![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sudden onset of stroke symptoms is suggestive of vascular or tumor |
Vascular |
|
|
Imbalance, slurred speech and visual disturbances is suggestive of an anterior or posterior cva |
Posterior |
|
|
By what factor does diabetes increase risk of stroke |
2 |
|
|
How much, in grams does the brain use in glucose |
120 g |
|
|
Glutamate transporters to astrocytes are primary or secondary active transporters |
Secondary |
|
|
What does basillar artery bifurcate into |
Posterior cerebral |
|
|
In homunculus where is foot located |
Medial margin |
|
|
What is largest cerebral artery and most commonly affected by stroke |
Middle cerebral |
|
|
Occlusion of mca leads to... |
Contralatetal paralysis and sensory deficits of lower face, arm. Aphasia of dominant hemisphere and hemianopia of Contralatetal visual field |
|
|
Which supplies more medial region of brain, anterior or middle cerebral artery |
Anterior |
|
|
Occlusion of anterior cerebral artery leads to... |
Paralysis/sensory deficit to Contralatetal leg and perineum, cognitive, emotional problems, dysphasia |
|
|
Occlusion of posterior cerebral artery leads to.. |
Contralatetal visual field defects. Hemisensory deficits, can get memory deficit |
|
|
How do perforating differ from anterior and middle cerebral arteries |
They are end arteries |
|
|
What is trigger for spreading depolarisation |
Potassium and glutamate in extracellular space |
|
|
Risk of late reperfusion of cva |
Hemorrhagic conversion |
|
|
Where does calcium move to in cva, intra or extra cellular |
Intra |
|
|
Forebrain parts and locations |
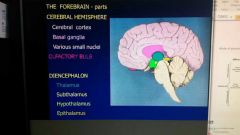
|
|
|
How many layers in allocortex and neocortex |
3 and 6 |
|
|
Which layer, supragranular or infragranular has intracortical connections |
Supra |
|
|
Which numbered layer is the granular layer |
4 |
|
|
Central sulcus is separation between which two lobes |
Frontal and parietal |
|
|
Damage to secondary motor cortex - what sort of signs would you see |
Reflex reactions |
|
|
Damage to superior parietal lobule causes deficits in what |
Conscious proprioception Contralatetal |
|
|
Damage of dominant and non dominant inferior parietal lobule causes what |

Dominant is language, non is somatosensory disregard |
|
|
"What" visual processing stream is dorsal or ventral? |
Ventral |
|
|
Damage to brocas area causes what |
Loss of fluency - can't get words out tho knows what to say |
|
|
Which region, fore, mid or hindbrain are sounds processed |
Mid |
|
|
Language processing goes into brocas or wernickes first |
Wernickes |
|
|
Give example of disconnection syndrome |

|
|
|
What does superior longitudinal fasciculus connect |
Frontal and occipital |
|
|
Inferior longitudinal fasciculus connect what |
Occipital to temporal for visual recognition |
|
|
Which association fibres connect wernickes to brocas |
Arcuate fasciculus |
|
|
3 primary control areas of movement are |
Spinal cord, brain stem, cerebrum |
|
|
Idea of movement originates where |
Prefrontal cortex |
|
|
Blood supply of premotor cortex |
Lateral side so middle cerebral |
|
|
Blood supply of supplementary motor area |
Medial so anterior cerebral |
|
|
Cerebellum functions |
Balance, coordination and motor memory |
|
|
Where do 3 cerebellar arteries arise from |
Basillar |
|
|
Blood supply to basal ganglia |
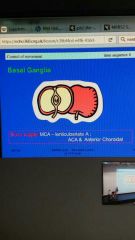
|
|
|
Would you expect spasticity or flaccidity after acute pathology to motor pathways (motor cortex, internal capsule) |
Contralatetal flaccid paralysis |

