![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is functional morphology?
|
being able to determine the function of a cell based upon the number and kinds of organelles present in the cell
|
|
|
all organelles are delimited by ____ membrane, except in the case of the ______ and the ______, which each have 2 membranes.
|
1; mitochondrion, nucleus
|
|
|
the characteristics of each organelle are defined, in large part, by which constituents?
|
protein
|
|
|
how many subunits compose a ribosomes? where are the subunits assembled?
|
2; nucleolus
|
|
|
what are polysomes?
|
groups of ribosomes which perform translation at the same time.
|
|
|
free ribosomes create proteins which have where as their final destination?
|
intracellular
|
|
|
what are 4 examples of proteins produces by free ribosomes?
|
1) soluble enzymes in the cytosol
2) nuclear enzymes 3) proteins for the replacement or repair of cell organelles 4) unique components of new plasma membranes |
|
|
proteins synthesized on ribosomes located on RER are destined where? how do they get there?
|
outside the cell, plasma membrane, lysosome ; exocytosis
|
|
|
in which location, free ribosomes or on RER, are lysosomal proteins produced?
|
RER
|
|
|
in which location, free ribosomes or on RER, are majority of new plasma membrane proteins created?
|
RER
|
|
|
with what are proteins tagged for their final destination?
|
signal peptide
|
|
|
for a translated polypeptide to enter ER, which factors must be involved? through which of these does the peptide enter the ER? what energy molecule facilitates this process?
|
SRP (signal recognition protein), SRP receptor protein, and transcolon apparatus; transcolon apparatus; GTP
|
|
|
to what does SRP bind?
|
signal peptide
|
|
|
is GTP needed to open translocon apparatus? if not, how it is used?
|
no; used to dissociate SRP and receptor from translocon.
|
|
|
signal peptide is eventually cleaved by which protein?
|
signal peptidase
|
|
|
is the folding of a protein into secondary, tertiary, and quartenary structure energetically favorable or unfavorable?
|
favorable (spontaneous)
|
|
|
what kind of proteins are sometimes involved in the proper folding of a protein?
|
chaperone proteins
|
|
|
which ER, rough or smooth, has a lamellated appearance, like pita bread?
|
rough
|
|
|
what is the main role of the RER?
|
protein synthesis
|
|
|
what is the principle type of protein found in RER (not a protein product but part of RER function)?
|
chaperone proteins
|
|
|
which post-translational modification is performed in the RER?
|
N-linked glycosylation
|
|
|
which, the RER or smooth ER, exhibits a tubuvascular morphology?
|
Smooth ER
|
|
|
what are 5 cellular processes in which SER plays a very important role and in which kind of cells do these processes take place?
|
1) glycogen metabolism (liver/muscle)
2) detox via p450 complex (liver) 3) Ca storage (skeletal/cardiac muscle) 4) lipid metabolism (all cells) 5) steroid metabolism (adrenal glands, ovary, testes) |
|
|
following protein synthesis and glycosylation in the RER, where does the nascent protein travel?
|
Golgi apparatus
|
|
|
with what protein are vesicles leaving the RER coated with, as they are shipped to the Golgi?
|
COPII
|
|
|
at which end of the Golgi do proteins arrive from the RER?
at which end are they shipped off? |
cis-Golgi; trans-Golgi
|
|
|
what is the name for the 'distribution center' in the Golgi?
|
trans-Golgi network (TGN)
|
|
|
what kind of system is most likely used for getting proteins to their extracellular targets?
|
receptor/ligand-like interactions
|
|
|
how do protein vesicles travel from RER to cis-Golgi network?
|
via microtubules with motor proteins
|
|
|
with what are vesicles from Golgi to ER coated?
|
COPI
|
|
|
with what are vesicles from ER to Golgi coated?
|
COPII
|
|
|
what information does an abundance of mitochondria give us about a cell?
|
high metabolic requirements, active cell.
|
|
|
what is the average width of mitochondria?
|
.5 micons
|
|
|
how many domains do mitochondria have? what are they?
|
4; outer membrane, inner membrane, intramembrane space, matrix
|
|
|
what is the name for the folds formed by the inner mitochondrial membrane?
|
cristae
|
|
|
how many moles of ATP are produces from 1 mole of glucose?
|
36-38 moles
|
|
|
are mitochondria capable of dividing?
|
yes, independent of cell cycle.
|
|
|
what is the average diameter of a peroxisome?
|
.2-1 microns
|
|
|
in which kind of oxidation are peroxisomes involed?
|
fatty acid (beta) oxidation
|
|
|
where are small fatty acids metabolized?
|
mitochondrion
|
|
|
where is the difference between fatty acids metabolized in mitochondrion and peroxisome?
|
mitochondrion metabolizes smaller FA's and peroxisome oxidized larger FA's
|
|
|
which class of enzymes plays an active role in the breakdown of fatty acids and peroxides in the peroxisome?
|
catalases and oxidases
|
|
|
which marker in peroxisomes is useful in distiguishing the organelle from others in the cell?
|
catalases
|
|
|
which important phospholipid, which is found in myelin, is produced in the peroxisomes?
|
plasmalogens
|
|
|
proteasomes are the sites of destruction for which molecules?
|
proteins
|
|
|
with what are materials destined for proteasomes tagged?
|
ubiquitin
|
|
|
why do many peroxisomal diseases often lead to neurological disorders?
|
defects in plasmalogen production can have a profound impact on the workings of the nervous system.
|
|
|
do proteasomes degrade primarily endogenous or exogenous proteins? by what are the others digested?
|
endogenous; lysosomes
|
|
|
how many proteasomes are present in the average cell? how many proteases are present in each of these proteasomes?
|
20-30k proteasomes; 30 proteases.
|
|
|
hematoxylin has a positive or negative charge? is it basic or acidic? what color does it stain?
|
positive; basic; purple/blue
|
|
|
acidophilic substances are substances that have an affinity for which stain?
|
eosin
|
|
|
what are 3 general functions of organelles in animal cells?
|
1) congregate enzymatic reactions
2) segregate competing metabolic processes 3) separate harmful products from rest of cell |
|
|
RER
|
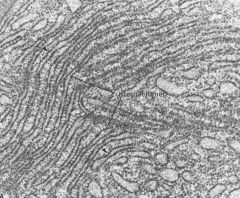
what is the organelle pictured here?
|
|
|
polysomes
|
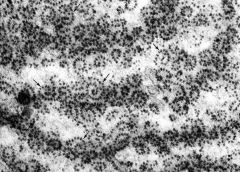
what is depicted in this image?
|
|
|
what are the 3 possible destinations for proteins produced in the RER and processed in the Golgi?
|
secretory vesicle, membrane vesicle, storage vesicle (lysosome)
|
|
|
which of the cytoskeletal element are important in the integrity of RER and Golgi?
|
microtubules
|
|
|
Golgi apparatus
|
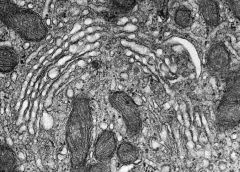
which organelle is dipicted in this image?
|
|
|
inactive due to lack of vesicles at TGN.
|
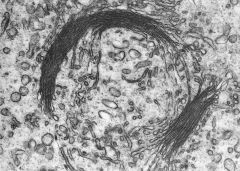
is this image an active or inactive form of Golgi? how do you know?
|
|
|
trans-Golgi Network (TGN)
|
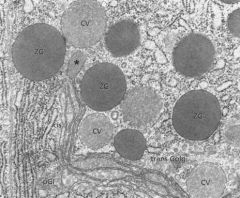
which part of the cell does this image represent?
|
|
|
what is the difference between constitutive and non-constitutive protein formation?
|
constitutive proteins are released into extracellular environment in a non-discriminatory fashion. non-constitutive proteins wait for a signal to release to the outside.
|
|
|
SER
|
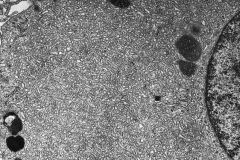
which organelle is depicted here?
|
|
|
are all organelles inherited from the mother's egg or father's sperm?
|
mother's egg
|
|
|
which organelles are involed in the detox of ethanol, phenol, and formaldehyde?
|
peroxisomes
|
|
|
what percentage of all fatty acids are metabolized by mitochondria?
|
75%
|
|
|
how many enzymes are present in the average peroxisome?
|
around 50
|
|
|
what is the name for the disorder in which an organelle's function affects neurological function? which organelle is damaged in this case?
|
Zelwegger's syndrome; peroxisome
|
|
|
what is the width of a ribosome?
|
25nm
|
|
|
via which pathways are Golgi vesicles marked for export to lysosomes?
|
mannose-6-phosphate pathway (m6p)
|
|
|
which products are created de novo in the Golgi?
|
proteoglycans
|
|
|
what percentage of misfolded proteins are tagged with ubiquitin?
|
90%
|
|
|
which disease linked to emphysema is linked to protein cloggage in the ER?
|
a-1 anti-trypsin deficiency
|

