![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
peripheral artery Dz (PAD)
|
-casued by atherosclerosis
-causes intermittent claudication -increase risk of CV M/M |
|
|
PAD agents
|
-antiplatelets: aspirin, clopidogrel
-Lipid Lowering agents -ACE inhibitors |
|
|
what happens in PAD
|
plaque causes downstream decrease in pressure and flow distal to atheroma; endothelial dysfnx causes reduced NO production; RBCs deform and align in planar manner, reducing viscosity and allowing them to pass through
|
|
|
what happens in PAD summary
|
chronic tissue ischemia and hypoxia cause decreased ability of RBCs to deform and increased platelet aggregation and activation of clotting factors
-these events increase viscosity and further inhibit blood flow and O2 delivery... giving a vasodilator won't help |
|
|
PAD drugs
|
Cilostazol
Pentoxifylline |
|
|
Cilostazol MOA
|
Inhiit PDE 3 →
↑cAMP in platelets= ↓aggregation ↑cAMP in vessels= vasodilation -- decreased intermittent claudication |
|
|
where does cilastozal primarily dilate vessels?
|
Femoral AA.
|
|
|
why is cilostazol contraindicated in HF?
|
Milrinone PDE Inhibitor decreaes survival with chronic use in HF… translates to cilostazol, even though no one is going to volunteer for that study
|
|
|
Pentoxifylline MOA
|
*↑RBC flexibility*
↓plasma fibrinogen -- ↑blood flow and tissue oxygenation |
|
|
Cilostazol clinical use
|
-more effective than pentoxifylline
-first line in absence of HF |
|
|
Raynaud's Dz
|
vasospasm of small arteries in skin of hands and feet with intermittment pallor and cyanosis
Tx: vasodilators: -CCBs -a antagonists -direct vasodilators (nitrates) -ACE Is -- prazosin, amlodipine, nitroglycerine, lisinopril |
|
|
pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH, Group 1)
|
Right HF... essential HTN is Left HF
|
|
|
Which would you use for stage 1 HTN and Raynaud's: prazosin, propanolol, amlodipine, nitroglycerine or hydrochlorothiazed?
|
amlopdipine; used for both... prazosin also, but not a first line drug
|
|
|
ultimate cause of increased pulmonary vascular resistance
|
neurohumoral imbalance
|
|
|
endothelin
|
vasoconstriction, increased muscle proliferation
|
|
|
Prostacyclin & NO
|
vasodilation, decreased muscle proliferation, aggregation inhibition
|
|
|
PAH mechanism: Endothelial Dysfnx
|
--overproduction of endothelin
-too much vasoconstriction -too much proliferation --underproduction of prostacyclin & NO -not enough vasodilation -not enough platelet aggregation inhibiion -no enough antiproliferation |
|
|
PAH mechanism: Abnormal Ca2++ handling
|
--increased Ca2++ in smooth muscle cells
-too much vasoconstriciton -too much proliferation |
|
|
PAH summary
|
-proliferation of intima, media and adventitia
-excess smooth muscle tone (vasoconstriction) -thrombosis in situ |
|
|
PAH Tx goals
|
-prevent thromboembolism= anticoags
-reduce peripheral edema= diuretics (from HF) -reduce pulmonary vascular resistance remodeling of the pulmonary arteries to increase CO, exercise capacity and reduce mortality |
|
|
vasodilators for PAH?
|
most ineffective in chronic reduction of pulmonary vascular resistance
|
|
|
PAH: to much Ca in cell
|
CCB
|
|
|
PAH: too much endothelin
|
endothelin antagonist
|
|
|
PAH: not enough PGI2
|
PGI2
|
|
|
PAH: not enough NO
|
PDE-5i (cGMP)
**remember, PDE-3i → cAMP (Cilostazol) |
|
|
CCBs for PAH
|
-Nifedipine, verapamil, diltiazem
-decrease pulmonary vascular resistance in 10-15% (sucks) -doses 2-3x higher than use for systemic HTN -people that do respond may have longer survival |
|
|
remember, inotropic effect of verapamil, diltiazem and amlopidine
|
negative inotropic effect of verapimil > diltiazem >>> amlodpine
|
|
|
How can u be sure a person will respond to a CCB?
|
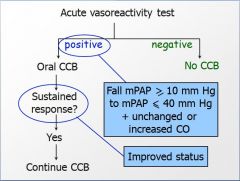
Acute Vasoreactivity Test: super short 1/2 life ... IV epoprostenol, IV adenosine or inhaled NO
[mPAP= main pulmonary arterial pressure] |
|
|
Acute Vasoreactivity Test - Summary
|
-Administer a very short acting vasodilator, either IV epoprostenol, IV adenosine, or inhaled NO
-Measure mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) and CO -If mPAP falls to an acceptable level AND CO is unchanged or increased, then… -Try a CCB -If they exhibit a sustained response on a CCB, then… -Long term treatment with CCB |
|
|
Prostacyclin Analogues
|
-Epoprostenol (Flolan) – IV
-Treprostinil (Remodulin) – subcutaneous, IV -Treprostinil (Tyvaso) - inhalation -Iloprost (Ventavis) – inhalation |
|
|
Prostacyclin Analogues MOA
|
Prostacyclin (PGI2)
-Dilates pulmonary vessels -Decrease pulmonary vascular resistance -Probably a small degree of systemic vasodilation -Inhibits platelet aggregation -Antiproliferative effects |
|
|
Epoprostenol- end result
|
-improve hemodynamics
-relieve symtpoms -increase exercise capacity -improve quality of life and survival |
|
|
Epoprostenol AEs
|
**Jaw Pain**
nausea, diarrhea hypotension headache flushing thrombocytopenia leukocytic classic vasculitis leg/foot pain |
|
|
What is the difference between epoprostenol, treprostinil and iloprost?
|
pharmicokinetics
|
|
|
prostacycln analogue 1/2 lives
|
Epoprostanol- 6min
Iloprost- 20-30 min Treprostinil- 4hr |
|
|
Epoprostenol admin/comps
|
central venous catheter (CVC)
-must be cold -once on Ep, must continue or die -infections at catheter site -increase mortality |
|
|
Iloprostenol admin/comps
|
SQ infusion or CVC or Inhalation
-SQ injection site pain -Inhalation 2-3min/4x/day |
|
|
Treprostinil admin/comps
|
Inhalation
10-12min/6-9x/day |
|
|
have clinical trial shown increased mortality for prostacyclin analogues?
|
Epoprostenol only
|
|
|
Endothelin Receptor antagonists
|
Bosentan
Ambrisentan -- both oral |
|
|
Endothelin Receptor antagonists: MOA
|
-Plasma endothelin increased in patients with pulmonary HTN and correlates with Dz severity
-Bosentan blocks both Endothelin A & B receptors -Ambrisentan blocks Endothelin A receptor only -- block endothelin-induced vasoconstriction, fibrosis, hypertrophy, hyperplasia and vascular permeability |
|
|
Endothelin Receptor antagonists: end result
|
-improve pulmonary hemodynamics
-increase exercise capacity -decrease exercise dyspnea -decrease time/rate of clinical worsening -- patients showed improved survival at 2 years |
|
|
Endothelin Receptor antagonists:
AEs |
--Bosentan
-↑ liver aminotransferases (11% incidence) -enzymes must be checked monthly --Ambrisentan -FDA removed liver enzyme check recommendation |
|
|
Endothelin receptor antagonist AEs
|
-decrease in Hb and hematocrit
-teratogenic in some animals -induces CYP3A4, 2C9 and 2C19 -decrease concentration of some drugs such as hormonal contraceptives... recommend two forms of contraception **Cat X contraindication: pregnant women** |
|
|
PDE 5 inhibitors
|
Sildenafil
Tadalafil |
|
|
L-arginine to cGMP pathway
|
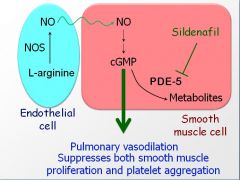
|
|
|
In PAH, endothelial dysfnx causes a reduction in ______
|
NO synthase... end up with more pulmonary vasoconstricton
|
|
|
what does inhibiting PDE 5 do?
|
raises concentration of cGMP in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells to enhance dilation of the pulmonary vasculature, decreased platelet aggregation and decrease smooth muscle proliferation
|
|
|
PDE 5i end result
|
-increase exercise tolerance
-improve mPAP (mean pulmonary arterial pressure, cardiac index and pulmonary vascular resistance |
|
|
PDE 5 AEs
|
-headache
-flushing -IBD -epistaxis -nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy |
|
|
PAH Tx summary
|
-CCB in patients that respond to vasoreactivity test
*for other PAH drugs: -use oral drugs in less severe patients -use parenteral drugs in more severe patients -Epoprostenol: first line for the worst patients |

