![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
222 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
stridor, wheezing
|
upper airway obstruction
tracheal lesions rings and slings foreign bodies asthma |
|
|
upper airway obstruction
|
inflammation
epiglottitis (h.inf) croup (rsv) retropharyngeal abscess exogenous caustic ingestion foreign body extrinsic upper airway compression thyroglossal duct cysts branchial cleft cysts other masses |
|
|
bubbly lungs in neonates
|
bronchopulmonary dysplasia (most common)
pulmonary interstitial emphysema cystic fibrosis wilson-mikity syndrome |
|
|
mass lesions in airways
|
lymphangioma and hemangioma may occur in any 3 locations
nasal cavity, nasopharynx antrochoanal polyp meningoencephalocele angiofibroma lymphadenopathy neuroblastoma rhabdomyosarcoma oropharynx lymphadenopathy ectopic thyroid tissue hypopharynx, larynx, or trachea retention cysts papillomas |
|
|
neonatal lung masses
|
lung bases; cp angle obliterated
sequestration cdh ccam hypoplastic lung (scimitar syndrome) phrenic nerve paralysis other lung zones pulmonary tumor neuroblastoma pulmonary blastoma pnet (askin tumor) congenital lobar emphysema (only early in disease) |
|
|
hyperlucent lung
|
large anterior pneumothorax (common)
congenital lobar emphysema congenital lung cyst bronchiolitis obliterans (swyer-james syndrome, not until > 7 yo) obstructive emphysema obstruction at the bronchiolar level-cf, ashtma, pneumonia, foreign body extrinsic compression-rings and sligns, adenopathy, bronchogenic cyst ccam |
|
|
neonatal pnumothorax
|
pressure ventilation
interstitial pulmonary emphysema pulmonary hypoplasia (fetal anurai syndrome, potter sequences, oligohydramnios) |
|
|
solitary pulmonary nodule
|
congenital
bronchogenic cyst (common)-65% in long, 35% from tracheobronchial tree sequestration avm, varix bronchial atresia infection round pneumonia, most common granuloma abscess cavity tumor primary-pnet, pulmonary blastoma neuroblastoma, wilms' tumor mets |
|
|
multiple pulmonary nodules
|
tumor
mets-wilms, teratoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma laryngeal papillomatosis (pulmonary lesions are rare) infection septic emboli tb, fungus inflammatory wegeners disease (sinuses also involved) |
|
|
pediatric interstitial pattern
|
congenital
storage disease-gauchers, neimann pick lymphangiectasia other common causes viral pneumonia bronchopulmonary dysplasia hyaline membrane disease histiocytosis x |
|
|
pediatric chest wall tumors
|
common signs-pleural effusions, rib destruction, soft tissue density
eosinophilic granuloma askin tumor (PNET) neuroblastoma met's Ewing's sarcoma |
|
|
Dilated stomach
|
hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
pylorospasm antral web antral gastritis rare duplication cysts ectopic pancreatic tissue polyps, neoplasm |
|
|
double bubble sign of stomach
|
little or no gas distally
duodenal atresia-associated with downs-or stenosis, most common annular pancreas, 2nd most common duodenal diaphragm, bands midgut volvulus vascular preduodenal vein sma syndrome rare duplication cysts adhesions |
|
|
proximal bowel obstruction
|
neonates (congenital causes)
atresia/stenosis of small bowel midgut volvulus Ladd's bands children (>1 year) intussusception (most common) incarcerated inguinal hernia (6-24 months) perforated appendicitis |
|
|
distal bowel obstruction
|
hirschsprung's disease
meconium plug syndrome colonic atresia/stenosis imperforate anus meconium ileus rare causes volvulus presarcral tumors post-nec strictures |
|
|
microcolon
|
diabetic mothers
maternal mgso4 use unused colon ileal atresia mecononium ileus total colonic hirschsprung's disease |
|
|
pediatric pneumatosis intestinalis
|
necrotizing enterocolitis
less common causes (benign) cystic fibrosis collagen vascular disease leukemia milk intolerance immunodeficiency obstruction steroid use |
|
|
gasless abdomen
|
severe vomiting (most common)
gastroenteritis appendicitis impaired swallowing esophageal atresia neurologic impairment mechanical ventilization (paralyzed bowel) |
|
|
displaced bowel loops
|
bowel not in abdomen (hernia, omphalocele)
masses ascites |
|
|
abdominal calcifications
|
intraabdominal-meconium peritonitis (most common)
renal neuroblastoma, wilm's tumor nephrocalcinosis renal cysts urinary tract calculus bowel-fecallith of appendix, meckel's bladder-hemorrhagic cystitis (cytotoxan therapy) adrena-hemorrhage, wolman's disease cholelithiasis (ss) liver-hepatoblastoma, granuloma |
|
|
abdominal mass lesions in neonate (<1month)
|
renal 55%
hydronephrosis mcdk gastrointestinal 15% duplication meconium pseudocyst pseudocyst proximal to atresia retroperitoneal 10% adrenal hemorrhage genital 15% ovarian cyst hydrometrocolpos hepatobiliary 5% hemnagioendothelioma choledochal cyst |
|
|
abdominal mass lesions in older infants, children
|
renal 55%
wilms tumor hydronephrosis gastrointestinal 15% appendiceal abcess intussusception neoplasm retroperitoneal 25% neuroblastoma genital 5% ovarian cyst hydrometrocolpos hepatobiliary 5% hepatoblastoma |
|
|
gastric filling defect
|
foreign bodies
lactobezoar, phytobezoars, trichobezoars congenital anomalies duplications ectopic pancreatic tissue inflammation, rare crohns disease chronic granulomatous disease tumors, rare hamartoma peutz, jeghers disease |
|
|
thick folds
|
submucosal edema
enteritis submucosal tumor lymphoma, leukemia submucosal hemorrhage henoch-schonlein purpura HUS coagulopathies |
|
|
gi hemorrhage
|
meckel diverticulum
juvenile polyps ibd portal hypertension |
|
|
pediatric liver lesions
|
benign
cysts hemangioendothelioma mesenchymal hamartoma malignant hepatoblastoma hemangioendothelioma (neonate) hepatocellular carcinoma if underlying liver disease (glycogen storage disorders, phtn) mets from wilms tumor or neuroblastoma |
|
|
fatty liver
|
chronic protein malnutrition (most common)
congenital cystic fibrosis glycogen storage disease wilsons disease galactosemia fructose intolerance reye's syndrome hepatitis drugs-chemotherapy, steroids, hyperalimentation |
|
|
pediatric cholelithiasis
|
hemolysis
sickle cell anemia thalassemia splenocystosis other cystic fibrosis drugs-furosemide metabolic disorders-hyperparathyroidism premature infants with hyaline membrane disease |
|
|
hydrops of gallbladder
|
sepsis
burns leptospirosis kawasaki's disease |
|
|
cholecystitis
|
sickle cell
hemolytic anemia |
|
|
biliary strictures
|
pancreatitis
gallstones ascending cholangitis post-kasai procedure liver transplant |
|
|
fatty replacement of pancreas
|
cystic fibrosis
schwachman-diamond syndrome metaphyseal dysplasia cyclic neutropenia pancreatic fatty replacement flaring of ribs |
|
|
pediatric pancreatitis
|
trauma
viral infection sepsis idiopathic anomaly drugs (steroids, etc) metabolic cystic fibrosis hyperlipidemia |
|
|
cystic renal masses
|
cystic disease
arpckd mcdk multilocular nephroma cysts associated with phakomatoses vh ts other cystic disease tumors cystic wilms tumor cystic adenocarcinoma |
|
|
hydronephrosis
|
most common abdominal mass in neonates
reflux upj obstruction uvj obstruction ectopic ureterocele posterior urethral valves prune belly |
|
|
solid renal masses
|
wilms tumor-most common solid tumor in children, rare in newborn
mesoblastic nephroma-only solid renal mass in newborns nephroblastomatosis-subcortical masses associated with wilms angiomyolipoma, assoc with ts secondary tumors lymphoma neuroblastoma leukemia, diffuse bilateral enlargement rare renal tumors clear cell sarcoma malignant rhabdoid renal cell carcinoma |
|
|
diffusely hyperechoic renal kidney in newborn
|
increased size
arpckd (bladder usually empty) cmv glomerulonephritis (bladder may have some urine) glomerular cystic disease diffuse cystic dysplasi decreased size renal dysplasia from obstructive uropathy or necrosis |
|
|
echogenic kidney (cortex similar to the spleen or liver with preserved corticomedullary differentiation)
|
ATN
glomerulonephritis renal infiltration glycogen storage disease diabetes renal vein thrombosis leukemia hiv kawasaki disease |
|
|
loss of normal corticomedullary differentiation
|
pyelonephritis, focal nephronia
infantile polycystic kidney adult polycystic kidney medullary cystic kidney late renal vein thrombosis |
|
|
medullary nephrocalcinosis
|
furosemide therapy
hyperparathyroidism RTA hypercalcemia or hypercalcuria milk aklali idiopathic hypercalcuria sarcoidosis hypervitaminosis D oxalosis medullary sponge kidney |
|
|
congenital ureteric obstruction
|
primary megaureter
ureterocele (ectopic or orthotopic) distal ureteral stenosis ureteral atresia circumcaval ureter bladder diverticulum |
|
|
adrenal masses
|
neonatal hemorrhage
neuroblastoma rare teratoma adenoma carcinoma pheochromocytoma other retroperitoneal masses wilms tumor hydronephrotic upper pole retroperitoneal adenopathy hepatoblastoma splenic mass |
|
|
cystic structure in or near bladder (us)
|
bladder
hutch diverticulum urachal remnant (dome of the bladder) normal "bladder ears" (incompletely filled bladder extends to femoral/inguinal canal) ureter ectopic insertion of ureter ureterocele megaureter other ovarian cyst mesenteric, omental cyst |
|
|
large abdominal cystic mass
|
lymphangioma (multiseptated noncalcified)
enteric duplication cyst (unilocular noncalcified with bowel signature) meconium pseudocyst (unilocular containing echoes and debris) choledochal cyst adrenal hemorrhage ovarian cyst |
|
|
presarcral mass
|
rectal duplication
anterior meningocele teratoma neuroblastoma |
|
|
interlabial mass
|
ectopic ureterocele
periurethral cysts rhabdomyosarcoma of the vagina prolapsed urethra imperforate hymen |
|
|
enlarged head (macrocephaly)
|
hydrocephalus (most common cause before closure of sutures)
communicating noncommunicating rate subdural hematoma calvarial abnormalities benign macrocrania chrondrodystrophies brain abnormalities beckwith-wiedemann syndr hemiatrophy cerebral gigantism |
|
|
small head (microcephaly)
|
absent or atrophic brain (congenital infection, fetal alcohol syndrome)
craniosynostosis shunt placement |
|
|
thick skull
|
metabolic/systemic
healing stage of renal osteodystrophy hyperparathyroidism (salt and pepper skull) anemias tumor leukemia, lymphoma other chronic decreased intracranial pressure (shunts) dilantin dysplasia fibrous dysplasia engelmann's disease |
|
|
lytic skull lesions
|
eg
leukemia, lymphoma fibrous dysplasia dermoid, epidermoid hyperparathyroidism |
|
|
normal intracranial calcifciation
|
choroid plexus calcification
habenula calcification pineal gland calficiation falx-dura, pacchionian bodies hemangioblastoma calcifcation |
|
|
abnormal intracranial calcifications
TIC MTV |
Tumor
children-craniopharyngioma>oligodendroglioma>gliomas>other tumors adults-meningioma>oligodendroglioma>ependymoma infection children-TORCH adults-cysticercosis, TB congenital, degenerative atrophic lesions congenital atrophy or hypoplasia tuberous sclerosis sturge weber syndrome metabolic idiopathic hypercalcemia lead poisoning hypoparathyroidism fahr's disease trauma vascular lesions avm (vein of galen) hematoma aneurysms |
|
|
enlarged sella turcica
|
tumor (most common)
craniopharyngioma optic chiasm-hypothalamic glioma less common-germ cell tumors, meningioma, pituitary adenoma increased intracranial pressure empty sella nelson's disease |
|
|
common pediatric bone tumors
|
primary
EG ewing's sarcoma osa bone cysts UBC (fallen fragment sign) ABC (eccentric) secondary neuroblastoma mets lymphoma leukemia tumors with fluid fluid level ABC telangiectatic OSA giant cell tumor single cysts with path fracture |
|
|
widened joint space
|
joint effusion
septic arthritis hemarthrosis (intraarticular fracture, hemophiliac) transient toxic synovitis JRA synovial thickening without articular cartilage destruction JRA hemophiliac arthopathy |
|
|
bowed bones
anterior and posterior bowing (fetal malposition) is always abnormal. anterior bowing maybe associated with medial and lateral bowing. isolated medial bowing is usually idiopathic |
common causes of anterior bowing
metabolic rickets dysplasia neurofibromatosis osteogenesis imperfecta fibrous dysplasia |
|
|
diffuse pediatric osteopenia
|
rickets
hyperparathyroidism immobilization JRA uncommon causes infiltrative disease-gangliosidosis, mucolipidosis same causes as in adults |
|
|
diffuse dense bones in children
|
congenital
osteopetrosis pyknodysostosis melorheostosis progressive diaphyseal dysplasia (engelmanns disease) infantile cortical hyperostosis idiopathic hypercalcemia of infancy (williams syndrome) generalized cortical hyperostosis (van buchems disease) pachydermoperiostosis other hypothyroidism congenital syphillis hypervitaminosis D |
|
|
symmetrical periosteal reaction in children
can be physiological in first 6 months of life TIC MTV |
tumor
neuroblastoma leukemia, lymphoma infection congenital infection-syphillis, rubella congenital caffeys disease (infantile cortical hyperostosis) osteogenesis imperfecta metabolic hypervitaminosis A,D prostaglandin E therapy scurvy trauma battered child syndrome (subperiosteal hematoma) vascular bone infarctions (sickle cell) |
|
|
periosteal reaction
SCALP |
scurvy
caffey's disease accident, hypervitaminosis A leukemia, lues physiological, prostaglandin inhibitors |
|
|
deformed epiphysis
|
acquired (single epiphysis)
avn lcp disease steroids trauma (ocd) infection hypothyroidism congenital dysplasia (multiple epiphyses) multiple epiphyseal dysplasia myer's dysplasia morquio's syndrome |
|
|
enlarged epiphysis
|
most commonly caused by hyperemia associated with chronic arthritis
hemophiliac joints JRA chronic infectious arthritis healed LCP disease epiphyseal dysplasia hemimelia (Trevor's) |
|
|
transverse metaphyseal lines
result of abnormal enchondral bone growth; undermineralization leadis to lucent lines and repair leads to dense lines, some diseases, dense and lucent lines coexist |
lucent lines
neonates-stress lines (hypoperfusion of rapidly growing metaphyses of long bones) due to fever, congenital heart disease, any severe disease >2 years consider tumors neuroblastoma, mets lymphoma, leukemia dense lines neonates-growth recovery lines >2 yo heavy metal poisoning (lead bands) healing rickets |
|
|
widened growth plate
|
>1mm
rickets (most common) salter-harris type 1 fx tumor-lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma infection-osteomyelitis |
|
|
metaphyseal fragments
|
battered child-corner fx
trauma blount's disease osteomyelitis |
|
|
vetebral plana
|
mets (neuroblastoma most common)
eg leukemia, lymphoma infection trauma |
|
|
generalized platyspondyly
|
osteogenesis imperfecta
dwarfism (thanatophoric, metatropic) morquios syndrome cushing syndrome |
|
|
fused vertebrae
|
isolated fusions
klippel-feil syndrome (c2-c3 fusion, torticollis, short neck) post-traumatic |
|
|
large vertebral body or other abnormal shape
|
blood dyscrasia (expansion of red marrow)-sickle cell, thallasemia
|
|
|
atlantoaxial subluxation
|
down syndrome
morqios syndrome JRA trauma |
|
|
disc space narrowing
|
common
infection-pyogenic, tb, brucella, typhoid) block vertebra-congenital or acquired scheuermanns disease severe kyphosis or scoliosis uncommon congenital cockayne kniest dysplasia morquio's spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia acquired inflammatory arthritis herniated disc neuropathic arthropathy (syrinx) trauma |
|
|
enlarged disc space
|
osteoporosis
binconcave vertebra gauchers disease platyspondyly sickle cell anemia trauma |
|
|
intravertebral disc space calcification
|
common
idiopathic (transient in children) posttraumatic uncommon spinal fusion ochronosis aarskog syndrome ankylosing spondylitis cockaynes syndrome homocystinuria hpercalcemia hyperparathyroidsm hypervitaminosis D infection paraplegia juvenile chronic arthritis |
|
|
pediatric sacral abnormalities
|
meningocele
neurofibromatosis presacral teratoma agenesis |
|
|
radial ray deficiency
|
absence of 1st and/or 2nd digits of hand; often involves radius
holt-orams syndrome (cardiac, chest wall anomalies) polands syndrome fanconis anemia thrombocytopenia-absent radius syndrome |
|
|
polydactyly
|
familial polydactyly
chondroectodermal dysplasia (ellis-van creveld syndrome) trisomies 13-15 laurence-moon-bardet-biedel syndrome |
|
|
abnormal 4th metacarpal
|
short metacarpal
normal variant turners syndrome pseudo, pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism acrodysostosis MED growth arrest-sickle cell, infections acquired trauma, chronic arthritis long metacarpal macrodystrophia lipomatosa neurofibromatosis |
|
|
delayed bone age
|
systemic disease (most common)
hypothyroidism (cretinism, typical hypoplastic T12 and L1) cyanotic congenital heart failure chronic pulmonary disease HGH deficiency (pituitary dwarfism) isolated HGH deficiency craniopharyngyoma, infections peripheral tissue nonresponsive to HGH african pygmies turners syndrome constitutional short stature |
|
|
hemihypertrophy
|
enlargement of an extremity (rare)
intraabdominal tumors (frequently Wilms) arteriovenous fistula lymphangioma isolated anomaly (idiopathic) |
|
|
down syndrome
|
duodenal atresia
tracheoesophageal fistula, esophageal atresia endocardial cushion defect hirschsprungs disease multiple sternal ossification centers 11 ribs |
|
|
williams syndrome (idiopathic hypercalcemia)
|
aortic stenosis (supravalvular)
peripheral pulmonic stenosis diffuse coarctation of abdominal aorta and stenosis of visceral branches multisystem abnormalities retardation dentation abnormalities elfin facies |
|
|
beckwith wiedmann syndrome
|
macroglossia
visceromegally gigantism omphalocele wilms tumor |
|
|
premature infants
|
hyaline membrane disease
necrotizing enterocolitis germinal matrix hemorrhage periventricular leukoencephalopathy PDA |
|
|
urachal remnants
|
patent urachus (50%)
urachal cyst (30%) urachal sinus (15%) vesicourachal diverticulum (5%) late complication mucinous adenoca-> resected |
|
|
mullerian duct abnormalities in males
|
prostatic utricle
infants hypospadias, incomplete testicular desent mullian duct cysts not associated with other pelvic structures can be associated with seminal vesicle cyst |
|
|
cystic pelvic masses in children
|
dilated fluid filled vagina
transverse vaginal septum dermoid (girls) duplication cyst mullerian duct cyst |
|
|
hydronephrosis with megaureter in children
|
reflux megaureter
primary primary reflux prune-belly secondary neuropathic bladder posterior urethral valve obstructed megaureter primary stenosis (UVJ) ureterocele secondary intrinsic obstruction (stone, clot) extrinsic obstruction (tumor) nonreflux, nonobstructed megaureter primary congenital adynamic segment secondary infection persistent after surgery |
|
|
weigert-meyer rule
|
in duplicated collecting systems and ureters, the upper pole ureter is ectopic and often associated with an ureterocele and orifice inserts inferomedially in the bladder in relationship to the lower pole normal ureter which is prone to reflux
|
|
|
urolithiasis in children
|
chronic infection
metabolic disorders hypercalcemia hyperoxaluria hyperuricosuria congenital anomalies that cause obstruction |
|
|
pediatric renal cystic disease
|
simple renal cyst
intrarenal parapelvic cystic medullary disease nephronophthisis medullary sponge kidney polycystic renal disease ADPCKD ARPCKD-see striated nephrograms early on and then small multiple cysts as get older, pulmonary hypoplasia, inversely proportional to liver fibrosis and liver failure, if survive infancy renal dysplasia MCDK cystic tumors multilocular cystic nephroma cystic wilms tumor acquired renal cysts infectious cysts pyogenic cysts chronic dialysis |
|
|
simple renal cyst in children
|
very rare, so if you see it think of TS, VHL, caroli disease, and NF
|
|
|
striated nephrograms in children
|
infection
arpckd medullary sponge kidney |
|
|
Von Hippel Lindau Disease
|
AD
hemangioblastomas (brain, retina, spinal cord) renal cysts + RCCs type 1- no pheos type II- pheos pancreatic cysts, islet cell serous cystadenomas |
|
|
tuberous sclerosis
|
adenoma sebaceum, seizures, mental retardation
renal cysts, AML rhabdomyomas of the heart cortical hamartomas and subependymal nodules, giant cell tumors liver and pancreatic adenomas |
|
|
multilocular cystic nephroma
|
bengin cystic part. diff. nephroma-baby boys (3m-4y)
thin septa, herniates into renal pelvis, septa enhance, bosniac 3 cystic nephroma-yong women well-circumscribed multicystic renal mass, single multiloculated thickwalled cyst with enhancing septa may have small foci of soft tissue, rim enhancement microscopic foci of wilms or sarcoma no mets ddx cystic wilms cystic rcc mcdk (segmental)-septation dont enhance |
|
|
Wilms tumor
|
mean age 3 years
WT1 (11p13), WT2 (11p15.5) 5% bilateral claw sign, pseudocapsule calcifications, inhomogenous enhances tumor thromus in IVC negative urine catecholamines |
|
|
neuroblastoma
|
mean age 2 years
from adrenal gland/sympathetic chain encases abdominal vessels, grows behind aorta invades spinal canal inhomogenous, ca++ in 40-60% T1 hypo, T2 hyper postivie MIBG >90% +urine catecholamines |
|
|
meosblastic nephroma
|
benign tumor, fetal renal hamartoma
spectrum from benign to malignant spindle cell sarcoma most common renal tumor in neonates complex abdominal mass, looks like wilms in baby <10 mo |
|
|
nephroblastomatosis
|
mean age 3 years
WT1, WT2 often bilateral specific appearance, 4 types homogenous, well defined does not enhance no extension into renal vein or IVC most regress, follow, however, can turn into wilms |
|
|
solid renal or perirenal tumors of kids
|
wilms
neuroblastoma mesoblastic nephroma nephroblastomatosis RCC renal medullary carcinoma |
|
|
renal medullary carcinoma
|
sickle cell disease
|
|
|
pediatric nose obstruction
|
anterior inlet stenosis-assoc with single central incisor, midline brain defects
choanal atresia polyps tumor trauma encephalocele dacrocystocele |
|
|
pediatric nasopharynx obstruction
|
adenoids-ie mononucleosis
lymphoma abcess juvenile angiofibroma-desnse enhancement, bone erosion, vascular, needs preembolization teratoma rhabdomyosarcoma |
|
|
pediatric oropharynx obstruction
|
palatine tonsils-inf mono
peritonsillar abscess macroglosssia micrognathia termatoma lingual tonsil thyroglossal duct cyst ranula |
|
|
pediatric supraglottic obstruction
|
epiglottitis
aryepiglottic fold cyst hemangioma lymphangioma |
|
|
pediatric subglottic obstruction
|
croup
hemangioma |
|
|
pediatric trachea obstruction
|
tracheomalacia/innominate artery impression
stenosis, congenital (complete cartilaginous rings) stenosis, post-traumatic-granuloma, web vascular ring/anomalous vessels trachael foreign body esophageal foreign body lymphoma granulomatuous disease papilloma |
|
|
double arch (right arch usually dominant)
right arch with anomalous left subclavian artery and ligamentum arteriosum |
posterior tracheal narrowing
esophageal impression posteriorly |
|
|
pulmonary sling
|
anomalous left PA from RPA
anterior esophageal impression/between trachea and esophagus tracheal narrowing variable-associated with congenital tracheal stenosis/complete cartilaginous rings |
|
|
innominate artery impression
|
not anomalous
anterior impression on trachea occasionally causes sx along with tracheomalacia |
|
|
agenesis-hypoplasia complex ie hypogenetic lung ie congenital pulmonary venolobar (scimitar) syndrome
|
agenesis, aplasia, hypoplasia
bronchial anomalies anomalous pulmonary venous return "scimitar" appearance associated anomalies-sequestration, cardiac, skeletal, diaphragm horseshoe lung-part of spectrum, right lung crosses midline posteriorly, usually pleura separates r and l lung |
|
|
congenital lobar emphysema
|
fluid-filled in utero, and initially at birth, but clears over time
inflated with air-mass effect pulmonary vessels markedly attenuated LUL, RML most common>rUL, 5% two lobes CT hyperaeration with vascular structures assoc with cv anomalies in 14-50%-pda, vsd, tof ddx bronchial atresia-hyperaeration plus bronchial impaction on CT |
|
|
sequestration
|
intralobar
systemic arterial supply pulmonary venous drainage solid, cystic, air trapping extralobar systemic arterial supply systemic venous drainage (occ. pulm., porta) lower lobe L>R above, at, or below diaphragm associcated with other congenital malformations-hypoplasia/venolobar occassionally systemic arteries are recruited to lung in chronic lung/pleural inflammation |
|
|
bronchopulmonary foregut malformations
|
esophageal duplication
bronchogenic cyst mediastinal>parenchymal fluid filled>air filled neuroenteric cysts-rare, vertebral anomalies CCAM type 1-large cysts, most common type 2-small cysts type 3-rare, solid overlap with sequestration-systemic arteries associated with pleuropulmonary blastoma sequestration |
|
|
brochiolitis obliterans
|
radiograph-hyperaeration or normal
unexplained respiratory symptoms ? prior infection (adenovirus not RSV) s/p bone marrow or organ transplantation CT-mosaic pattern, small airway disease, asthma on CT has similar appearance expiratory phase-air trapping swyer james-unilateral lung, decreased pulmonary vascularity |
|
|
pneumoperitoneum in a newborn
|
NEC
gastric perforation isolated small bowel perf from intraurterine ischemic event perf secondary to obstruction (hirschsprung, atresia, meconeum ileus) iatrogenic colon perforation (thermometer, enema tip) decompression of pneumothorax or pneumomediastinum |
|
|
associations with malforation/midgut volvulus
|
congenital diaphragmatic hernia
omphalocele gastroschisis prune-belly syndrome heterotaxy |
|
|
hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
|
muscle thickness > 3mm
length of pyloric channel > 15 mm absence of fluid through pyloric channel |
|
|
intussuception
|
6 month to 4 years, if older think underlying cause
most common lead point if not idiopathic is meckel's diverticulum |
|
|
salter harris classification
|
type 1-through growth plate
type 2-through metaphysis and growth plate (75%) type 3-through epiphysis and growth plate type 4-through metaphysis, growth plate, and epiphysis type 5-compression fracture of growth plate |
|
|
bowing fracture
|
may remodel without manipulation if <20 degree angulation
|
|
|
bunk bed fracture
|
buckle fracture of the proximal 1st metatarsal
3-6 yo history of fall or jump from height onto hardwood floor |
|
|
ossification centers in elbow
CRITOE |
capitellum 1-2 yr
radial head 3-4 yr Internal epi 5-6 yr trochlea 7-8 yr olecranon 9-10 yr external 11-12 yr |
|
|
juvenile tillaux fracture
|
salter harris 3
|
|
|
triplane fracture
|
salter harris 4
evaluate congruence of the articular component and displacement of fracture fragment |
|
|
abdominal wall defects
|
cephalic fold defect-pentaology of cantrell (CHD, ventral hernia, sternal defect, absent anterior diaphragm, percardial defect)
lateral fold defect-omphalocele, gastroschisis caudal fold defect-cloacal extrophy (omphalocele, epispadias, and bladder extrophy) |
|
|
omphalocele
|
2/3 have-cardiovascular, chromosomal (13,18,21), malrotation abnormalities
|
|
|
esophageal atresia/tracheoesophageal fistula
|
maternal polyhydramnios
drooling, coughing, choking, cyanosis can't pass ngt 50% have associated anomalies most common type-proximal atresia, distal TE fistula |
|
|
VACTERL
|
vertebral segmentation anomalies
anal atresia cardiac te fisula and ea renal limp |
|
|
esophageal atresia w/o te fistula
|
no distal bowel gas
associated with down's patients |
|
|
proximal bowel obstruction in neonate
|
gastric atresia or web
pyloric stenosis duodenal atresia, stenosis or web-80% of atresias occur just distal to ampulla of vater duodenal duplication cyst malrotation and midgut volvulus jejunal atresia and stenosis |
|
|
duodenal atresia associated abnormalities
|
double bubble sign
bile duct or pancreas ie. annular pancreas and preduodenal portal vein other insestinal atresia CHD down syndrome 30% VATER |
|
|
duodenal web associated abnormalities
|
wind sock deformity
downs syndrome |
|
|
distal bowel obstruction
|
ileal atresia/stenosis-almost all have CF, but 5-10% CF present with this, complications ie volvulus of distal intestinal loop, perf, peritonitis
meconium ileus colonic atersia functional immaturity of the colon-small left colon, meconium plug, associated with diabetic mothers, mothers who receive MgSO4 hirschsprung disease imperforate anus |
|
|
hirschsprung's disease
|
failure of bowel to relax
continuous from region of neuronal arrest to the anus M>F assoc with downs 5%, congenital neuroblastoma |
|
|
imperforate anus
|
high-ends above puborectalis sling
low-ends below sling, air below line between coccyx and pubic bone on prone xtable lateral more frequently associated with high lesions than low-spine and urinary tract anomalies, rectourethral fistula |
|
|
right upper quadrant cystic masses in children
|
gallbladder hydrops
choledochal cyst cystic mesenchymal hamartoma pancreatic pseudocyst cystic pancreatic tumor duplication cyst mesenteric cyst cystic adrenal tumor, adrenal hemorrhage upper pole r hydronephrosis/renal cyst ovarian cyst lymphangioma dermoid/teratoma csf pseudocyst cystic hemangioendothelioma |
|
|
large radiolucent hemithorax
|
obstructive emphysema-inspir/exp views
asp foreign body extrinsic compression of bronchus compensatory emphysema pneumothorax cystic disease of the lung large pneumatocele |
|
|
aerated chest mass
|
ccam/cystic airway pulmonary malformation
CDH congenital lobar emphysema |
|
|
mediastinal neuroblastoma
|
posterior mediastinal mass
<2 yo 10-15% neuroblastomas in thorax neurogenic tumors, most common mediastinal masses of childhood ddx-ganlioneuroblastoma, ganglioneuroma |
|
|
double bubble sign
|
ddx
duodenal atresia ladd's bands/malrotation annular pancreas duodenal stenosis/web |
|
|
achondroplasia
|
interpediculate distances decrease from uppter to lower lumbar spine
flattening of acetabular angles iliac bone with decreased height and square shape rhizomelic shortening of the long bones (slowed endochondral ossification) craniofacial dysproportion with large calvaria and decreased size of skull base small jugular foramen, foramen magnum, and spinal canal short ribs, decreased AP diameter of chest |
|
|
spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia
|
x-linked recessive
5-10 yo presentation generalized platyspondyly abnormal epiphyses, irregular flattened, premature OA irregular acetabulum short trunk platyspondyly odontoid hypoplasia ddx dysostosis multiplex mucopollysaccharidoses |
|
|
stippled epiphyses
|
ddx
chondrodysplasia punctata (conradi's dz) avascular necrosis cretinism morquio's syndrome multiple epiphyseal dysplasia trisomy 18 and 21 prenatal infections warfarin embryopathy |
|
|
cleidocranial dysplasia
|
ddx
womian bones abent clavicles |
|
|
wormian bones
PORKCHOPS |
ddx
pyknodysostosis osteogenesis imperfecta rickets kinky hair syndrome cleidocranial dysostosis hypothyroidism / hypophosphatasia otopalatodigital syndrome primary acroosteolysis (hajdu-Cheney)/ pachydermoperiostosis / progeria syndrome of Downs |
|
|
hydrometrocolpos
|
dilation of vagina and uterus proximal to obstructiong
imperforate hymen vaginal or cervical atresia or septum neonatal or perimenarchal period of presentation exclude GI and GU tract anomalies |
|
|
posterior urethral valves
|
most common cause of bilateral hydronephrosis in boys
vur in 50% with valves kidneys exposed to reflux at high pressures don't develop normally if no vur, kidneys develop normally to detriment of bladder |
|
|
calculi in nonfunctioning kidney
|
ddx
xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis renal tb fungal infection |
|
|
renal tb
|
initially>focal caseating lesion in upper pole
enlarging nidus, papillary necrosis enlarged kidney which will atrophy over time hydrocalyces with infundibular strictures, without pelviectasis putty kidney dystrophic ca++ |
|
|
pott's puffy tumor
|
abscess and osteomyelitis of the frontal bone associated with frontal sinusitis
|
|
|
optic globe calcification
|
ddx
retinoblastoma! retinal astrocytic hamartomas of TS |
|
|
pediatric optic lesions
|
ddx
retinoblastoma persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous retinopathy of prematurity congenital cataract coats disease |
|
|
retinoblastoma
|
95% ca++
30% bilateral 2-8% b/l dz will develop intracranial midline tumor (trilateral retinoblastoma) |
|
|
neurofibromatosis type 1
|
skull
macrocranium dysplasia orbits lambdoidal suture sphenoid wing enlarged foramina, IAC sellar abnormalities orbital enlargement CNS optic gliomas cerebral gliomas hydrocephalus plexiform neurofibroma vascular dysplasia CNS hamartoma |
|
|
pediatric toxoplasmosis
|
ca++ typically basal ganglia, periventricular, and cortex
periventricular ca++ and chorioretinitis ddx toxoplasmosis cmv |
|
|
pediatric CMV
|
more commonly associated with malformations of cortical development, microcephaly
|
|
|
anhydramnios
|
ddx
PUV-big bilatera, hydroureteronephrosis bilateral MCDK-bilateral cystic masses bilateral renal agenesis-look for lying down adrenal |
|
|
amniotic band syndrome
|
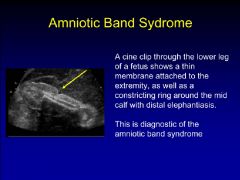
|
|
|
thanatophoric dysplasia
|
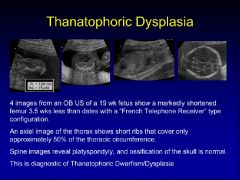
|
|
|
osteogenesis imperfecta type 2
|
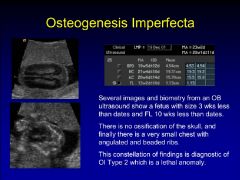
|
|
|
gastroschisis
|
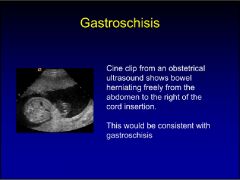
|
|
|
fetal sequestration
|
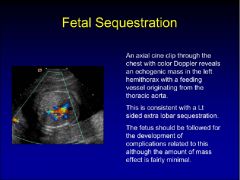
|
|
|
pediatric brain ca++
|
ddx
toxoplasmosis ca++ in bg and t/o cortex cmv more commonly periventricular and assoc with malformations of cortical development and microcephaly herpes hiv metabolic tuberous sclerosis neoplasm cysticercosis |
|
|
pediatric ca++ only of the basal ganglia
|
ddx
metabolic hiv carbon monoxide |
|
|
fibromatosis coli
|
benign mass of neonatal scm
neck mass and torticollis etiology birth trauma in utero torticollis venous occlusion leading to fibrosis usually resolves with PT |
|
|
CHF in newborn period
|
ddx
lv inflow obstruction (normal heart size) lv outflow obstruction (enlarged heart) muscle disease noncardiogenic hypervolemia, asphyxia, metabolic, arrythmias, hydrops, peripheral av fistula |
|
|
vein of galen malformation
|
intracranial arteriovenous malformation from thalamoperforator, choroidal, ant cerebral arteries to a persistent midline prosencephalic vein
>90% present as neonate with CHF and intracranial bruit |
|
|
pineal region tumors
|
germ cell tumors
germinoma pineal parenchymal tumors pineoblastoma (pnet) glioma malformative tumor dermoid/epidermoid |
|
|
grading of neonatal intracranial hemorrhage
|
grade 1-confined to subependymal germinal matrix
grade 2-blood in nondilated ventricles grade 3-hemorrhage dilating the ventricles grade 4-intraparenchymal hemorrhage |
|
|
germinoma of the brain
|
65% intracranial germ cell tumors
35% occur in the pituitary region pineal region most common sx's include DI, emaciation, precocious puberty |
|
|
craniosynostosis
|
primary (idiopathic)
secondary syndromic crouzon, apert, carpenter, treacher collincs, etc. associations metabolic disease ie rickets bone dysplasia ie hypophophatasia, achondroplasia, etc postshunt hydrocephalus |
|
|
sagittal synostosis
|
most common form
scaphocephaly, dolicocephaly |
|
|
coronal synostosis
|
second most common suture involved
brachycephaly harlequin eye deformity |
|
|
metopic synostosis
|
trigonocephaly
quizzical eye appearance with hypotelorism |
|
|
neuroblastoma
|
most common extracranial solid tumor of childhood, third most common malignancy in childhood
stage 1-confined to structure of origin stage 2-tumor extension in continuity not across midline stage 3-tumor extension in continuity across midline stage 4-disseminated disease stage 4s primary stage 1 or 2 mets to liver, skin, or bone marrow |
|
|
primary ciliary dyskinesian/kartageners syndrome
|
autosomall recessive
chronic sinusitis bronchiectasis situs inversus 50% male sterility middle ear disease |
|
|
base of pediatric tongue lesions
|
lymphadenopathy
lingual thyroid lymphangioma/hemangioma rhabdomyosarcoma |
|
|
anomalies of the thyroid
|
agenesis, unilateral or complete
ectopic thyroid most common at foramen cecum maybe only functioning tissue thyroglossal duct cyst common midline developmental anomaly of the neck occurs base of tongue to suprasternal region |
|
|
pediatric cystic neck/upper chest mass lesions
|
cystic hygroma
vascular malformation branchial cleft cyst paramedian thyroglossal duct cyst suppurative adenopathy thymic cyst duplication cyst |
|
|
medical lung disease in the newborn
CHIMP + TTN |
cardiac
hyaline membrane disease immature lung meconium aspiration pneumonia transient tachypnea of the newborn |
|
|
cystic left upper quadrant pediatric lesions
|
cystic neuroblastoma
mcdk upper pole hydronephrosis cystic extralobar seq. |
|
|
abdominal masses in neonates
|
usuall benign and of renal origin
renal 55% hydronephrosis mcdk mesoblastic nephroma renal vein thrombosis polycystic kidney disease genital masses 15% hydrometrocolplos ovarian mass gastrointestinal 15% duplication mesenteric/omental cyst complicated meconium ileus nonrenal/retroperitoneal 10% adrenal hemorrhage-f/u! neuroblastoma hepatobiliary 5% mets hemangioendothelioma hepatoblastoma mesenchymal hamartoma choledochal cyst |
|
|
hemangioendothelioma of liver
|
hypercellular tumor with hypervascularity
av shunting proliferative phase during first 18 month then slow involution present with hepatomegaly, chf, anemia, jaundice, kasabach-merritt syndrome ddx hepatoblastoma (elev afp) |
|
|
abdominal masses in older children
|
renal 55%
wilms hydronephrosis cystic disease hematoma multilocular cystic nephroma nephroblastomatosis other tumors nonrenal retroperitoneal 23% neuroblastoma rhabdomyosarcoma other tumors gi and biliary 18% appendiceal abscess intussusception |
|
|
wilms tumor associations
|
sporadic aniridia
hemihypertrophy beckwith-wiedemann sotos syndrome (cerebral gigantism) perlman syndrome (fetal gigantism) drash syndrome wilms tumor, glomerulopathy, and pseudohermaphroditism WAGR wilms tumor, aniridia, genitourinary malformations, retardation |
|
|
nephroblastomatosis
|
persistent foci of metanephric blastema present >36 week gestation
potential for malignant degen into WT 3 developmental phases dormant regressing/sclerosisng dar on t2, oblong, lenticular hyperplastic-risk of transf. lesions homogenous t1 hypointense to cortex t2 hyperintense enhance less than normal tiss |
|
|
renal lymphoma
|
appearances, hypoechoic, hypodense
single renal mass multiple renal masses diffuse infiltration of kidney extrinsic renal mass that may cause obstruction |
|
|
rhabdoid tumor
|
highly malignant
80% mortality rare over 5 yo mets to lung, liver, and brain |
|
|
splenic abnormalities
|
congenital
asplenia and polysplenia accessory splenic tissue ectopic spleen vascular malformation acquired splenomegaly chronic liver disease leukemia or lymphoma metabolic disorders hematologic disorders splenic cyst infection trauma |
|
|
hemolytic uremic syndrome
|
arf, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, and thrombocytopenia
colitis, cns manifestations 25-50%, rhabdomyolysis, diabetes children 1-5 yo |
|
|
disciitis
|
6mo to 4yo
tend to refer pain to hip or knee narrow disc space, adjacent vertebral marrow edema, maybe contrast enhancement of disc and vb |
|
|
focal/diffuse periosteal reaction in infants
|
ddx
primary or secondary to malignancy ewings leukemia neuroblastoma histiocytosis physiological scurvy hypervitaminosis a stress fracture osteomyelitis post-traumatic infantile cortical hyperostosis prostaglandin induced periostitis met bone disease caffey disease |
|
|
osteopetrosis
|
autosoma recessive lethal type
short stature hepatosplenomegaly hydrocephalus cranial nerve dysfxn blindness, deafness marrow enchroachment->anemia and thrombocytopenia and recurrent infection bone within bone app frequent fracture intmdte recessive type autosomal dominant type most mild form recessive type with tubular acidosis |
|
|
turners syndrome
|
45 xo
1/5000 short stature webbed neck, low hairline, cystic hygroma shield shaped chest/wide spaced nipples high palate coarctation of aorta, aortic stenosis horseshoe kidney primary amenorrhea |
|
|
ewing sarcoma
|
second most common primary bone malignancy of children
60% arise in extremities femur>pelvis>tibia>humerus metaphyseal (eccentric) or diaphyseal (central) most common ddx is osteosarc highly variable appearance varies from lytic 62% to sclerotic 15% poorly marginate bone destruction periosteal reaction (onion skin) |
|
|
tarsal coalition
|
fibrous, cartilaginous or osseous fusion of two or more tarsal bones
asx to painful spastic/rigid pes planus types calcaneonavicular 50% talocalcaneal 50% talonavicular calcaneocuboid |
|
|
macrodactyly
|
ddx
macrodystrophia lipomatosa neurofibromatosis vascular malf hemangioma ktw |
|
|
filling defects renal pelvis
|
calculus
neoplasm clot fungus ball sloughed papilla pyeoureteritis cystica leukoplakia malakoplakia |
|
|
prune belly syndrome
|
distended bladder, urachal cyst or diverticulum
hypoplastic prostate, scaphoid megalourethra urine ascites oligohydramnios, pulmonary hypoplasia group 1 potters group 2 less severe lung abn group 3 mild ddx posterior urethral valve urethral stricture bladder neck obstruction anterior urethral diverticulum |
|
|
bladder exstrophy
|
1/30000 persistent cloacal membrane separates mesoblast
rectus muscles separate lower abdominal wall and anterior wall of bladder absent ilia rotated outward, widened pubic symphysis complications ureteral reflux cystitis glandularis bladder ca 200x more common 90% adenoca |
|
|
posterior urethral valves complications
|
vesicourethral reflux 30-70%
renal dysplasia 15-20% oligohydramnios lung hypoplasia ddx severe reflux prune belly syndrome posterior urethral polyp anterior urethral diverticulum |
|
|
mullerian duct cyst
|
midline cyst arising behind verumontanum extending above base of prostate
prostatic secretions arising from sinoutricular plate are blocked cystic dilatation of utricle develops after puberty (prostatic utricle is there in newborn) no sperm or fructose no anomalies of external genitalia complications stones increased incidence of adenoca or scca ddx prostatic utricle-usually assoc wiht ambig genitalia or hypospadias, in infancy prune belly seminal vesicle cyst-not in midline, renal agenesis |
|
|
primary megaureter
|
fusiform dilatation of ureter proximal to adynamic distal segment
juxta vesical segment aperistaltic causing function obstruction insufficient musculature near uvj 20% of neonatal hydronephrosis bilateral 8-50% associated anomalies in 40% contralateral agenesis ipsilateral upj ddx refluxing megaureter-vur, prune belly, bph, urethral valves obstructed megaureter-ureteral stenosis, valve, ureterocele, urethral valve nonrefluxing nonobstructed megaureter-primary megaureter, post-obstruction, diabetes insipidus |
|
|
angiomyolimpoma
|
20% have ts
80% of ts pt have aml, often bilateral in pat w/o ts 90% unilateral, in females > 40 hypervascular + pseudoaneurysms + fat on ct/us/mri |
|
|
rta type 1
|
most common cause of medullary nephrocalcinosis in kids
maybe associated with rickets and osteomalacia |
|
|
developmental dysplasia of the hip
|
f>m
breech position swaddling +family hx alpha angle greater than 60 delayed femoral head ossification normal femoral head ossification by 2-6 months in girls and 3-7 monhts in boys ddx delayed ossification endocrine d/o ie hypothyroidism-bilateral |
|
|
legg calve perthes
|
groin pain or limp
idiopathic avascular necrosis of the immature femoral head age 5-8 yo m/f 4/1 caucasian boys usually unilateral, when bilateral (15%) asymmetric ddx meyer dysplasia-osteochondroses, irregular ossification <5 yo, asx, incidental secondary femoral head avn ss steroids infection trauma gauchers |
|
|
septic arthritis
|
most common cause of arthritis in children, usually monoarticular
organisms-staph, strep, coliform bacteria in neonates ddx toxic synovitis |
|
|
tonic synovitis
|
nonspecific inflammatory response to antecedent infection (viral or bacterial)
b>g, 3-10 yo limp over 1-2 days complete recover within 5-14 days |
|
|
child with limp
|
ddx
legg calves perthes septic hip toxic hip |
|
|
slipped capital femoral epiphysis
|
salter type 1
12-15 yo m/f 2.5/1 african american, obese, tall unilateral, 20-30% bilateral, almost always asymmetric stable vs unstable/acute vs chronic slip is usually posterior and medial |
|
|
osteochondritis dissecans
|
secondary to repetitive compressive microtrauma
adolescent athletes distal femur, talar dome, capitellum of humerus males mr to assess stability and guide management |
|
|
osgood sclatters disease
|
osteochondroses of tibial apophysis
10-15 yo local pain, swelling, tendnerness clinical dx irregularity of tibial tubercle in an asx patient a normal variant |
|
|
blounts disease
|
secondary to stress induced injury of proximal tibial physis
infantile form 1-3 yo early walkers, aa, obese 80% bilateral may respond to conservative mgt otherwise surgery adolescent form 8-14 yo aa children usually unilateral, present with knee pain needs surgical correction |
|
|
genu vara/tibia vara
|
ddx
physiological up to 2yo blounts rickets renal osteodystrophy osteogenesis imperfecta fibrous dysplasia |
|
|
nonaccidental trauma
|
common fx
mult fx classical metaphyseal lesions diaphyseal fractures skull fractures less common spine small bones of hands and feet clavicular fx uncommon scapular pelvic sternal facial and mandibular |
|
|
enchondromatosis syndromes
|
olliers syndrome-multiple enchondromas, maybe segmental
mafuccis syndrome-assoc with multiple hemangiomas, malignant transformation |
|
|
expansile lytic bone lesion in childrens
|
ddx
giant cell tumor aneurysmal bone cyst unicameral bone cyst fibrous dysplasia osteoblastoma telangiectatic osteosarcoma |
|
|
focal lytic calvarial lesion in children
|
histiocytosis
osteomyelitis mets-neuroblastoma intradiploic dermoid, epidermoid hemangioma prominent parietal foramina |
|
|
vertebra plana
|
ddx
posttraumatic infective spondylilitis histiocytosis lymphoma |
|
|
pediatric aggressive appearing bone lesions
|
ewings
histiocytosis osteomyelitis lymphoma |

