![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common site for CVA's?
|
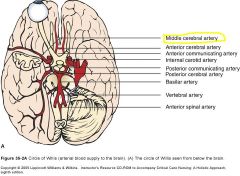
Middle Cerebral artery
|
|
|
What is a CVA?
|
*Permanent reduction of blood flow
*Infarct of brain tissue caused by oxygen deprevation |
|
|
What is the most common diagnosis seen by OTs
|
CVA
|
|
|
What is hemiplegia?
|
paralysis of one side. The side opposite the CVA
|
|
|
What is hemiparesis?
|
weakness; partial motor loss on one side. The opposite side of the CVA
|
|
|
What is a TIA?
|
Trans Ischemic Attack
It is a temporary reduction of blood flow, a mini-stroke |
|
|
Define:
Ischemia |
blockage (reduction in flow)
|
|
|
Define:
Necrosis |
Death (tissue dies)
|
|
|
Name 3 etiologies of CVA
|
1 Thrombus
2 Embolus 3 Hemorrhage |
|
|
Which etiology is the most common?
|
Thrombus 53-58% of CVA
|
|
|
Which etiology is the most deadly?
|
Hemorrahge type CVA's
|
|
|
Describe Thrombus
|
-Due to blockage from blood clot
-atheroscherosis: fatty deposits in arteries -Due to lifestyle choices -Occurs at night, & pt's unaware |
|
|
Describe Embolus
|
-Traveling blood clot
-clot can be a piece from thrombus or other material |
|
|
Describe Hemorrhagic
|
-Ruptured aneurysm or caused by a trauma (MVA)
|
|
|
Characteristic of Strokes are?
|
-come on suddenly
-symptoms are focal (specific area of brain) -can be mild or severe |
|
|
What are the Risk Factors for a CVA? 2 most common
|
1- age
2- cardiac disease |
|
|
What are the controllable factors:
|
-stress
-birth control w/headaches and smoking -HTN -alcohol -smoking -obesity -diabetes (along w/other unhealthy habits) |
|
|
What are the UNcontrollable factors:
|
Usually genetics.
Chinese, Japanese and African Am -Age |
|
|
What is the most modifiable risk factor
|
High blood pressure
|
|
|
What are the 2 effects of a stroke?
|
-Motor and sensory
(problems with movement) |
|
|
What are the warning signs?
|
TIA
|
|
|
How long do TIAs last? And what are they a prelude to?
|
*they can last 2-15 minutes, rarely over 30 minutes.
* A major stroke! may follow after 1 or more TIA's |
|
|
How long before a major stroke after TIA's
|
major stroke can follow hours, weeks or months after TIA
|
|
|
Dysfunctions following a CVA
|
- flaccidity/hypotonicity
- sensation loss/chg - cognition deficits - behavior/personality chgs - speech/language deficits - vision impairments/chgs |
|
|
What do the outcomes and severity of CVA depend on?
|
It depends on the
type, size, location, and density of the brain damage |
|
|
Poor Prognosis is indicated by what factors?
|
1. the amt of edema causing intracranial pressure
2. edema in comatosed pts. 3. How long the pt is flaccid |
|
|
What can cause a favorable prognosis?
|
Early spasticity
|
|
|
How long before the brain stops swelling due to CVA?
|
Usually reaches at peak in 3-4 days then subsides
|
|
|
What is the recovery period for small infarcts vs severe infarcts?
|
small infacts(mini-strokes): 1-2 days
In severe CVA's: spontaneous recovery of motor func can occur in 3 months. But typically it takes pt's 5-6 months then they plateau. Studies do show that improvments continue years post CVA |
|
|
What type of medical complications are stroke pt's prone too?
|
-DVT
-Subluxation of the GH joint 1. due to spasticity 2. due to flaccidity -Decubitus Ulcers |
|
|
What are the problem areas?
|
-abnormal reflexes
-abnormal MS tone -motor skills deficits (recovery begins proximal to distal) -balance impairments -motor problems (fine & gross) |
|
|
OT treatment techniques: 11 of them
|
-PROM/AROM: maintain ROM to prevent deformity; serial casting
-Treat pain and subluxation: rest arm on lap trays, arm trough, use a sling only when walking -Motor retraining: work on posture and movement (include the affected arm- it can hold things down, up, stablizer) -normalize MS tone: facilitate for flaccilidity & inhibit for spasticity -bilateral integration -strength and endurance -edema control: elevation, retrograde massage,PAMS (cold) -compensatory techniques: one-handed techniques -sensory retraining- rubbing area, exposing to diff textures -visual: hemianopsia-use anchoring technique, diplopia-patch one eye -tactile: (any of the sensory losses) compensate w/vision -olfactory and gustatory: safe guard the environment |

