![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
name 3 criteria standards for meeting network standards |
performance reliability security |
|
|
What is a network? |
the interconnection of a set of devices capable of communication |
|
|
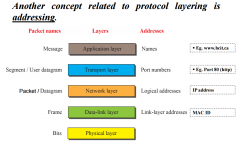
What is OSI? What is TCP/IP? |
Open System Interconnection Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol |
|
|
List the protocol layers for the OSI and TCP/IP models. hint: 7, 5 |
OSI: Physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation application TCP/IP: Physical, data link, network, transport, application |
|
|
TCP/IP brief desc of: Physical Layer |
coordinates the functions required to transmit a bit over a transmission medium: bit representation, type of encoding. |
|
|
TCP/IP brief desc of: Data Link Layer |
responsible for delivering frames from one station to the next without errors: Data Link Control (DLC) sublayer: framing, error detection, and correction of frames/bits; Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer: physical hardware address, medium access control.
|
|
|
TCP/IP brief desc of: Network Layer |
responsible for the source-to-destination (host-to-host) delivery of a packet/datagram across multiple network links: host-to-host communication routing. |
|
|
TCP/IP brief desc of: Transport Layer |
responsible for the process-to-process delivery of the entire message: process-to-process communcation - User Datagram Protocol/Transmission Control Protocol. UDP: Best effort delivery of user datagrams. TCP: flow, error and congestion control of segments.
|
|
|
TCP/IP brief desc of: Application Layer |
enables the user to access the network: HTTP, FTP, SMTP, Telnet, ect. |
|
|
List the 4 topology's |
Mesh, Star, Bus, Ring |
|
|
Mesh Topology Facts |
-Every device has a dedicated point-to-point link to every other device. -n(n-1)/2 duplex links -dedicated links, robust, secure, easy fault id -requires a ton of cables and I/O ports $$$ |
|
|
Star Topology Facts |
Every device has a p2p link to a central controller Does not allow traffic btwn devices Cost less, robust, easy fault id. If hub fails we all fail... |
|
|
Bus Topology Facts |
multipoint connection: one cable to all devices
easy installation, less cable if cables fails all fail... hard to isolate fault too |
|
|
Ring Topology Facts |
p2p with 2 devices to ea side easy to install, easy fault id, ring break = network break |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

