![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
154 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the cause of nodular cortical or subcortical enhancement
2 |
hematogenous dissemination of mets neoplasm and emboli
|
|
|
What is the DDx open ring enhancement
|
MS
Tumefactive demyelination Fluid Secreting neoplasm |
|
|
What are 3 causes of subependymal enhancement
|
Primary CNS lymphoma
Primary glial tumors Infectious ependymitis |
|
|
What is another name for a pleomorphic adenoma
|
parotid benign mixed tumor
|
|
|
What percent of parotid tumors are benign
|
80%
|
|
|
What is the MC tumor of the parotid gland
|
a pleomorphic adenoma
|
|
|
What are general characteristics of a pleomorphic adenoma
|
well defined, smooth capsule
|
|
|
What is the density of a pleomorphic adenoma on CT
|
CT: similar in density to muscle
|
|
|
What are the signal characteristics of a pleomorphic adenoma on MR
|
MR: hypo T1, bright T2
|
|
|
What percent of pleomorphic adenomas undergo malignant degeneration
|
20% malignant degeneration (CA ex pleomorphic adenoma)
|
|
|
What is the 2nd MC tumor of the parotid gland
|
warthins gland tumor
|
|
|
Are warthins glands sometimes multicentric
|
yes, 20% of the time
|
|
|
Do warthins gland tumors sometimes have a cystic component
|
yes 30% of the time
|
|
|
What part of the parotid gland to warthins glands most commonly occur
|
the tail
|
|
|
What demographic will tend to get warthins gland tumor
|
elderly men
|
|
|
What are the MR findings of a warthins gland tumor
|
heterogeneous appearing, hypo T1, variable T2
|
|
|
What nuclear study can be used to examine a warthins gland tumor
|
pertechnetate
|
|
|
What are the findings on a Tcm 99 pertectnetate study if a pt has a warthins gland tumor
|
it will be hot
|
|
|
What are the less common parotid gland tumors
|
oncocytoma (looks like BMT), hemangioma (peds, very bright T2, intense enhancement +/- phleboliths), neurofibroma, schwannoma (CN 5 or 7), lipoma
|
|
|
What is the appearance of a warthins gland tumor on MR
|
heterogeneous
|
|
|
What is a common finding of a malignant tumor of the parotid gland
|
a facial palsy
|
|
|
Are parotid tumors commonly dark on T2 weighted images
|
yes, but not always
|
|
|
What is the most common malignant parotid tumor
|
Mucoepidermoid CA is MC malignant parotid tumor
|
|
|
Can you t rely on border or shape to distinguish malignant from benign in parotid
|
no
|
|
|
What occurs for a every parotid tumor
|
biopsy
|
|
|
What are other less common tumors of the parotid glands
5 |
`adenoid cystic CA, squamous cell CA, adenocarcinoma, undifferentiated, basal cell and squamous cell CA from skin or EAC, acinic cell (rare), lymphoma
|
|
|
Do basal an squamous cell sometimes cause parotid cancer
|
yes
|
|
|
Does adenoid cystic cancer occur in the parotid gland
|
yes
|
|
|
Can lymphoma cause tumors in the parotid
|
yes, lots of lymph nodes
|
|
|
What are the causes of inflammatory/infectious changes in the parotid glands
|
sialolith (stone)
viral (esp mumps) bacterial autoimmune (Sjogren and Sarcoid) |
|
|
When are lymphoepithelial cyst seen in the parotid gland
|
AIDS
|
|
|
Are lymphoepithelial cyst usualy bilateral
|
yes
|
|
|
What do lymphoepithelial cyst look like
|
cystic warthins gland tumor
|
|
|
What is an indication that a cyst may be a warthins gland tumor and not lymphoepithelial cyst
|
the age of the patient. If you see cyst in the parotid glands and the patient is young you should be suspicious for an HIV infection
|
|
|
What do the cyst of lymphoepithelial cyst look like
|
cystic parts follow CSF density/intensity
|
|
|
What is the ddx of cystic chang of the the parotid gland
6 |
lymphoepithelial cysts, Warthin, Sjogren, sarcoid, mets, acinic CA
|
|
|
Can acinar Ca, sjogrens and sarcoid cause cystic change of the parotid glands
|
yes
|
|
|
If there is a lot of swelling around the parotid gland what should you always look for
|
a stone in stensons duct
|
|
|
What do you see in the late stages of sjogrens (in the parotids)
|
calcifications, enlargement, heterogeniety
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a lacrimal gland lesion
|
mixed benign tumor
lymphoma iodiopathic orbital disease (pseudotumor) adenoid cystic Ca sarcoidosis sjogrens dermoid and epidermoid |
|
|
Is it easy to differentiate a dermoid from other pathology
|
Can tell dermoid by fat/fluid level, otherwise cannot really distinguish lesions
|
|
|
If there is bony destruction adjacent to a lesion what should be considered
|
malignancy
|
|
|
What do the lacrimal glands look like on imaging in sarcoid
|
T2- with increased signal intensity.
T1 with contrast-, prominent enhancement of the lacrimal glands |
|
|
Are the lacrimal glands enlarged in sarcoidosis
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a lacrimal gland tumor
8 |
Benign mixed tumor
Lymphoma Idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease (pseudotumor) Adenoid cystic CA Sarcoidosis Sjogren Dermoid epidermoid |
|
|
What are the clinical findings in a patient with tuberous sclerosis
|
seizure
mental retardation facial angiofibroma |
|
|
What is another name for a facial angiofibroma seen in tuberous sclerosis
|
adenoma sebaceum
|
|
|
What 2 renal findings are associated with tuberous sclerosis
|
angiomyolipoma
renal cyst |
|
|
What cardiac anomaly is associated with tuberous sclerosis
|
rhabdomyoma (50-60%)
|
|
|
Renal: angiomyolipoma and cysts 40-80%
Cardiac: rhabdomyomas 50-65%; majority involute Lung: lymphangioleiomyomatosis/fibrosis Solid organs: adenomas, leiomyomas Skin: ash-leaf spots (majority) including scalp/hair; facial angiofibromas; shagreen patches 20-35% post pubertal Extremities: subungual fibromas 15-20%; cystic bone lesions; undulating periosteal new bone formation; bone islands Ocular: giant drusen (astrocytic hamartoma) (50%) Dental pitting of permanent teeth in most adults with TS |
Renal: angiomyolipoma and cysts 40-80%
Cardiac: rhabdomyomas 50-65%; majority involute Lung: lymphangioleiomyomatosis/fibrosis Solid organs: adenomas, leiomyomas Skin: ash-leaf spots (majority) including scalp/hair; facial angiofibromas; shagreen patches 20-35% post pubertal Extremities: subungual fibromas 15-20%; cystic bone lesions; undulating periosteal new bone formation; bone islands Ocular: giant drusen (astrocytic hamartoma) (50%) Dental pitting of permanent teeth in most adults with TS |
|
|
What are 4 CNS findings in patients with TSC
|
Periventricular subependymal nodules
cortical and subcortical tubers WM lesions subependymal giant cell astrocytomas |
|
|
Do subependymal nodules and cortical tubers tend to calcify
|
yes, 80% of subependymal tubers are Ca+, 50% of parenchymal tubers Ca+
|
|
|
What is more common subependymal nodule or tubers
|
subependymal nodules
|
|
|
Do subependymal giant cell astrocytomas enhance
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the MR signal characteristics of tubers
|
Tubers low T1, high T2
|
|
|
What are the hallmarks of SGCA
|
Hallmarks are growth and enhancement
|
|
|
What is a common complication of SGCA
|
Often causes obstructive hydrocephalus b/c located at/near foramen of Monro
|
|
|
Where do esthesioneuroblastomas arise from
|
Arises from the olfactory nerve
|
|
|
What are the clinical findings in a patient with esthesioneuroblastomas
|
Causes nasal obstruction, epistaxis, decreased sense of smell
|
|
|
Do Esthesioneuroblastoma commonly have calcifications
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the signal characteristic of a esthesioneuroblastoma on MR
|
intermediate to low T2, tend to cross cribriform plate into anterior cranial fossa
|
|
|
Do SCC of the nasal cavity tend to calcify
|
no, helps to differentiate from esthesioneuroblastoma
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a nasal cavity tumor
|
squamous cell CA (not Ca+), lymphoma, SNUC, inverted papilloma, adenoCA, chondrosarcoma of nasal septum, mets
|
|
|
What is a common cause of a cerebellar infarct
|
vetebral dissectionq
|
|
|
What is the typical demographic to get vetebral dissections
|
older men
|
|
|
What are the clinical findings of a vertebral artery dissection
|
HA, vertigo, dysarthria, N/V, nystagmus, dysmetria, gait disturbance
|
|
|
What are indirect finds of a infarct of the cerebellum on MR
|
Check 4th ventricle for symmetry to find subtle mass effect, and check temporal horns for hydrocephalus
Can cause upward or downward transtentorial herniation |
|
|
What causes 10-25% of infarcts in the younger population
|
carotid or vetebral artery dissections
|
|
|
What are the common etiologies for carotid or vetebral artery dissections
|
spontaneous
HTN major trauma trivial trauma (chiropractic = classic) iatrogenic |
|
|
What are the MRA and angiogram findings in a dissection
|
MR: high T1 from intramural hemorrhage, irregular or narrow lumen.
Angiogram: string sign (segmental tapering), sometimes 2 lumens, aneurysmal dilatation, vascular occlusion, intimal flap, retention/poor washout from dissection |
|
|
What causes the string sign on an angiogram
|
the string sign is caused by thrombus in the false lumen compressing the true lumen
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a CPA tumor
|
vestibular schwannoma
meningioma ependymoma neuroepithelial cyst aneurysm |
|
|
What causes 80% of CPA tumors
|
vestibular schwannoma
|
|
|
Do vestibular schwannomas have arachnoid cyst occasionally
|
yes
|
|
|
What is a clue that a CPA tumor is a vestibular schwannoma
|
if it expands the IAC
|
|
|
What are 2 neuroepithelial cyst
|
Epidermoid (bright DWI), arachnoid cyst (mirrors CSF)
|
|
|
Are epidermoids typically bright on DWI
|
yes
|
|
|
What must always be excluded when dealing with a CPA tumor
|
an aneurysm (pica or vetebral)
|
|
|
What is the 2nd MC CPA tumor
|
meningioma
|
|
|
What should be done if you see a intramedullary cystic lesion
|
If see cystic intramedullary cord lesion, give contrast to differentiate syrinx from cystic tumor or syrinx secondary to tumor
|
|
|
Are syrinx commonly associated with intramedullary tumors
|
yes, sometimes
|
|
|
What is the ddx of an intramedullary tumor that may have an associated syrinx
3 |
astrocytoma, ependymoma, hemangioblastoma
|
|
|
Where do myxopapillary ependymomas occur
|
in the lumbar region
|
|
|
What are the findings of a ependymoma in the spinal cord
|
Circumscribed, enhancing cord mass with hemorrhage
|
|
|
Are spinal cord ependymomas associated with central canal widening
|
yes, 20% of the time
|
|
|
Do ependymomas of the spinal cord often have cyst and hemorrhage
|
yes, commonly
|
|
|
What is the cause of the focal hypointense signal around an ependymoma
|
hemosiderin
|
|
|
Do ependymomas of the spinal cord often have homogenous enhancement
|
yes, well defined homogenous enhancement in 50%
|
|
|
What are the findings of an astrocytoma of the spinal cord
|
Usually large, involving full diameter of cord
Enhances Often infiltrating and unresectable Cannot reliably distinguish from ependymoma |
|
|
What is one subtle difference between an ependymoma and astrocytoma of the spinal cord
|
ependymomas tend to be posterior while astrocytomas tend to involve the entire spinal cord
|
|
|
What portion of the spinal canal do ependymomas tend to involve
|
the lumbar, and posteriorly
|
|
|
Where do hemangioblastomas tend to occur
|
cervical and thoracic
|
|
|
Do most hemangioblastomas have a solid and cystic component
|
yes
|
|
|
Hemangioblastomas have solid components enhance, may have hemorrhage
|
yes
|
|
|
What vascular characteristic is unique to hemangioblastomas (in differentiating spinal cord tumors)
|
Flow voids in tumor or prominent posterior draining veins
|
|
|
1/3 of pts with spinal cord hemangioblastoms have VHL
|
yes
|
|
|
What is a disc herniation
|
Localized (< 50% of disk circumference) displacement of disk material beyond confines of disk space...annulous pulposa
|
|
|
What is a disc protrusion
|
Herniated disk with broad-base at parent disk
Greatest dimension of disk herniation in any plane ≤ distance between edges of the base in same plane |
|
|
What is a disc extruction
|
Herniated disk with narrow or no base at parent disk
Greatest dimension of disk herniation in any plane > distance between edges of the base in same plane |
|
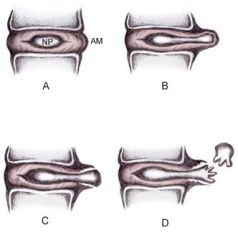
Disc herniation classification. A: Normal disc anatomy demonstrating nucleus pulposus (NP) and annular margin (AM). B: Disc protrusion, with NP penetrating asymmetrically through annular fibers but confined within the AM. C: Disc extrusion with NP extending beyond the AM. D: Disc sequestration, with nuclear fragment separated from extruded disc.
|
Disc herniation classification. A: Normal disc anatomy demonstrating nucleus pulposus (NP) and annular margin (AM). B: Disc protrusion, with NP penetrating asymmetrically through annular fibers but confined within the AM. C: Disc extrusion with NP extending beyond the AM. D: Disc sequestration, with nuclear fragment separated from extruded disc.
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a intramedullary spinal tumur ( within the spinal cord below the pia matter)
|
ependymoma
astrocytoma hemangioblastoma syrinx intramedullary AVM |
|
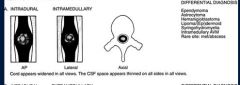
intramedullary
|
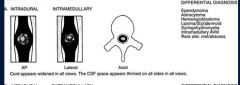
intramedullary
|
|
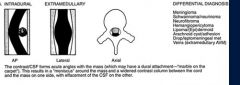
Intradural extramedullary (subarachnoid or subdural space)
|
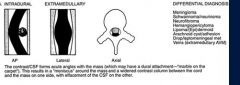
Intradural extramedullary (subarachnoid or subdural space)
|
|
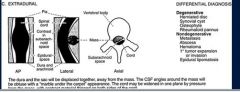
extradural
|
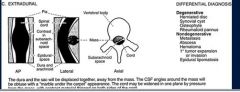
extradural
|
|
|
What is the ddx of an intradural extramedullary tumor
5 |
meningioma
schwannoma neurofibroma hemangiopericytoma |
|
|
What is the ddx of a extradural lesion
9 |
herniated disc
synovial cyst osteophyte rheumatoid pannus mets abscess hematoma epidural lipomatosis |
|
|
Where are trigeminal schwannomas usually located
|
Can be based in middle cranial fossa, Gasserian ganglion, or posterior fossa
|
|
|
What are the MRI characteristics of a schwannoma
|
iso T1, hyper T2, with avid enhancement
|
|
|
What is the ddx of lesions that may erode the petrous apex
|
cholesterol granuloma
epidermoid mets meningioma chordoma chondrosarcoma schwannoma |
|
|
what should be suspected if there is enlargement of the foramen ovale, rotundum or SOF
|
swchwannoma
|
|
|
What is the appearance of a meningioma in the region of the cavernous sinus
|
Follows lateral margin of the cavernous sinus
May extend posterior along tentorium in “dove’s tail” appearance |
|
|
What encases the ICA rather than displace it
|
meningiomas tend to encase the ICA rather than displace it, opposite of a schwannoma
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a parasellar or cavernous sinus lesion
8 |
aneurysm
meningioma trigeminal schwannoma pituitary adenoma extending lateral perineural spread from mets or H&N lesion chondrosarcoma from sellar bone |
|
|
What are the findings of thyroid orbitopathology
|
CT: enlarged extraocular muscles (“I’M SLow”), spares musculotendinous insertions
|
|
|
What is a potential complication of the muscular hypertrophy in thyroid disease
|
possible compression of the optic nerve by enlarged muscles
|
|
|
Besides muscular hypertrophy what other orbital findings are there thyroid disease
3 |
increased orbital fat
proptosis Lacrimal glands may be involved |
|
|
Is a orbital pseudotumor usually bilateral or unilateral
|
unilateral
|
|
|
What is the radiographic appearance of an orbital psuedotumor
|
will involve the muscular insertion, orbital fat and appear as muscular thickening, a mass or stranding
|
|
|
Is orbital thyroid disease usually unilateral
|
no symmetric
|
|
|
What diseases is pseudotumor associated with
|
Wegener
PAN retroperitoneal fibrosis sclerosing cholangitis Reidel thyroiditis mediastinal fibrosis |
|
|
What is the T2 signal characteristic of pseudotumor
|
MR: low T2
|
|
|
What are 3 ddx of pseudotumor
|
lymphoma
wegners sarcoid |
|
|
Is a classic appearance of a pilocytic juvenile astrocytoma a cyst with a mural nodule
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the most common brain tumor diagnosed in children
|
pilocytic astrocytoma
|
|
|
What is the radiographic appearance of a pilocytic astrocytoma
|
Usually cyst with enhancing mural nodule, off midline
Occasionally solid, then similar to medulloblastoma, ependymoma |
|
|
What is a potential complication of pilocystic astrocytoma
|
hydrocephalus
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a tumor with a cyst and nodule
|
JPA (anywhere), pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma and ganglioglioma (temporal lobe), hemangioblastoma (posterior fossa)
|
|
|
Where do gangliogliomas tend to occur
|
in the temporal lobe
|
|
|
What type of tumor is the cause of the majority of brainstem gliomas
|
astrocytome (grade 2)
|
|
|
Where is the MC location for a brainstem glioma
|
the pons
|
|
|
What are the radiographic findings in a patient with a brainstem glioma
|
expansile enlargement of brainstem, ventral pons extends beyond anterior margin of basilar artery, exophytic growth into cisterns (20%)
Cranial nerve palsies pyramidal tract |
|
|
Are brainstem gliomas usually situated anteriorly or posteriorly
|
anterior
|
|
|
What is the prognosis and treatment of a brainstem glioma
|
20-30% 5y survival
chemotherapy and radiation |
|
|
How often is there exophytic growth of a brainstem glioma with out
|
20%
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a brainstem lesion
8 |
brainstem glioma
tuberculoma lymphoma rhombic encephalitis demyelination diseasse infarction resolving hematoma vascular malformation |
|
|
Where should the conus be located in an infant
|
In infant, normal conus should be above L2-3
|
|
|
What are the findings in an infant with a tethered cord
|
conus ends below L2 inferior endplate
tethered by thickened filum +/- fibrolipoma, terminal lipoma |
|
|
What are the US findings of a tethered cord
|
nerve roots do not float freely, filum may be short and thick (> 2 mm)
|
|
|
Is there often a fibrolipoma or terminal lipoma in a patient with a tethered cord
|
yes
|
|
|
What should be investigated closely in pts with a tethered cord
|
The spine becuase there may be an occult spinal dysraphism such as lipomyelomeningocele
|
|
|
What are the types of a carotid cavernous fistula
|
direct and indirect
|
|
|
What is the cause of an indirect carotid cavernous fistual
|
dural arteriovenous fistual of cavernous sinus, typically supplied by numerous ECA +/- cavernous ICA branches
|
|
|
What does a dural AVF look like
|
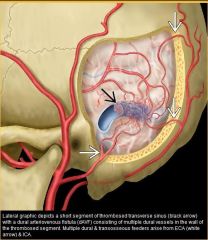
|
|
|
What is the MCC of indirect carotid cavernous fistuala (dural avf)
|
idiopathic
|
|
|
What is the cause of a direct CC fistula
|
: high-flow, single hole fistula between ICA and cavernous sinus
|
|
|
What are the causes of direct CC fistula
|
trauma (MC)
ruptured aneurysm iatrogenic spontaneous |
|
|
What disease will predispose a pt to a direct CC
|
ehlers danlos
|
|
|
What is the ddx of enlarged extraocular muscles
|
pseudotumor, Graves, CCF
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a dilated superior opthalmic vein
5 |
CCF
cavernous sinus thrombosis, venous varix Graves normal variant |
|
|
What may be seein in a patient with a CC AVF during angiogram
|
can show communication and may show filling of superior +/- inferior ophthalmic veins, petrosal sinus to IJ, and cortical veins
|
|
|
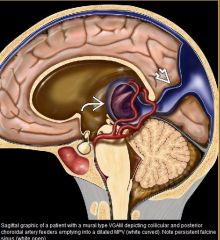
vein of galen malformation
|
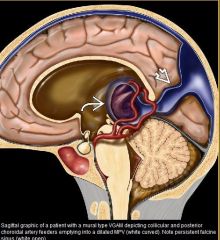
|
|
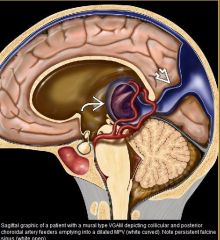
Vein of galen malformation
|
|
|
|
What vessels are involved in a vein of galen malformation
|
VGAM is misnomer; malformation actually involves the median prosencephalic vein (MPV) of Markowski which becomes "aneurysmal"/dilated
|
|
|
What is the MC extracardiac cause of highoutput failure in a newborn
|
VGAM
|

