![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

eclipse that occurs when the Earth's shadow falls on the moon
|
lunar eclipse
|
|

What is this a picture of?
|
lunar eclipse
|
|
|
eclipse that occurs when the moon passes directly between the sun and Earth and casts a shadow over part of Earth
|
solar eclipse
|
|
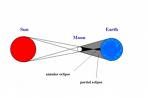
What is this a picture of?
|
solar eclipse
|
|
|
occurs when the moon passes directly between the sun and Earth and casts a shadow over part of Earth
|
solar eclipse
|
|

occurs when the moon passes directly between the sun and earth and casts a shadow over part of earth
|
solar eclipse
|
|
|
describes phases following a new moon as more of the moons lighted side becomes visible (getting bigger)
|
waxing
|
|
|
describes phases that occur after a full moon, as the visible lighted side of the moon grows smaller
|
waning
|
|
|
phase that occurs when all the moons surface facing earth reflects light
|
full moon
|
|
|
phase that occurs when the moon can not be seen because it is between the sun and earth and the dark side is facing earth
|
new moon
|
|

What phase is this?
|
waxing crescent
|
|

What phase is this?
|
waning crescent
|
|

What phase is this?
|
waning gibbous
|
|

What phase is this?
|
waxing gibbous
|
|

What phase is this?
|
half moon, first quarter, or last quarter
|
|

the pattern of phases the moon goes through as it revolves around earth
|
lunar cycle
|
|
|
the amount of time that it takes the moon to go through one complete cycle
|
29.5 days or about a month
|
|
|
spinning of earth on its imaginary axis
|
rotation
|
|
|
rotation causes __________
|
day and night
|
|
|
How long does it take the earth to make one complete turn or rotation?
|
1 day or 24 hours
|
|
|
earth's elliptical orbit around the sun
|
revolution
|
|
|
How long does it take earth to make one complete revolution?
|
365 days or 1 year
|
|
|
rhythmic rise and fall in sea level created by the gravitational attraction of Earth, moon, and sun
|
tide
|
|
|
day when the sun reaches its greatest distance north or south of the equator
|
solstice
|
|
|
longest day of the year
|
summer solstice
|
|
|
shortest day of the year
|
winter solstice
|
|
|
occurs when the sun is directly above the earth's equator
|
equinox
|
|
|
occurs during the fall when the number of daylight hours are equal to the number of nighttime hours
|
autumnal equinox
|
|
|
occurs during the spring when the number of daylight hours are equal to the number of nighttime hours
|
vernal equinox
|
|
|
this causes the earth to have seasons
|
tilting of earth
|
|
|
this place on earth has the same temperatures all year long because it receives the same amount of sunlight all year long
|
areas around the equator
|
|
|
hemisphere that is receiving more direct rays at a higher angle from the sun is having what type of season
|
summer
|
|
|
hemisphere that is receiving less direct rays at a lower angle from the sun is having what type of season
|
winter
|
|
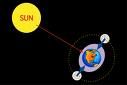
What kind of tide would we expect to have?
|
neap tide or low tide
|
|

What type of tide would you expect to have?
|
spring tide or high tides
|
|
|
the continuous process by which water moves from earth's surface to the atmosphere and back
|
water cycle
|
|
|
process by which nitrogen is removed from the atmosphere fixed in the soil by bacteria, incorporated into other living things, and then released back into the atmosphere
|
nitrogen cycle
|
|
|
process in which carbon is transferred from living and nonliving things back into the atmosphere
|
carbon dioxide cycle
|
|
|
series of processes on the surface and inside earth that slowly changes rocks from one kind to another
|
rock cycle
|
|

process by which a liquid absorbs energy and turns into a gas
|
evaporation
|
|

process of water being evaporated from leaves
|
transpiration
|
|

matter changing from a gaseous state to a liquid state by the removal of energy
|
condensation
|
|

forms of water that falls from clouds and reaches earth's surface
|
precipitation
|
|

organism that breaks down tissue and releases nutrients and carbon dioxide back into the ecosystem
|
decomposer
|
|

organisms that changes the nitrogen in the soil into a form of nitrogen that plants can use
|
nitrogen-fixing bacteria
|
|

changes nitrogen in the air to nitrates which is a form of nitrogen that plants can use
|
lightning
|
|
|
series of chemical processes in which oxygen combines with food molecules, energy is released, and carbon dioxide and water are given off as wastes
|
cellular respiration
|
|
|
process by which organisms use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make food and oxygen
|
photosynthesis
|
|
|
layers of small sediments are compressed by the weight of layers above them
|
compaction
|
|
|
process in which rocks are broken down into smaller pieces
|
weathering
|
|
|
movement of weathered material by either: wind, ice, water, or gravity
|
erosion
|
|
|
process in which sediments are held together natural cements that are produced when water soaks through rock and soil
|
cementation
|
|
|
process by which the sediments settle out of the wind, water, or gravity that is carrying it and is deposited in a new location
|
deposition
|
|
|
rocks that are formed from the cooling of magma
|
igneous rock
|
|
|
rocks that are formed from extreme heat and pressure
|
metamorphic rock
|
|
|
rocks formed from cementation and compaction
|
sedimentary rock
|
|
|
igneous rocks that are formed from lava on Earth's surface
|
extrusive
|
|
|
igneous rocks that are formed when magma hardens beneath earth's surface
|
intrusive
|
|
|
thick gooey molten rock material that flows on earth's surface
|
lava
|
|
|
hot, molten rock material that is found beneath earth's surface
|
magma
|
|

process of burning materials, such as fossil fuels
|
combustion
|
|

loose material that have been broken down and moved by wind, water, ice, or gravity
|
sediments
|

