acids |
|
|
Two regulatory mechanisms of Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA (Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex) |
Enzyme E1 a kinase associated with the complex phosphorylates and inactivates E1 A phosphatase, also in the complex, removes the phosphate and thereby activates the enzyme Energy Charge ATP, Acetyl CoA, NADH inhibit the complex ADP and pyruvate stimulate the complex |
|
|
The two stages of the CAC |
decarboxylation and regeneration of oxaloacetate |
|
|
Cellular respiration involves |
two pathways 1. CAC 2. Oxidative phosphorylation both in the mitochondria |
|
|
CoASH |
reduced acetyl attaches to H after oxidation |
|
|
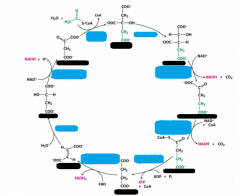
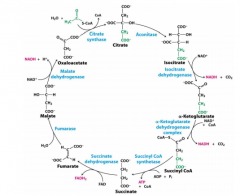
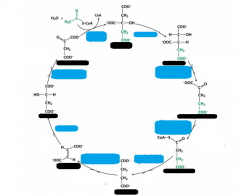
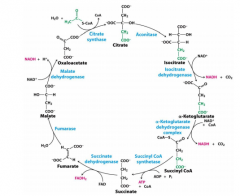
Substrates of CAC in order |
Citrate Isocitrate α ketoglutarate Succinyl CoA Succinate Fumarate Malate Oxaloacetate Citrate |
|
|
Enzymes of CAC in order |
Citrate *Aconitase Isocitrate *Isocitrate dehydrogenase α ketoglutarate *αKetoglutarate dehydrogenase complex Succinyl CoA *Succinyl CoA synthetase Succinate *Succinate dehydrogenase Fumarate *Fumarase Malate *Malate dehydrogenase Oxaloacetate *Citrate synthase Citrate |
|
|
Rxns of CAC stage one |
1. Introduction of two carbons as acetyl-CoA-formingcitrate 2. Citrate isomerization 3. Isocitrate is oxidized to form NADH and CO2 4. a-Ketoglutarate is oxidized; forms NADH and CO2 Reactions 3 and 4 are oxidative decarboxylationreactions |
|
|
Rxns of CAC stage two |
5. Cleavage of Succinyl-CoA leads to substrate-levelphosphorylation 6. Succinate is oxidized to form fumarate and FADH2 7. Fumarate is hydrated and forms L-malate 8. Malate is oxidized to form oxaloacetate and a thirdNADH |
|
|
The key catabolic function of CAC |
is the production of high energy electrons in the form of NADH and FADH2 |
|
|
Electrons from NADH and FADH2 |
each NADH has 2 e forms 2.5 ATP when used to reduce oxygen in e transport chain FADH2 forms 1.5 ATP with the reduction of oxygen in the e transport chain |
|
|
how many oxidation reactions are in the CAC |
5--> 4 dehydrogenases and one fumarase of 5 two are oxidative decarboxylation |
|
|
what is special about step 1,2,8 |
1 condensation 2 dehydration 8 coupled with one with concentration to overcome positive change in G |
|
|
CAC regulated by |
Isocitrate dehydrogenase + ADP - ATPand NADH α ketogluterate dehydrogenase - ATP, succinyl CoA, and NADH |
|
|
Biosynthesis through oxaloacetate |
glucose aspartate-->other aas, purines, pyrimidines |
|
|
Biosynthesis through Succinyl CoA |
Porphyrins, heme, chlorophyll |
|
|
Biosynthesis through α ketogluterate |
Glutamate-->other aas-->purines |
|
|
Biosynthesis through Citrate |
fatty acids, sterols |
|
|
Anapleuretic rxn |
replenishing rxn. replenish intermediates that occur within a cycle. Pyruvate to oxaloacetate catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase |
|
|
Citrate * Isocitrate |
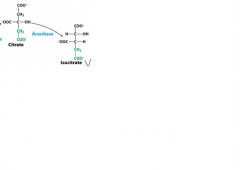
Citrate *Aconitase Isocitrate |
|
|
Isocitrate * α ketoglutarate |
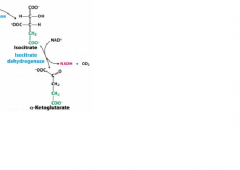
Isocitrate dehydrogenase |
|
|
α Ketoglutarate * Succinyl CoA |
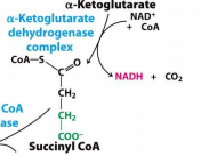
α Ketoglutarate deydrohenase complex |
|
|
Succinyl CoA * Succinate |
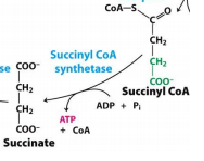
Succinyl CoA sythetase |
|
|
Succinate * Fumarate |
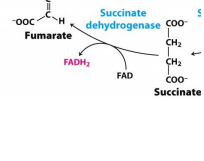
Succinate Dehydrogenase |
|
|
Fumarate * Malate |
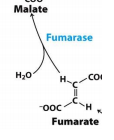
Fumarase |
|
|
Malate * Oxaloacetate |
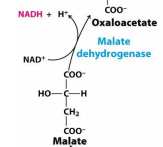
Malate dehydrogenase |
|
|
Oxaloacetate * Citrate |
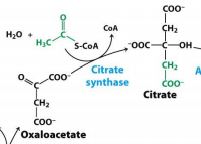
Citrate Synthase |
|
|
|
|
|
|

