![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
DNA gets packaged into _____ then chromosomes
|
chromatin
|
|
|
which chromatin is actively transcribed DNA and appears light in light micrographs and EM?
|
euchromatin
|
|
|
>46 chromosomes is called
|
aneuploidy
|
|
|
go through chromatin packaging
|
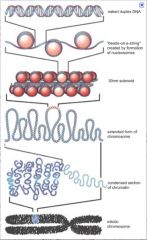
|
|
|
_____ is the site of ribosomal RNA synthesis and consists of the tips of chromosomes
|
nucleolus
|
|
|
T or F. The nucleolus can contain one or more nuclei
|
True
|
|
|
______ are intermediate filament proteins that tether chromosomes to the nuclear membrane
|
lamins (nuclear matrix)
|
|
|
Progeria syndrome (accelerated aging)
Limb girdle MD type 1B are all caused by mutations in the |
LMNA gene
|
|
|
what are the functions of the mitochondria
|
regulation of cyto Ca2+
ATP synthesis TCA cycle fatty acid cycle urea cycle apoptosis |
|
|
def. multiple ribosomes attached to a single RNA
|
polysomes
|
|
|
what are the functions of teh RER
|
synthesis of proteins for export, antibodies, growth factors, digestive enzymes
modification of proteins especially N linked glycosylation |
|
|
name the functions of the SER
|
phospholipid synthesis
cholesterol synthesis detox steroid hormone synthesis regulation of calcium conc |
|
|
name the functions of the GA
|
packaging and concentrating secretory proteins
trimming and adding oligosacs proteolytic cleavage of proproteins processing and sorting of lysosomal enzymes lipoprotein packaging sulfating proteins phosphorylating proteins |
|
|
what are four means of vesicular traffic
|
exocytosis
endocytosis transcytosis lysosomal processing |
|
|
def. secretory vesicles contain proteins ready for export to the extracellular environment. Secretio may be either constitutive or regulated
|
Trans golgi network TGN
|
|
|
what does clathrin coat
|
regulated exocytotic vesicles
receptor mediated endocytotic and lysosomes |
|
|
_____ and _____ mediate docking and fusion of vesicles
|
SNARES and SNAPS
these facilitate fusion and regulate correct targeting of vesicles that leave the TGN |
|
|
do snares or snaps have an anchor in the membrane bilayer
|
SNARES
|
|
|
______ is a process whereby molecules on the outside of the cell are taken into the cell by invagination and pinching off of parts of the plasma membrane
|
endocytosis
|
|
|
name some types of endocytosis
|
RME
potocytosis phagocytosis pinocytosis transcytosis |
|
|
left off on slide
|
18
|
|
|
t or f. RME is highly specific
|
TRUE
|
|
|
definition. vesicles with proton pumps in their membranes
|
endosomes
|
|
|
explain how endosomes work
|
fuse with vesicles contianing receptor ligand complexes... drop pH causing release of ligands from receptor
|
|
|
what mediates docking and fusion of vesicles
|
SNARES
SNAPS |
|
|
definition. transmembrane proteins that mediate fusion of cellular transport vesicles with the cell membrane or with a target compartment such as a lysosom
|
SNARE
|
|
|
what interacts with SNARES to facilitate fusion?
|
SNAPS
|
|
|
give several examples of vesicular traffic
|
exocytosis
endocytosis transcytosis lysosomal processing |
|
|
what does consitutive mean?
|
unregulated membrane fusion (for example in TGN)
|
|
|
t or f. secretory vesicles contain proteins ready for exprot to the extracellular environ. Secretion may be either consitutive or regulated
|
TRUE
|
|
|
what is coated with clathrin?
|
exocytotic vesicles
endocytotic vesicles lysosomes |
|
|
______ and _____ mediate docking and fusion of vesicles
|
SNARES
SNAPS |
|
|
what are four routes the ligands and receptor may take
|
receptor recycles, ligand degraded
rec. recycles, ligand recycles rec. degraded, lig degraded receptore transported, ligand transported |
|
|
describe RME of LDL
|
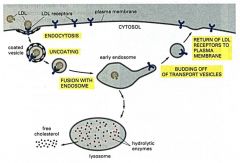
|
|
|
Potocytosis is like RME except
|
caveolin instead of clathrin
don't fuse with endosomes or any organelle |
|
|
_______ is a type of receptor-mediated endocytosis in which small molecules are transported across the plasma membrane of a cell
|
potocytosis
|
|
|
_____ uses GPI anchored membrane proteins and vesicles that stay close to the plasma membrane
|
potocytosis
|
|
|
def. complement and immunoglobulins coat an invading microorganism allowing it to be recognized by receptors in a process called opsonization
|
phagocytosis
|
|
|
Phagosomes fuse with ______ to digest a microorganism
|
lysosome
|
|
|
_______ is the non specific uptake of fluid in vesicles
|
pinocytosis
|
|
|
in ________ a loaded endocytotic vesicle is transported through th ecell where exocytosis releases its contents on the opposite side
|
transcytosis
|
|
|
how do babies get abs from mom?
|
transcytosis
|
|
|
Proteins to be exported interact directly with acidic phopholipids of the plasma membrane, disrupting the membrane, and allowing them to escape the cell This is called...
|
non classical secretion
|
|
|
def. covalent addition of an oligosac to a protein
|
glycosylation
|
|
|
def. precipitate divalent cations in mitochondrial matrix
|
matrix granules
|
|
|
def. intermediate filament proteins that link chromosomes to the nuclear envelope
|
nuclear lamins
|
|
|
def. nuclear region contianing rDNA
|
nucleolus
|
|
|
def a chain of ribosomes translating mrna
|
polysome
|
|
|
def. vesicles that move between organelles within the cell to transfer proteins in the vesicular transport pathway
|
transfer vesicle
|
|
|
what is the functional unit of a chromosome
|
gene
|
|
|
what is the function of the nucleoskeleton
|
scaffolding for functions including transcription, repression of transcription, and DNA replication
|
|
|
a key component of the nucleoskeleton called ______ is a dense meshwork of intermediate filament proteins that line the nuclear envelope
|
lamins
|
|
|
what happens to the nuclear envelope during mitosis
|
lamins are phosphorylated and nuclear envelope is destabilized and recued to small vesicles. dephosphorylation at the end of mitosis leads to reformation of the envelope and nuclear lamins around the chromosomes
|
|
|
______ ______ is made up of proteins some of which contain molecular motors for directed transport of other molecules within the nucleas
|
actin nucleoskeleton
|
|
|
There are eight different laminopathies resutling from mutations withint the ____ gene
|
laminA or LMNA
|
|
|
disease affecting striated muscle and peripheral nerves, skeletal and fat development and homeostasis, premature aging.... all these diseases are examples of
|
laminopathies
|
|
|
what is the function of the nucleolus
|
ribosomal DNA is transcribed into rRNA
|
|
|
what is the function of nuclear pores
|
allow movement of molecules between the nucleoplasm ad the cytoplasm
|
|
|
what guards the nuclear pore
|
nuclear pore complex
|
|
|
how big is the nuclear pore hole?
|
10nm
|
|
|
name the functions of the mitochondria
|
ATP synthesis
cytoplasmic Ca2+ conc TCA fatty acid cycle urea cycle cell death |
|
|
where would you find the mitochondrial DNA, mitochondrial tRNAs, and ribosomes?
|
all in the mitochondria itself@
|
|
|
what happens inside the mitochondria if Ca2+ level is to high?
|
ATP synthesis stops
calcium granules precipitate and form |
|
|
what is the "typical" size of the mitochondria
|
.5-1 microns in diameter and 3-10 in length
|
|
|
where might you find high levels of mitochondria?
|
kedney for pumping
neurons for transport along microtubules and pumping ions across membranes |
|
|
describe the sizes of the ribosomal subunits
|
18S rRNA and 30 proteins in the small subunit
28S and 5.8S rRNA and 5S rRNA and 50 proteins |
|
|
what transcribes the ribosomes as a single transcript in the nucleolus
|
RNA pol I
|
|
|
the ___ rRNA is NOT transcribed in the nucleolus and is transcribed by a different RNA pol III
|
5S
|
|
|
how do the ribosome subunits know to come together
|
primed for protein synthesis by binding of initiator tRNA to the small subunit
|
|
|
______ _______ are extremely prominent in some of teh nuerons you will see in the HA
|
nissl bodies
|
|
|
all SER proteins are found in the ____ but not all ___ proteins are found in th eSER
|
RER RER
|
|
|
why are the RER and SER continuous?
|
integral proteins of the SER are made on the ribosomes of the RER
|
|
|
name the functions of the RER
|
synthesis of membrane proteins
secreted proteins proteins destined for th elumens of various organelles such as peroxisomes, lysosomes and GA |
|
|
name the functions of the SER
|
phospholipid synthesis, cholesterol snthesis, steroid hormone synthesis, detox, and regulation of Ca2+
|
|
|
why might the liver have high amounts of SER
|
detox
|
|
|
how does the GA help proteins find their address
|
pattern of added sugars through N linked glycosylation
|
|
|
how many cisternae are in a GA stack
|
4 to 8
|
|
|
what is inlcuded in the TGN
|
tran face of GA
associated vesicles |
|
|
what is thicker the trans or cis face of the golgi
|
trans
|
|
|
what vesicles are always found in association with the golgi complex especially in th eperimeter dilations of the cis face
|
transfer vesicles which carry protein from the RER to the golgi stacks
|
|
|
once contents of the large vesicles in the trans face of the TGN, these structures are sometimes called ____ _____
|
zymogen granules
|
|
|
what are nissl bodies
|
RER of neurons
|

