![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ms. Heddy Fail’s heart failure is getting worse because she just had an episode of pulmonary edema. Remember before that she had left ventricular hypertrophy and a reduced ejection fraction. What will you use to treat her heart failure?
What stage is she? |
ACE inhibitor and B Blocker and Diuretic for the edema
Stage C |
|
|
what are the only drugs that will control fluids in people with HF?
|
Diuretics
|
|
|
what effect will a loop diuretic have on preload? what does this do to pulmonary edema?
|
decrease it
gets rid of pulmonary edema |
|
|
What effect will diuretics have on CO in a patient with heart failure?
|
Little/no effect
|
|
|
Which class of diuretics is most useful in the treatment of edema associated with heart failure?
|
LOOPS
ya know, a jockey, a pro caddy |
|
|
What stage HF do you use loop diuretics?
|
C and D (remember A and B don't have any symptoms!)
|
|
|
can thiazide diuretics adequately control fluid retention in HF on their own? what about K sparing?
|
ONLY LOOPS WORK
|
|
|
hypokalemia can be an adverse effect of what?
|
Loop diuretics
|
|
|
What is one of the major problems associated with K+ or Mg++ depletion?
|
can predispose a patient to cardiac arrhythmias
|
|
|
How do you prevent the hypokalemia associated with loop or thiazide diuretics?
|
add a K sparing diuretic
|
|
|
_______ levels may be _____ times greater in patients with HF
|
Alsodosterone
20x |
|
|
what two negative effects do high levels of aldosterone have?
|
vascular injury
cardiac remodeling |
|
|
what are the 3 drugs used to prevent remodeling in the heart?
|
ACEi, B blocker, aldosterone antagonists
|
|
|
what are the 2 alodosterone antagonists?
|
Spironolactone
Eplerenone |
|
|
What Stage do you use aldosterone antagonists? What NYHA class?
|
Stage C
NYHA Class III-IV |
|
|
A patient has Stage C, NYHA Class III HF. If their serum creatinine is > 2.5 mg/dL (normal 0.8-1.2 mg/dL), would you use an aldosterone antagonist?
why |
NO
if serum creatinine is high, you want to minimize the risk of life threatening hyperkalemia that would accompany the kidney's lack of filtration |
|
|
A patient has Stage C, NYHA Class III HF. If their serum K is > 5.0 mEq/L (normal 3.5 - 5.0 mEq/L), would you use an aldosterone antagonist?
why |
NO
you want to minimize the risk of life threatening hyperkalemia |
|
|
What is the advantage in using eprelerenone vs spironolactone ?
|
both are aldosterone antag
eplerenone does not block androgen or progesterone receptors so it is better |
|
|
Ms. Heddy Fail complains of being pretty fatigued with short walks. She has had to go into the hospital several times for her heart failure. She is on ramipril, metoprolol, eplerenone, and furosemide. What will you use to treat her heart failure?
what stage HF is she? |
keep her on what she is already, but add in DIGOXIN
Stage C HF. |
|
|
back in the day what was HF known as?
|
Dropsy
|
|
|
please list the mech of action for Digoxin, including the different ion exchangers involved
|
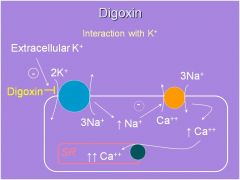
inhibits the K/Na ATPase
this increases intracellular Na This then decreases the activity of the Ca/Na exchanger (meaning less Ca is going out) Ca is then taken back up via the Ca-ATPase on the SR membrane thus on the next conduction you can get a huge release of Ca giving you a more forceful contraction (positive inotropic effect) |
|
|
what inhibits digoxin from binding to the extracellular K/Na ATPase?
|
High extracelluar K+
|
|
|
What happens if serum K+ is too low or too high with respect to dig use?
|
Hypokalemia will increase the effect/toxicity of digoxin (this is because less potassium will prevent the inhibition of digoxin from binding to the extracellular K/Na ATPase)
Hyperkalemia reduces the action of digoxin |
|
|
What class of drugs can cause hypokalemia? 2
|
Thiazide and loop diuretics
|
|
|
Hyperkalemia _____ the action of digoxin
|
reduces
|
|
|
what are 2 indirect effects of digoxin? what do these effects lead to?
|
Increases vagal activity
Sensitizes baroreceptors and decreases sympathetic activity Leads to--> decrease in activity of the SA and AV node |
|
|
at lower doses what is a toxic effect on of digoxin the heart?
|
Sinus bradycardia, AV block
----due to: Excess vagal tone |
|
|
at higher doses what is a toxic effect of digoxin on the heart? 2
|
increased sympathetic tone (centrally induced)
Ca overload |
|
|
What is Ca overload?
|
too much Ca leads to cardiac arrhythmia damage
|
|
|
In a damaged heart, what can excessive sympathetic tone and Ca overload cause?
|
cardiac arrhythmias
|
|
|
what causes a delayed after depolarization (DAD)? they can be seen with use of?
|
Calcium overload, which leads to a spontaneous release of Ca from the SR, which then leads to the DAD
seen with use of digoxin |
|
|
what is meant by a low therapeutic index? what HF drug has this characteristic?
|
the toxic dose is very close to the therapeutic dose
digoxin |
|
|
Nausea and vomiting can be a side effect of digoxin toxicity...what is dig doing that is causing this?
|
activating the chemoreceptive trigger zone in the brain which leads to nausea and vomiting
|
|
|
what is the first sign of digoxin toxicity?
|
they are vomiting, because digoxin is hitting the chemoreceptive trigger zone
|
|
|
what does digoxin do in the GI tract?
|
anorexia and diarrhea due to increased motility
|
|
|
person is in hospital, on alot of medications but is being treated for heart failure. they start reporting weird dreams and hallucinations...what drug is the culprit?
|
Digoxin
|
|
|
a HF patient comes in complaining of green and yellow halos around objects... what is this a side effect of
|
digoxin toxicity
|
|
|
gynecomastia can be the result of what 2 drugs
|
spironolactone and digoxin
|
|
|
what do you do when you have digoxin toxicity? do you do this if they are nauseous? what if they have a cardiac arrhythmia
|
give FAB fragment of digoxin specific antibody (Digibind)
nauseous: NO, it has too many side effects arrhythmia: YES, this could kill you |
|
|
Ms. Heddy Fail’s serum creatinine has been increasing (remember she has Stage C HF). Further testing reveals renal artery stenosis. She is on ramipril, metoprolol, digoxin and furosemide. do you want to continue your treatment? anything additional?
|
all except ramipril (renal artery stenosis contraindicates this)
Hydralazine and isosorbide dinitrate |
|
|
mechanism of isosorbide dinitrate? end result?
|
NO to the veins
causes vasodilation decrease Preload end result: reduces edema and wall stress |
|
|
mechanism of hydralazine? end result?
|
dilates arteries
decreases afterload end result: increases ejection fraction and decreases wall stress |
|
|
when do you want to use Isosorbide Dinitrate + Hydralazine?
|
in african american patients
reduces mortality |
|
|
What is the goal in the pharmacological treatment of acute decompensated HF? 2
|
remove pulmonary congestion (edema) if present
decrease pump failure (poor CO), if present |
|
|
How can pulmonary edema be reduced? (2)
|
Loop diuretic (reduced blood volume) or reduce preload
|
|
|
how can CO output be increased in acute decompensated HF
|
reduce afterload
increase myocardial contractility |
|
|
when do you want to increase myocardial contractility (what stage)
|
Stage D
|
|
|
How can afterload be reduced?
|
arteriodilator
|
|
|
please list the 4 IV drugs for acutely decompensated heart failure
|
Loop diuretics
Nitroglycerin Nitroprusside Nesiritide |
|
|
What do you have to be concerned about when using loop diuretics for decompensated HF? 4
|
hypotension
worsened renal function hypokalemia excessive diuresis |
|
|
What is the best choice for treating congestion or pulmonary edema in a patient with acute decompensated heart failure?
|
Loop diuretic
|
|
|
what does nitroglycerin do?
|
increases NO mainly in veins
|
|
|
what does nitroprusside do?
|
increase NO in both arteries in veins
|
|
|
what is Nesiritide?
|
Recombinant human B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
|
|
|
what is the MOA of Nesiritiede? (for blood vessels)
|
Activates guanylyl cyclase on vascular smooth muscle cells
this increases cGMP which vasodilates arteries and veins |
|
|
what is the MOA of Nesiritiede? (for kidney) 3
|
constricts the efferent arteriole and dilates the afferent (leads to increased GFR)
antagonizes Na reabsorption (leads to natiuresis) |
|
|
what is a serious side effect of nesiritide?
|
Worsening of renal function, so don't use with people that have problems with kidneys
also can have possibly increased mortality vs other treatments |
|
|
A 76-year-old male presents in the emergency room with dyspnea. Physical exam reveals 2+ pitting edema, blood pressure of 110/80 and bibasilar rales. He has a history of heart failure (Stage C, NYHA Class II) and hypertension. His current medications include furosemide, ramipril and carvedilol. Which drug would most likely treat his acute problems?
|
IV Furosemide
|
|
|
what are the 3 general types of positive inotropic drugs for short term, hemodynamic support in patients with severe heart failure?
|
dobutamine
dopamine phosphodiesterase inhibitors |
|
|
what is the mechanism of action of dobutamine?
|
activates B1 > B2 > alpha
so it hits the B1 receptor to cause a positive ionotropic effect and B2 on vasculature to cause vasodilation |
|
|
does dobutamine cause an increase in HR?
|
NO
even though it activates B1 > B2 > alpha |
|
|
what receptor(s) are affected by dopamine??
|
1st: activates D1
2nd: activates B 3rd: activates alpha |
|
|
how does low dose dopamine work in HF?
|
low dose dopamine hits DA receptors leading to:
Vasodilation of renal, splanchnic, cerebrospinal, and coronary blood vessels |
|
|
how does an intermediate dose of dopamine working in HF?
|
hits B1 receptors
positive inotropic effect |
|
|
how does a high dose of dopamine working in HF? when do you use this?
|
hits a1 receptors
vasoconstriction of arteries can help if extremely hypotensive with problems profusing organs |
|
|
mechanism of phosphodiesterase inhibitors in acute HF?
|
increase cAMP leading to positive ionotropic effect
|
|
|
what is a long term effect of milrinone? what kind of drug is this?
|
this is a PDE III inhibitor....
can cause death with prolonged used |
|
|
what does nitroglycerine do to preload?
what does reduced preload do |
decreases it
reduces edema |
|
|
how do you reduce edema?
|
reduce preload...aka vasodilate veins
|
|
|
for a patient in severe HF (stage D) what are the 3 drugs you want to be thinking about giving?
|
Dobutamine
Dopamine PDE Inhibitors (Milrinone) |
|
|
For stage A HF, what drugs should your pt be on?
|
ACE inhibitor/ARB
|
|
|
For stage B HF, what drugs should your pt be on?
|
ACE inhibitor/ARB + B Blocker
|
|
|
For stage C HF, what drugs should your pt be on?
|
ACE inhibitor/ARB
B Blocker Diuretic Digoxin Aldosterone antag |
|
|
For stage D HF, what drugs should your pt be on?
|
ACE inhibitor/ARB
B Blocker Diuretic Digoxin Aldosterone antag and positive ionotropic effect drug (IV) |

