![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Follicular lymphoma
|
t(14;18)
|
|
|
Mantle cell lymphoma
|
t(11;14)
Cyclin D1 |
|
|
Burkitts
|
t(8;14)
cmyc & IgH |
|
|
Ewings
|
t(11;22)
|
|
|
Lynch syndrome
|
MLH1
MSH2 MSH6 PMS2 |
|
|
Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (evans tumor)
|
t(7;16)
|
|
|
Endometrial stromal sarcoma
|
t(7;17)
|
|
|
CML
|
t(9;22)
bcr-abl |
|
|
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma
|
t(2;5)
|
|
|
t(17;22)
|
DFSP
Nodular fasciitis |
|
|
Peutz Jeghers
|
STK11 / LKB1
19p13 AD |
|
|
FAP
|
APC gene
|
|
|
DFSP
|
t(17;22)
COL1A1-PDGFB |
|
|
ESS
|
t(7;17)
JAZF1-JJAZ1 |
|
|
Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic tumor
|
t(1;10)
TGFBR3-FGF8 |
|
|
ASPS
|
t(x;17)
TFE3-ASPSCR1 |
|
|
What else has TFE3 translocation?
|
ASPS and Xp11 RCC
|
|
|
Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma
|
t(7;16)
FUS Evans tumor |
|
|
Other FUS mutation?
|
Myxoid Liposarcoma t(12;16)
Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma t(12;16) |
|
|
IHC lg - fibromyxoid sarcoma
|
MUC4
|
|
|
Best Synovial sarcoma IHC
|
TLE1
|
|
|
FLI1
|
11
Ewings Blood vessels, benign and malignant |
|
|
Most common supernumary chromosome marker?
|
A relatively high proportion of markers derive from chromosome 15.
|
|
|
Ataxia-telangiectasia involves spontaneous translocations and inversions in T cells. What are the genes for the Ig & TCR?
|
7: TCR B, gamms
14: TCR A, delta 2: kappa 22: lambda |
|
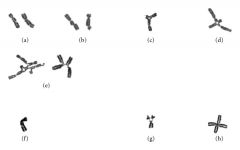
triradial forms on cytogenetics
|
Fanconi anemia
|
|
|
What & of spontaneous abortions have trisomies?
What is the most common trisomy in spontaneous abortions? |
25%
Trisomy 16 most common |
|
|
Velocardiofacial syndrome
|
microdeletion 22q
also DiGeorge syndrome |
|
|
Beckwith Wiedeman
Charcot Marie Tooth |
+11p
+17p |
|
|
Williams
Wilms Rb alpha thal |
-7q
-11p -13q -16p |
|
|
Prader Willi
Angelman |
-15q: Paternal copy mutated, maternal copy imprinted/silenced (normal). Loss of PATERNAL
(#1 cause) #2 is maternal uniparental disomy Best test is DNA methylation -15q: Maternal copy mutated, paternal copy imprinted |
|
|
In Fragile X, expansion of the CGG repeat from the premutation to the full mutation occurs in?
|
MATERNAL MEIOSIS, not paternal meiosis
|
|
|
Clear cell sarcoma
|
t(12;22)
|
|
|
granulosa cell tumor
|
trisomy 12
|
|
|
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
|
beta-myosin heavy chain chrom 14
sudden death myofiber disarray SEPTAL hypertrophy |
|
|
2 syndromes with hepatoblastoma
|
FAP
Beckwith Wiedemann |
|
|
What are the hamartomatous polyposes?
|
Peutz-Jegher
Familial juvenile polypsos Cronkhite-Canada Cowden |
|
|
What are the adenomatous polyposes?
|
FAP
Gardners Turcot All are AD and have APC gene mutations |
|
|
Fibrous dysplasia
|
GNAS1 gene
|
|
|
Osteosarcoma
|
13q14 (Rb locus, 500x risk)
LOH 3, 17, 18 MDM2 amplification with inactivation p53 (Li Fraumeni, 500x risk) |
|
|
Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma
|
t(9;22)
|
|
|
t(12;16)
FUS-CHOP |
myxoid/round cell liposarcoma
|
|
|
desmoplastic small round blue cell tumor
|
t(11;22) EWS-WT1
|
|
|
primary aneurysmal bone cysts
|
t(16;17) CDH11-USP6
|
|
|
angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma
|
t(12;16) FUS-ATF1
|
|
|
Meningioma
|
monosomy 22
|
|
|
Mesoblastic nephroma
Infantile fibrosarcoma |
t(12;15)
ETV6-NTKR3 |

