![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is hypertension for a pt greater than 18
*** (give both diastolic and systolic) |
The average of two or more diastolic measurements on each of two or more visits being 90 mmHg or higher
The average of two or more systolic measurements on each of two or more visits being 140 mmHg or above. |
|
|
What is Essential Hypertension?
|
Hypertension with no identifiable cause
90% of all cases of hypertension are essential |
|
|
is essential hypertension prevalent?
|
shit ya! tons of fatties
|
|
|
what is the relationship between BP and CVD?
|
continuous
For those 40-70 each 20/10 mmHg increase from 115/75-185/115 mmHg doubles the risk |
|
|
how long should the patient be seated before taking a BP?
|
5 minutes
|
|
|
how much of the cuff bladder should encircle the arm?
|
80%
|
|
|
A patient walks in and just put their cigarette out, should you take their BP?
|
no wait 30 mins
|
|
|
if you have a normal BP classification, what range are your systolic and diastolic BP
|
SBP <120
DBP <80 |
|
|
if you have a prehypertension BP classification, what range are your systolic and diastolic BP
|
SBP 120-139
DBP 80-89 |
|
|
if you have a stage 1 hypertension BP classification, what range are your systolic and diastolic BP
|
SBP 140-159
DBP 90-99 |
|
|
if you have a stage 2 hypertension BP classification, what range are your systolic and diastolic BP
|
SBP >160
DBP >100 |
|
|
if you have a patient with dyspnea orthopnea, edema
what should you be thinking? |
Secondary Hypertension
|
|
|
Narrowing of Arterioles are indicative of what grade retinopathy?
|
grade 1
|
|
|
AV nicking is indicative of what grade retinopathy?
|
grade 2
|
|
|
flame hemorrhage is indicative of what grade retinopathy?
|
grade 3
|
|
|
Soft exudates are indicative of what grade retinopathy?
|
grade 4
|
|
|
Papillemedema is indicative of what grade retinopathy?
|
grade 5
|
|
|
What is goal of therapy for hypertension with respect to BP? what if you have renal disease or are diabetic?
|
<140/90
130/80 if you have diabetic or renal disease |
|
|
what is DASH with respect to hypertension?
|
Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension
goal of therapy |
|
|
if someone had diabetic or renal disease what is the goal to lower their BP to?
|
130/80 if you have diabetic or renal disease
|
|
|
Discuss the use of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and
home monitoring in the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension. |
basically you can compare their home readings to your office reading and look for changes
|
|
|
what type of pharmacologic treatment is unsurpassed in preventing CV complications of hypertension?
|
diuretics
|
|
|
what are 2 drug types you can use for stable angina
|
B-blocker
Calcium channel Blocker |
|
|
what are 2 drug types you can use for acute coronary syndrome
|
B blocker
ACE I |
|
|
what are 2 choices for first line treatment of HT in a pt with Diabetes?
|
ACE and ARB
|
|
|
when is a pt. said to have chronic kidney disease? if you are treating this pt what would you use for their HT?
|
GFR<60
use ACEI or ARB |
|
|
Recurrent stroke rates lowered with a combination of?
|
ACEI and Thiazide diuretic
|
|
|
what is the best drug choice to treat HT in blacks? (2)
|
Diuretics or CCBs
|
|
|
what drug option should you use for children with HT?
|
YOU SHOULDN'T. make lifestyle changes (aka make them get their fat asses off the couch, put down the McDonalds, and run)
only if in 95th percentile |
|
|
what drug would you NOT want to use in someone with gout?
|
Thiazide because it increases uric acid
|
|
|
What drugs would absolutely not want to give to a preggo woman who was HT?
|
ACEI or ARB
|
|
|
If a pt has Diabetes, what do you want to use to treat HT? ***
|
ACE inhibitor (ARB would be second choice)
|
|
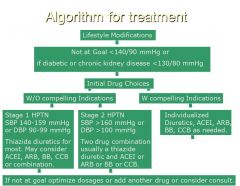
Know this
|
write it out
|
|
|
When do you use Methyldopa?
|
preggo with HT
|
|
|
Outline follow-up visits for the treatment of hypertension.
objective |
Monthly until BP goal reached
More frequent visits if Stage 2 or complicating conditions 3-6 month visits after goal is reached Serum creatinine and potassium 1-2 times/year Low dose aspirin only after goal is reached |
|
|
discuss patient compliance.
objective |
Must agree upon goal
Must understand the condition and treatment Overcome denial of illness Cost of medication and medical care |
|
|
what is resistant hypertension?
|
Failure to reach goal on full dose of appropriate three drug regimen that includes a diuretic
|
|
|
what are some of the possible causes of resistant hypertension?
|
Improper blood pressure measurement
Volume Overload (ie. excess Na+ intake, volume retention from kidney disease, inadequate diuretic therapy) Drug induced (ie. NSAID, illicit drugs, BCP, steroids, decongestants, licorice, ephedra) Associated Conditions (ie. obesity, excess alcohol intake) Identifiable Causes of Hypertension |
|
|
please list where the 3 different diuretics act and their names
|
Loop Diuretics: Loop of Henley
Thiazides: Distal Convoluted Tubule K-Sparing: Collecting ducts |

