![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
365 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is used to rinse to counterstain (OG AND EA) |
ALCOHOL |
|
|
What chemical dissolves millipore filter |
chloroform |
|
|
WHAT TYPE OF FIRE EXTINGUISHER IS USED IN THE CYTOLOGY LAB? |
FIRE CODE--ABC |
|
|
THE STAIN ON A SLIDE IS RED INSTEAD OF BLUE IN A PAP SMEAR, YOU SHOULD? |
DECREASE THE pH OF THE BLUING AGENT or renew hematoxylin stain |
|
|
WHAT STAIN DISTINGUISHES NUCLEOLI FROM DNA? |
Eosin stains cytoplasm of mature squamous cells, nucleoli and cilia |
|
|
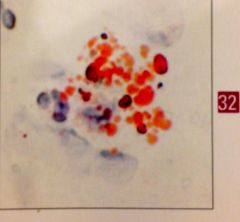
mordant of hematoxylin |
alum |
|
|
what common reagent in the cytology lab needs to be stored in a safety cabinet? |
alcohol |
|
|
what is xylene used for? |
cytoplasmic clearing |
|
|
low power view of PAP that is pale/air dried. why? |
clinician air dried before fixing so clinician needs to be notified |
|
|
what is used to extract a ferruginous body from the tissue? |
household bleach |
|
|
you received air dried conventional slide. what should you do to correct the problem? |
notify the clinician |
|
|
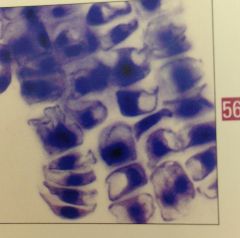
widely dispersed cells are most commonly seen in what kind of prepared specimens? |
homogenization (sacamanno) |
|
|
increased occurrence of infections by aerosols occur with what prep technique? |
homogenization (sacamanno/blender) |
|
|
95% ETHANOL |
DISSOLVES THE WAX |
|
|
WHY DO YOU HYDRATE THE SLIDE WITH WATER |
HYDRATING THE SLIDE WITH WATER PREPARES IT FOR HEMATOXYLIN |
|
|
gastric brushing with: spindle cells, central nuclei, necrotic debris, inflammation |
leiomyosarcoma |
|
|
BLUING |
TAP WATER pH 8-8.0 LiCO3 DILUTE AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE |
|
|
XYLENE PREVENTS? WHY? |
THIS IS THE CLEARING STEP, XYLENE AND WATER DO NOT MIX. MAKE SURE IT SITS IN XYLENE LONG ENOUGH. IT CAN MAKE A SLIDE HAZY |
|
|
woman with Hx of breast cancer has a pericardial effusion with: elongated cells with lacy cytoplasm and nucleoli, amorphous pink substance |
fibrotic pericarditis |
|
|
anucleated squames in a pregnant woman near term is? |
abnormal hormonal |
|
|
picture of 20 year old with atrophic smear. Recommend? |
cytogenic analysis |
|
|
HAZY APPEARANCE OF NUCLEI |
GLASSY DROPLETS OF WATER ON SLIDE PRIOR TO HEMATOXYLIN--INCREASE TIME IN WATER |
|
|
BROWN NUCLEI |
REPLACE HEMATOXYLIN OVER OXIDIZED
|
|
|
DARK STAINING NUCLEI |
OVERSTAINING IN HEMATOXYLIN--DECREASE TIME OR NOT ENOUGH DECOLORIZER INCREASE TIME IN HCL OR ADJUST BLUING SOLUTION |
|
|
PALE NUCLEI |
HEMATOXYLIN DILUTED IN WATER, SPRAY FIX NOT REMOVED PRIOR TO STAINING,HCL NOT REMOVED COMPLETELY OR CHECK CONCENTRATION |
|
|
PALE CYTOPLASM |
SPRAY FIX NOT REMOVED PRIOR TO STAINING, OVERSTAINING IN HEMATOXYLIN, ALCOHOL RINSE FOLLOWING STAINS TOO LONG |
|
|
CYTOPLASM TOO GREEN |
TOO MUCH TIME IN EA OR OVERSTAINING IN HEMATOXYLIN |
|
|
OVERALL DULL APPEARANCE IN CYTOPLASM |
CLEARING SOLUTION CONTAMINATED IN WATER |
|
|
picture of chronic cervicitis. what would most likely cause this in a young woman? |
chlamydia |
|
|
AIS is associated with? |
CIN (squamous dysplasia) |
|
|
likely diagnosis if normal ECs are seen in a smear of lateral vaginal wall. Patient Hx? |
Vaginal adenosis with Hx of DES exposure in utero |
|
|
HPV types associated with LGSIL |
6 and 11 |
|
|
HPV types associated with AIS? |
16 and 18 |
|
|
increased estrogen stimulation is associated with? |
Thecoma granulosa cell tumor |
|
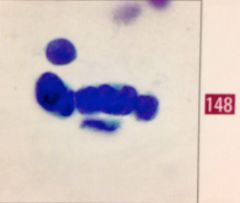
|
EM hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma are most often associated with |
stein leventhal syndrome |
|
|
DNA synthesized in what stage? |
S-phase |
|
|
PAS STAINS FOR? |
CARBOHYDRATES |
|
|
OVULATION IS TRIGGERED BY? |
LH |
|
|
# BARR BODIES, KARYOTYPE AND SMEAR PATTERN OF TESTICULAR FEMINIZATION? |
superficial and intermediates XY No barr bodies |
|
|
PIC OF LITTLE RED CELLS IN ALOT OF BLOOD |
NORMAL EM CELLS |
|
|
LOW POWER VIEW OF PAP THAT IS PARTIAL PRESERVED AND PART DISCOLORED (YELLOW-PALE) WHY? |
WATER CONTAMINATED WITH XYLENE |
|
|
desc on PAP: increased N/C, finely granular chromatin, hyperchromatic, no nucleolus |
squamous dysplasia |
|
|
pic of coursely granular chromatin, syncitial groups, almost no cytoplasm, no nucleoli |
CIS |
|
|
what substance do syncitiotrophoblasts produce |
HCG (gonadotropins) |
|
|
20 year old with large clusters of malignant cells in a PAP. source? |
Extrauterine AdenoCa |
|
|
Candida is associate with |
pregnancy, diabetes |
|
|
what organism is present in tonsillar crypts |
actinomyces |
|
|
Nipple discharge. Single cells with hyperchromatic, ugly nuclei |
Paget's disease |
|
|
What hormone peaks in the proliferative phase |
FSH |
|
|
Why are vulvar smears hard to read? |
air drying |
|
|
In a PAP, cells in a syncitial group will help in differentiating |
LGSIL AND HGSIL |
|
|
What has the highest incidence of mitosis in a PAP? Repair, CIS, EC adeno, mets adeno? |
repair |
|
|
Endometriosis is defined by? |
ectopic formation of EM stroma and glands outside the uterine cavity anywhere in the body
|
|
|
PAP from young woman with: large polygonal cells with abundant cytoplasm, slight nuclear atypia, inflammation in background. Dx? |
Reactive/repair |
|
|
Pic of CMV in a PAP. what is likely the history? |
HIV+ |
|
|
FNA of ovarian cyst and smear contains anucleated squames and necrotic debris. what is it? |
epidermoid cyst |
|
|
lab A reported PAP as abnormal. Colpo called it chronic inflammation. It was sent to lab B for eval. what is the Dx? (pic of navicular cells) |
NIL |
|
|
Common complication of salpingitis |
infertility |
|
|
Endometriosis is most commonly found in? |
Ovary |
|
|
Pic of repair. What criteria present or absent helps diagnose this? |
diathesis |
|
|
pic of repair: Nucleoli present what is going on in cell. |
protein synthesis |
|
|
Pic of dark, small cells with superficial in the background. what feature in the background helps diagnose this? |
cells likely EM, so presence of superficials due to estrogen effec |
|
|
Atrophic cervical smear. Recommend what? |
Topical estrogen |
|
|
List 2 protective reactions of the cervix |
parakaratosis and hyperkeratosis |
|
|
large, malignant cells with clear cytoplasm in cervical smear. likely patient history? |
DES exposure in utero (clear cell ca) |
|
|
description of abnormal parakeratotic cells. Dx |
ASCUS but if normal NILM |
|
|
pic of gardnerella clue cells in cervix. most consistent with? Leukoplakia, strawberry cervix, positive reaction to KOH |
Positive reaction to KOH |
|
|
vacuolated cluster of small cells in cervix |
IUD changes |
|
|
What is the purpose of cyto-histo correlation? |
verify diagnostic accuracy
|
|
|
Most sensitive way to subtype HPV |
PCR also useful when there is a small amount of DNA
|
|
|
Best way to distinguish EM adeno from EC adeno |
Test for HPV EM (-) EC (+16,18) |
|
|
Most common sarcoma in a post menopausal woman |
Leiomysarcoma |
|
|
what is your diagnosis of a PAP if only glandular cells are present |
unsat |
|
|
What is the lowest diagnosis that a pathologist must review slides |
reactive |
|
|
CIS in the vulva is called |
Bowens |
|
|
seeing EMs in which of the following is most abnormal? IUD, day 6, pregnant |
pregnant |
|
|
pic of repair in PAP. what would help most in diagnosis? nucleoli, or no single cells with atypia |
no single cells with atypia |
|
|
Epithelium of the vagina |
Non Keratinizing stratified squamous cells |
|
|
Epithelium of the ectocervix |
Non keratinizing squamous cells |
|
|
What substance is universally used to disinfect blood spills |
chemical germicide |
|
|
significance of air drying of a milipore filter either during processing or preparation? what is seen under the microscope |
cracking (flake or crumble too) |
|
|
what additive keeps blood from clotting |
heparin |
|
|
a cowboy from Oklahoma had a scraping of a white, oral lesion. He used smokeless tobacco for years. what do you call the white plaque? |
leukoplakia |
|
|
define universal precautions |
treat bodily fluids/specimens as if they were infectious |
|
|
Description of papillary clusters and acini formation of mesothelial cells in a culdocentisis are diagnostic for? |
benign ovarian cyst |
|
|
be able to identify pics of either EM adeno, EC adeno or IUD change |
will upload photos |
|
|
what prep method would cause aerosol inhalation |
homogenation |
|
|
what are pre disposing factors for endometrial adenoca |
obesity and hypertension |
|
|
what stain differentiates nucleoli from chromatin |
eosin |
|
|
what chemical/fixative do you want to avoid when you have a specimen with fat |
alcohol |
|
|
what is the most important universal precaution |
hand washing |
|
|
what is MSDS |
material safety data sheets |
|
|
If glandular cells are found in a smear from the lateral vaginal wall? Dx |
vaginal adenosis |
|
|
how would you classify a pap smear expressing atypical parakaratosis? |
ASCUS |
|
|
description of CIS criteria v SCC |
syncitial, no nucleoli, high N/C--CIS
Lower N/C, nucleoli
|
|
|
counterstains are removed from the cells if slides are allowed to remain in? |
alcohol |
|
|
proliferative days |
1-14 |
|
|
secretory days |
15-28 |
|
|
bowens disease looks like |
scc |
|
|
XY phenotype? |
no barr bodies, see intermediates and superficial cells |
|
|
PCOS |
causes infertility |
|
|
Pemphigus vulgaris |
causes acantholytic cells (atypical immature parabasal cells) Tzank cells |
|
|
Mosaic pattern in colposcopy? |
this is abnormal |
|
|
Thecomas? what hormone pattern would you see? |
secrete estrogen therefore would have a superficial pattern or mature |
|
|
Krukenburg tumor |
Metastatic malignancy from the GI to the ovary usually from the stomach |
|
|
describe endometrial adenoca |
tightly cohesive clusters of medium sized malignant cells with engulfed neutrophils with a dirty background |
|
|
description of AIS |
cells arranged in rosettes and crowded stratified strips. Nuclei elongated and hyperchromatic, feathering appearance on the edges of the groups. |
|
|
the difference between xylene and xylol |
unable to find info on this ask? |
|
|
cautery: would see in a smear afterward |
therapy induced atypia |
|
|
The purpose of using chloroform on a milipore filter? |
eliminates the pores |
|
|
navicular cells |
within normal limits |
|
|
how might cornflaking be corrected |
in lab re coverslip |
|
|
herpes in the mouth can be diagnosed by |
cold sores |
|
|
what is a common tumor in post-menopausal women |
leiomyosarcoma |
|
|
low power hazy smear of abundant squames not clear. discoloration yellow haze |
air drying prior to fixation |
|
|
high N/C ratio and syncytia help distinguish between what conditions |
HGSIL and LGSIL |
|
|
description of rosettes and palisading cells. even distribution of finely granular chromatin. micronucleolus clean background |
EC AIS |
|
|
EMs in a smear of mature squames. Several superficials. in a post menopausal woman . What else besides the presence of EMs is noteworthy in this smear |
The presence of superficials--due to estrogen |
|
|
endometriosis may be described as |
the ectopic growth of EM cells and stroma |
|
|
description of PAP smear: increased n/c ratio, finely granular chromatin, hyperchromatic, no nucleolus |
squamous dysplasia |
|
|
picture of single lying small cells with course chromatin, very high n/c ratio and irregular membranes |
severe dysplasia |
|
|
picture of single lying squamous cells with hyperchromatic slightly irregular, fairly high n/c ratio |
moderate dysplasia |
|
|
know histology pics |
will add pics |
|
|
given four events of the menstrual cycle, tell which choice in proliferative phase |
peak in FSH levels |
|
|
hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis are associated with |
protection |
|
|
what should HPV be classified in TBS |
LGSIL-abnormal |
|
|
a picture of a cell with no barr bodies--what is this representative of |
Kleinfelters syndrome |
|
|
picture of AIS: what HPV is this associated with |
18 |
|
|
who is required to complete proficiency training |
all personell that interpret cytological specimens |
|
|
tubal metaplasia is |
endocervical/endometrial to tubal |
|
|
what is a chocolate cyst |
endometriosis |
|
|
in a Brenners tumor what can be seen histologically |
cell nests |
|
|
small cells molding, streaking artifact due to their delicate nature |
small cell carcinoma |
|
|
Triad of benign ovarian tumor, ascites and pleural effusion |
Meig's syndrome |
|
|
granulosa cell tumor most concerned with adult or child |
adult |
|
|
What are call exner bodies associated with |
granulosa cell tumors |
|
|
what is the most common malignant germ cell tumor of the ovary |
dysgerminoma |
|
|
what type of has "tigroid" background |
germinoma or seminoma |
|
|
MMMT is composed of |
epithelial and mesenchymal |
|
|
A doctor wants to use cytology to check for pnemocystis, what method should be used to obtain sample? |
BAL is the procedure of choice, sputum is unreliable for diagnosis |
|
|
What is the advantage of seeing syncitial groups in a pap smear? |
distinguishing high grade from low grade |
|
|
Wavy, ribbon like, non septate organism? |
phycomyces (zygomycetes, mucormycosis) |
|
|
pic of muscle fragment in bronchial brush. ID? |
due to aggressive scrape, muscle contaminant |
|
|
pic of respiratory specimen with foamy macrophages and one macrophage with small dark spores inside the cytoplasm |
histoplasma capsulatum |
|
|
most likely cause of specimen with epithelial histiocytes, lymphs, multi-nucleated giant cells and caseating necrosis? |
tubercule bacilli |
|
|
know respiratory epithelium in detail |
Respiratory epithelium psuedo stratified ciliated columnar Large bronchi of the lung psuedostratified columnar terminal bronchioles simple columnar Oropharynx is lined with stratified squamous |
|
|
picture of sputum: One really giant cell with a giant round nucleus, abundant cytoplasm, polys in the background, what is it? |
Therapy changes |
|
|
a doctor wants to use cytology to check for pneumocystis. what method should he use to obtain sample? |
BAL |
|
|
What is the special stain for small cell carcinoma of the lung? |
chromogranin |
|
|
picture of psammoma bodies in respiratory specimen. Associated with? |
BAC |
|
|
Nice, distinct picture of Coccidiodes Immitis. Describe and where is this organism prevalent? |
large spherule with endospores. Found in patients from the South West US, San Joaquin valley. |
|
|
what prep would be used to obtain entity depicted? (picture of ferruginous body) |
Iron stain---Prussian Blue |
|
|
Lung FNA with description of loosely cohesive and single cells, micronuclei and a clean background. |
Carcinoid |
|
|
squamous metaplasia is most commonly found where (after its incidence in cervix?) |
Bronchi |
|
|
Description: broad, wavy non-septate organism |
rhizopus, mucor, phycomyces, zygomyces |
|
|
What is it called when the cells pull apart and the cytoplasm and nucleus are separate from the terminal bar and cilia? |
Ciliocytopthoria |
|
|
What would you use on Oil Red O stain for? |
lipids |
|
|
What stain would you use for Hemosiderin-laden macrophages? |
Prussian blue (Iron) |
|
|
What causes a coin lesion in the lung? |
Hamaratoma |
|
|
What causes pneumoconiosis? |
breathing in coal dust, silicone |
|
|
which carcinoma causes a central core of necrosis in the lung? |
SCCa |
|
|
Which preparatory technique would show the greatest amount of variation in a small cell carcinoma? |
Homogenization, blender |
|
|
why is small cell ca singled out from the rest of the carcinomas? |
treatment is different (no surgery) |
|
|
Color plate of Charcot-Leyden crystals. What are these from? |
Asthma |
|
|
From a color plate how would you tell the origin of a lesion? |
the cytoplasm |
|
|
What is the purpose of cyto/histo correlation? |
to help verify diagnostic accuracy |
|
|
What malignancy of the lung is capable of producing hormones? |
small cell ca |
|
|
PAS stains for? |
carbohydrates |
|
|
Description of smear pattern of epitheloid histiocytes and necrosis |
Granuloma (more general choice) |
|
|
what pathogen in lung is associated with granuloma? |
Blastomyces dermititidis |
|
|
description: Epitheloid histiocyte, plasma cells, lymphs, caseating disease. this is consistant with? |
general granuloma |
|
|
Basal bodies are associated with? |
cilia |
|
|
Esophageal brushing: Hard dark cells with double refractile walls; these cells probably originate from? |
Oral contamination |
|
|
plant cells; origin? |
oral contaminant |
|
|
Lung FNA of loosely cohesive/single cells with scant cytoplasm in clean background? |
Carcinoid tumor |
|
|
Location of different lung tumors? |
adeno--peripheral, squamous cell ca--central, small cell ca--central, |
|
|
where are carcinoid lesions found? |
in the submucosa |
|
|
know the findings of a Hamaratoma and cytological criteria |
FNA--gelatinous material contains reactive bronchial cells; muscle and cartilaginous matrix in the background; see fat smooth muscle, spindle and stellate cells |
|
|
What malignancy of the lung has the best prognosis? |
carcinoid |
|
|
Which stains would be useful in establishing a correct diagnosis of cryptococcus? |
GMS and PAS |
|
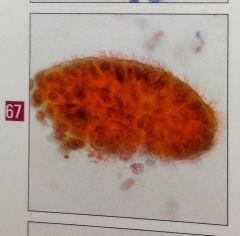
creola body is this normal? Associated with? |
hyperplastic mucosa may shed pseudopapillary aggregates of reactive/atypical bronchial cells that can be mistaken for adenoca. Associated with asthma. |
|
|
charcot leyden crystals are derived from? |
crystalized eosinophil proteins |
|
What is this? |
lipid pneumonia |
|
|
Kulchitsky cells |
Carcinoid tumors (large bronchus) from these cells or their precursors. |
|
|
What type of lesion causes cavitation in the lung? |
KSCC--results from extensive central necrosis of a kscc producing a central cavity |
|
Be able to recognize a very fuzzy pic of some molded cells. (Resp) |
small cell carcinoma of the lung |
|
|
what type of lung specimen is needed to do a fungal stain |
BAL |
|
|
What kind of histiocytes are associated with asthma? |
multinucleated, carbon-laden |
|
|
Smoking is a large risk factor for what types of lung cancers? |
small cell, squamous cell (adenocarcinoma is not generally linked to smoking) |
|
|
picture of charcot leyden crystals what else would be seen in this aspirate |
eosinophils are usually nearby, giant cells, type 2 pneumocytes |
|
|
a wavy, non-septated, cyanophilic organism? (no pic) |
phycomyces, rhizopus, mucor, absidia, zygomyces |
|
picture of square cells with no chromatin pattern and refractile walls in sputum. most likely dx? |
vegetable or plant cells |
|
|
pic from lung specimen |
squamous metaplasia or parakeratosis possibly originating in pharynx or upper respiratory |
|
|
what pathogen in the lung is associated with granuloma? |
blastomyces |
|
|
pic of ferruginous bodies and siderophages. diagnostic of? |
pnemoconosis |
|
|
pic of creola body. Huge clump of cells with smooth borders in resp sample. what other item might be helpful in dx? |
eosinophilic inflammation |
|
|
sputum with vegetable cells tell clinician to do what? |
nothing |
|
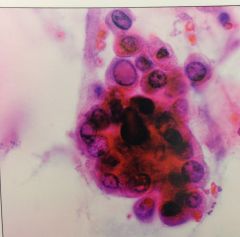
pic of psammoma bodies in resp specimen. assoc with? |
BAC |
|
|
pic of muscle fragment in bronch brush. id? |
aggressive scrape-muscle contaminant |
|
|
what organism of the respiratory tract can cause meningitis? |
crytococcus |
|
|
cryptococcus is a? |
fungus |
|
|
pancoast tumor symptoms? |
Horners syndrome, density of chest xray at extreme apex of lung, most likely squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
ciliated cells found in an esophageal specimen are most likely associated with? |
respiratory contamination |
|
|
Agenesis of mullerian ducts. what part of the reproductive tract is missing? |
uterus and fallopian tubes
|
|
|
cervical glands covered by sq metaplasia most likely produces? |
Nabothian cyst |
|
|
PID is most often assoc. with? |
Fallopian tubes (infertility) |
|
|
Papillary TCCa can be confused? |
lithiasis (stones) |
|
|
what kind of crystals are found in gout? |
Urea crystals (in and about the joints) |
|
|
TCC (UCC) AND SQCC IN THE SAME SMEAR ARE PROBABLY THE RESULT OF? |
squamous cell differentiation to TCC (UCC) |
|
|
Pic of urine specimen with ugly giant multinucleated cell. what treatment did this patient likely have? (chemo or irradiation?) |
irradiation usually these cells are large and multinucleated. (cytomegaly) |
|
|
pic of degenerated columnar cells in urine. Hx of prior cystectomy. Cells likely from? |
Intestine-Ileal conduit urine |
|
|
urine with huge cells in acinar formation and macronucleoli. Dx? what would help make a specific Dx? |
Prostate Ca-cytoplasmic differentiation |
|
|
schistosoma in urine. the clinical Hx of the patient includes? |
recent travel to Africa or bathing in the Nile |
|
|
pic of polyoma infection in a urine and kidney biopsy. Likely history? |
Kidney transplant |
|
|
BCG is? Used for? |
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) Rx. is an attenuated strain of Mycobacterium bovis. Used in treatment for superficial bladder cancer. |
|
|
What is used to treat prostate cancer and what would be seen in urine? Pic of sq met and it asked for what therapy? |
Estrogen--Sq metaplasia and sq cells |
|
|
where do normal transitional cells originate? *dome of bladder? (*urethra?*ureters?*renal pelvis?) |
research |
|
|
what feature would best help you ID plasmacytoma? (urine) |
mature plasma cells have eccentric nuclei with characteristic "clock face" chromatin and a perinuclear hof |
|
|
Location of Adeno Ca in urine of urachal origin? |
signet cell ring carcinoma is rare accounts for 10% of adenoca of bladder. About 20-25% are urachal origin. (note: adenoca is <2% of all cases of bladder cancer) DOME OF BLADDER |
|
|
pic of high grade TCC (UCC). What is the difference between high and low grade TCC? |
High grade has smaller cells with high N/C ratios with dyshesion |
|
|
where are cap cells(umbrella cells) found? |
these are found in the superficial layer |
|
|
papillary tumors in the urinary tract? |
indicate low grade UCC/TCC |
|
|
Malakoplakia? Associated with? |
is a granulamatous disease associated with Michaelis-Gutmann bodies. These are macrophages that have partially phagocytized ecoli (bacteria) |
|
|
Red eosin inclusion bodies in the cytoplasm in transitional cells indicate what? |
eosinophilic cystitis bladder condition associated with allergy, neoplasia, trauma, parasitic infections and chemotherapy |
|
|
what cell pattern will be seen in a man on estrogen therapy? |
squamous cells |
|
|
be able to identify a decoy cell by description |
large, round, homogenous opaque blue/black viral inclusion in the nucleus. note during processing the the viral inclusion often leaches out during processing, leaving coarse reticular network or bland, washed out empty viral look. |
|
|
squamous metaplasia in the bladder is most likely the result of? |
chronic inflammation (demay V1p444) |
|
|
Benign columnar cells in urine are most likely associated with |
cystitis glandularis |
|
|
classic pic of small cell carcinoma in urine |
present singly or in clusters with nuclear molding, high N/C ratios, hyperchromatic nuclei, granular chromatin in inconspicuous nucleoli. mitosis and apoptosis is prominent. |
|
|
description of renal pelvic wash with abnormal cells positive for oil Red O. |
Renal cell carcinoma |
|
|
urine with huge cells in acinar formation and macronucloli |
prostate carcinoma |
|
|
the most common site for any TCC (UCC) |
the trigone area |
|
|
no pic, 6 year old boy has a pleural effusion. seen are round small cells and spindle, elongated cells and (described stroma material). what is the diagnosis |
nephroblastoma (small blue cells, spindle cells, and epithelial component) |
|
|
pic of malignant looking cells with central nuclei, endo and ecto plasm, arranged in a group with knobby borders. what stain combo would be true for this entity? |
Mesothelioma CEA -/KERATIN + |
|
|
PIC Of CSF: oval pulmp nuclei with very scant cytoplasm, even chromatin, no molding |
lymphoma? |
|
|
Glioblastoma is characterized by? |
megacytosis |
|
|
pic of mesothelials what would be best differential? |
mesothelials v reactive mesothelials |
|
|
description of pericardial fluid post chemo/radiation (amorphis pink debris, epitheloid cells, elongated) |
fibrous pericarditis |
|
|
description of a culdescentesis with anucleate squames, squames and necrosis |
malignant teratoma |
|
|
pic of mesothelioma, what distinguishes from reactive mesothelial cells |
anisonucleosis (related to nucleolus size) and large tissue fragments |
|
|
pic of mesothelials/mesothelioma how to determine cell lineage, what is consistent with Dx? |
CEA (+) keratin (+) |
|
|
recognize Burkitt's lymphoma
|
small to medium sized blast like lymphocytes, with non cleaved nuclei, prominent, multiple nucleoli, scant to moderate cytoplasm, frequent mitosis, apoptotic bodies and tingible body macrophages |
|
|
description of pleural fluid with lymphocytes and NO macrophages. |
tuberculosis |
|
|
pic of body fluid with inflammatory background and classic Reed Sternberg Cells |
Hodgkin Disease |
|
|
unknown tumor positive for s100, negative for cytokeratin |
melanoma |
|
|
pic of elongated histiocytes, giant multinucleated histiocye, and grungy necrotic background. |
RA |
|
|
how would you differentiate the origin of a tumor in a fluid? |
by the cytoplasm |
|
|
multinucleated cells and single cells with eccentric nuclei with macronucleoli. the predicted pattern is most likely associated with which of the following? |
Hodgkin's Lymphoma |
|
|
peritoneal effusion possibly lipid filled vacuoles and mesothelials between the vacuoles. patient has history of? |
cirrhosis of the liver |
|
|
peritoneal/ascitic fluid in a man, showing malignant cells, most likely Dx? |
GI adenocarcinoma |
|
|
suspect a primary CNS tumor. what special stain would you use? |
GFAP |
|
|
CSF-pic of medulloblastoma CSF-pic of Astrocytoma |
medulloblastoma-small round blue cells, scant cytoplasm, clustering, cohesive, finely clumped chromatin, molding. Astrocytoma-spindle to stellate cells, nuclei varied with grade, wispy to fibrillar cytoplasm. |
|
|
pic of single file groups in pleural effusion |
small cell from lung |
|
|
Mercury drop of karyorrhexis in an effusion indicates? |
malignant lymphoma |
|
|
gout crystals |
deposition of monosodium urate crystals in and about the joints synovial fluid is dense yellow cloudy |
|
|
single vacuolated cells in pleural fluid |
can be degenerated mesothelials or carcinoma |
|
|
what would endometriosis look like in an effusions |
bloody chocolate brown. |
|
|
pic of sheet of cell with uniform nuclei, fine chromatin, microvilli, psammoma bodies..is it normal for peritoneal washes? source? |
yes this is normal in peritoneal washings. it is a benign proliferation of mesothelial cells |
|
|
which of the following entities stains positive for s100 and negative for 3 others |
melanoma |
|
|
what would be the most common site to consider in a male with ascites? |
GI |
|
|
where in the GI tract is lymphoma commonly found |
stomach |
|
|
what are some special stains for melanoma? |
Hmb45, fontanna mason, s100, melanin |
|
|
pleural fluid with predominately eosinophils. Dx? |
TB |
|
|
pic of 3 red circles with red outer cores and very dark centers. what was patient later dx with? |
cryptococcus |
|
|
what cell type predominates in bacterial meningitis? |
neutrophils |
|
|
what organism of the resp tract can cause meningitis? |
cryptococcus |
|
|
what cell type predominates in viral meningitis? |
small mature lymphocytes, plasma cells, and small macrophages |
|
|
what do LE cells engulf? |
hematoxylin body (nuclear material) |
|
|
what does synovial fluid look like? |
yellow and cloudy |
|
|
positive test for hyaluronic acid in effusions is presumptive evidence of? |
mesothelioma |
|
|
description of gastric specimen: isolated cells with scant cytoplasm, even chromatin, granular, with large nucleoli |
lymphoma |
|
|
desc: gastric brushing w/cigar shaped cells w/central oval nuclei and enlarged nuclei. dx? |
leiomyosarcoma |
|
|
rectal brush: tight groups of columnar cells, goblet cells, macrophages, leukocytes. dx? |
normal |
|
|
color plate of specialized columnar epith in esophageal brushing what is this called? |
glandular cells (like stomach cells) |
|
|
what does folate deficiency look like? GI-pernicious anemia |
macrocytes form, large squamous cells overall cell and nucleus are enlarged |
|
|
in the GI where is lymphoma most common? |
stomach |
|
|
pic of gastric brushing: group of cells with nucleoli, round nuclei, fine chromatin, N/C ratio normal. dx? |
pernicious anemia (reactive glandular atypia) |
|
|
pic of esophageal brushing: large group of cells with slight loss of polarity, enlargement, cleared chromatin and macronucleoli. dx? |
adenoca |
|
|
pic of gastric brushing: group of intact glandular cells with monomorphic, flat layer of round cells with normal chromatin and nucleoli. honey comb arrangement. dx? |
normal |
|
|
ciliated cells found in esophageal specimen are most likely associated with: |
Respiratory contamination |
|
|
gastric brush: cohesive flat sheet of cells with cyanophilic cytoplasm, prominent nucleoli. smear is consistent with: |
repair |
|
|
pic of ductal carcinoma. most important clinical hx? |
familial disease |
|
|
which area of the stomach is referred to as the cardia? |
narrow part next to the esophagus as you enter the stomach |
|
|
what do parietal and chief cells produce? |
parietal cells secrete HCL and intrinsic factor; and chief cells secrete proteolytic enzymes zymogen granules, pepsin, renin, lipase |
|
|
giardia lamblia: where is it a pathogen? |
duodenum (protozoa) pear shaped flagella |
|
|
pemphigus vulgaris? |
"bullet shaped" "bar shaped" nucleoli acantholytic cells/tzank cells |
|
|
what condition may have existed prior to ADCA? |
metaplasia |
|
|
Actinomyces |
found in the tonsillar crypts; they may grow on ulcers |
|
|
small curvilinear organisms that stain well with Romanowsky and silver stain and are assoc with MALT lymphoma? |
h pylori |
|
|
patient hx rectal bleeding and gastric distress, found organism with red blood cells ingested.dx? |
entamoeba histolytica |
|
|
paneth cells are found? |
small intestines |
|
|
cold nodule of thyroid with lymphs, rare macrophages, sheets of follicular cells, blood, and no colloid. Dx? (graves, hashimotos, PTC) |
hashimotos |
|
|
high levels of antithroglobulin in a thyroid suggests? (Hashimotos, graves, anaplastic ca, follicular neoplasm) |
HASHIMOTOS (hashimotos and graves both will show high levels of antithroglobulin.) |
|
|
pic of thyroid FNA. lots of thick amorphous material, indiv cells with high n/c ratio, coarse chromatin. (granulomatous inflam, medullary ca, PTC, hashimotos) |
meduallry ca (amourphos equal amyloid) |
|
|
description of 10y/o girl with lN FNA. numerous small lymphs, large lymphs,, macrophagges w/cyanophilic debris in cytoplasm (tingable body macrophages). (Burkitts, large cell lyphoma or RLNH) |
RLNH |
|
|
fna BONE WITH CLUSTERS OF CELLS WITH HUGE NUCLEI, MACronucleoli and coarse chromatin. (mets adeno, normal osteoclasts, giant cell tumor or bone regeneration) |
mets-adeno |
|
|
what helps make a diagnosis of lobular breast ca? |
eccentric nucleus and intracytoplasmic vacuoles. (signet rings) |
|
|
why is it difficult to obtain a lot of cells from a lobular breast ca? |
difficult to sample due to fibrotic nature of the tumor |
|
|
pic of oncocytes in a salivary smear. dx? and what if it had inflamation? |
oncocytoma (only oncocytes) or with inflammation would be Warthins tumor. |
|
|
pic of PTC. (thyroid) most likely history? |
neck irradiation |
|
|
breast: what are the granules in the cytoplasm of apocrine metaplasia called? |
mitochondria |
|
|
breast: pic of foam cells in breast aspirate. this indicates? |
cyst |
|
|
pancreas: primary carcinoma of the pancreas arises from what cell type? |
ductal cells |
|
|
warthins tumor consists of what? |
lymphocytes and oncocytes |
|
|
thyroid: special stain that would differentiate medullary ca from follicular ca? |
congo red + in medullary and stains amyloid |
|
|
breast: 20 y/o female with nipple discharge that has normal epith. cells and blood. dx? |
intraductal papilloma |
|
|
bone lesion FNA (BAD PIC) tell what important hx needed to know |
age and location of tumor/lesion |
|
|
breast: smear shows fragments of mature adipose tissue, some tight clusters of normal ductal cells with small regular nuclei and scant cytoplasm and groups of apocrine metaplastic cells with abundant cytoplasm and enlarged round nuclei with prominent nucleoli |
Fibrocystic changes |
|
|
LN-nuclei about the size of histiocytes, undifferentiated B cell lymphoma, small noncleaved lymphocytes, intermediate sized cells with deep blue finely vacuolated cytoplasm. |
Burkitts lymphoma |
|
|
thyroid: only Hurthle cells |
Hurthle cell neoplasm |
|
|
thyroid: hypercellular, poor cell cohesion, salt and pepper chromatin, spindle or plasmacytoid cells, red granular cytoplasm, amyloid often seen, anaplastic giant and spindle cells, cell pleomorphism, carcomatoid small types, prom nucleoli, mitosis, necrosis |
medullary ca |
|
|
bone: osteoclast type giant cells and slender fibroblasts (nidus) |
osteoid osteoma |
|
|
Bone: uniform osteoblasts, osteoid islands and interlacing trabeculae, uniform cells with round hyperchormatic nuclei, granular cytoplasm. |
osteoblastoma |
|
|
Bone: malignant spindle shaped cells and osteoid (must be present) |
Osteosarcoma |
|
|
thyroid: lympohcytes and Hurthle cells |
Hashimotos thyroiditis |
|
|
diagram of the ducts, lobes, lobules of the breast with an arrow to a lobule. what is it pointing to?
|
depends on the pic. |
|
|
breast: cohesive sheet of eosinophilic cells with granular cytoplasm with central nucleus and visible nucleoli. |
apocrine metaplasia |
|
|
what smear is characterized by isolated cells, multinucleation, bland chromatin, macronucleoli, cynophilic cytoplasm? |
melanoma |
|
|
fna: ovarian cyst smear contains anucleated squamous cells and necrotic debris. what is it? a. teratoma b. adenoca c. epidermoid cyst |
epidermoid cyst |
|
|
salivary: pic of salivary smear ductal cells in a long sheet, nuclei are all small, round smooth, some acinic cells in corner, background is fat and necrosis. Dx? A. medullary B. oncocytoma C. Warthins tumor D.normal salivary cells |
normal salivary cells |
|
|
thyroid: pic of thyroid smear, highly cellular, INCLs, coffee bean shaped nuclei. what predisposing factor is associated with pic?
family history, neck irradiation, gland formation, hyperplasia |
neck irradiation |
|
|
MALT: curvilinear organism assoc with peptic ulcer and malt lymphoma. |
Heliobacter |
|
|
breast: best criteria to make diagnosis of lobular breast carcinoma |
eccentric nuclei and cytoplasmic vacuoles |
|
|
pic of follicular cervicitis-ID |
germinal center cells--lymphs |
|
|
bone: pic of fna bone; clusters of cells with huge nuclei with macro-nucleoli, coarse chromatin. |
metastatic adenocarcinoma |
|
|
clusters of malignant cells with eccenctric nuclei description of 2 temporal masses in a woman |
metastatic adenocarcinoma |
|
|
if you see wall to wall plasma cells. dx? |
plasmacytoma/multiple myeloma |
|
|
what is important to see in benign nodules of the thyroid? |
colloid |
|
|
a parotid FNA that has epithelial cells and lymphs is called? |
Warthins |
|
|
what stain would you use for glycoproteins? |
alician blue stains acid (mesenchymal) mucins |
|
|
woman with hx of breast ca. gets radiation therapy, then develops a pericardial effusion. smear shows spindle cells with foamy macrophages. |
therapy induced |
|
|
Uniform osteoblasts, osteoid islands and interlacing trabeculae, uniform cells with round hyperchromatic nuclei, granular cytoplasm |
osteoblastoma |
|
|
Bone: malignant spindle shaped cells and osteoid. variations seen |
osteosarcoma |
|
|
20 y/o with nipple discharge that has normal epithelial cells, blood: |
intraductal papilloma |
|
|
Liver: person with recent blood transfusion has a liver FNA that contains hepatocytes with brown pigment. what stain would help in dx? |
Prussian blue is an iron stain for hemosiderin laden macrophages. PAS stains for lipofuscin (golden to dark brown in pap stain) |
|
|
38 y/o female with solitary liver lesion. desc of polygonal cells with abundant, granular cytoplasm, macronucleoli and intranuclear inclusions. dx? |
fibrolamellar variant of HCC |
|
|
Liver: younger patient with large nuclei with large nucleoli, oncocytic cytoplasm (dense, finely granular), cytoplasmic pale bodies, lamellar fibrosis. dx? |
fibrolamellar variant of HCC |
|
|
Liver: patient >60y/o, increased cellularity, malignant cells look like hepatocytes; polygonal outlines, central nuclei, granular cytoplasm, trabecular growth (plates of cells lined by endothelium), capillarization. Nucleoli can be extremely prominant. dx |
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) |
|
|
One pic of normal hepatocytes |
relatively large with round to polygonal outlines, centrally located nuclei, abundant granular cytoplasm and low n/c ratios. |
|
|
Islet cell tumor pic (pancreas) aka Neuroendocrine Islet cell tumor or Pancreatic endocrine neoplasm |
small to medium sized monotonous cells with salt and pepper chromatin. |
|
|
most common malignancy in the liver |
metastatic HCC if asked primary malignancy |
|
|
in a pleural effusion, cells with greenish granules were identified. where did they come from? |
bile from the liver |
|
|
description of two temporal masses in a woman, pic of clusters of malig cells with eccentric nuclei. |
mets adenocarcinoma |
|
|
pic of cigar shaped nuclei. lung FNA from patient who also has multiple liver lesions. primary? |
colon ca |
|
|
description of renal pelvic wash with abnormal cells positive for oil red o. Dx? |
RCC |
|
|
Neck aspirate of a cyst showing anucleated squames, squames and inflamation. DX? |
brachial cleft cyst |
|
|
pic of what looked like RCC in bladder irrigation: what helps to make a specific dx? choices: cytoplasmic qualities, multiple nucleoli, N/C ratio, hyperchromasia. |
cytoplasmic qualities due to vacuolization |
|
|
renal FNA, looked like huge papillary cluster |
papillary rcc |
|
|
pic of cells, patient with abdominal pain from renal barbotage. low n/c ratio, granular cytoplasm, some had macro nucleoli, somewhat in sheet/group. |
rcc |
|
|
which federal agency regulates market entry of medical devices, laboratory instruments, reagents, and systems?
|
FDA
|
|
|
What factor is the most common reason for CLIA proficiency testing failure?
|
bias: failure to control bias is the most common reason
|
|
|
what individual is qualified as a general supervisor under CLIA 88?
|
BS degree with 3 years of experience, 2 in cytopathology
|
|
|
Under CLIAA 88 guidelines a cytotechnologist may evaluate:
|
a total number established by the Technical Supervisor, not to exceed 100 slides (reevaluate this established rate on a periodic basis; at least every 6 months)
|
|
|
what is considered a necessary component of an annual report?
|
cytology-histology correlation, worklogs, workload stats, qc control data and quality assurance guidelines, total number of specimens processed, and a breakdown of number of specimens by diagnosis
|
|
|
The max number of slides in a 24hour period allowed by CLIAA is?
|
100
|
|
|
CLIAA 88 require that original requisitions be retained for?
|
2 years
|
|
|
CLIAA 88 copies of final reports are to be kept for?
|
10 years
|
|
|
CLIAA regulations stipulate that glass slides must be kept for a min of
|
5 years
|
|
|
a primary diagnostic error is defined as:
|
missing an obvious malignancy: a primary error is a misdiagnosis that would have changed the clinical managaement of the patient
|
|
|
A uniform, strict set of guidelines that apply to all lab reimbursable by medicare/medicaid are referred to as:
|
CLIAA 88
|
|
|
regarding lab procedure manuals, who is required to review and sign?
|
lab manual must be kept, reviewed periodically, and signed by the Technical Supervisor (Pathologist)
|
|
|
the governing agency overseeing safety?
|
OSHA
|
|
|
Define licensure
|
the legal process governing the right to professional practice
|
|
|
CLIAA require what?
|
HGSIL mandates follow up of the patient, daily record of number of slides reviewed as well as the amount of time spent reviewing the slides must be kept for each CT, board cert pathologists may not perform primary review of more than 100 cyto slides in any 24hr period
|
|
|
besides OSHA, which of the following fed agencies regulates lab operations?
|
Department of Transportation: regulates lab operations related to safe practices in packaging, transporting, and handling biological materials.
|

