![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
geography of Mesopotamia
|
- "land between the rivers" (between the Tigris and Euphrates)
- part of the Fertile Crescent - because the land was so rich, people became farmers |
|
|
|
Fertile Crescent
|
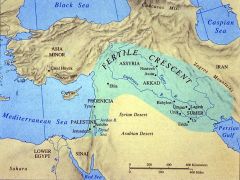
|
W: Mediterranean Sea
SE: Persian Gulf NE: Zagros Mountains S: Syrian Desert |
|
|
organization of ancient Sumerian society
|
- many independent city-states, each with its own leaders and government
- kings were believed to be chosen by gods (e.g. Gilgamesh) - developed many laws to facilitate the creation of irrigation systems, ziggurats, public buildings, etc |
|
|
|
Gilgamesh
|
- ruled Uruk, in Sumer, between 2700 B.C. and 2500 B.C.
- wanted to learn the meaning of life, traveled widely to find out - stories and legends were built up around his travels (The Epic of Gilgamesh) |
|
|
|
Assyrian Empire
|
- Assyrian empire first conquered northern Mesopotamia all the way to the Mediterranean Sea (1000 B.C., King Adad-Nirari)
- then Assyrian empire conquered Babylonia (745 B.C., King Tiglath-Pileser) - but their rule was unpopular, Chaldeans of Babylonia sacked the king (627 B.C.) |
|
|
|
Babylonian Empire
|
- Chaldeans of Babylonia sacked the Assyrian king and established Babylonian empire (627 B.C.)
- Nebuchadnezzar expanded Babylonian empire into Syria and Phoenicia (605 B.C. to 562 B.C.) - Cyrus the Great, king of Persia, invaded and conquered Babylonia (550 B.C.) |
|
|
|
Nebuchadnezzar
|
- king of Babylonian Empire 605 to 562 B.C.
- expanded empire into Syria and Phoenicia - best known for the hanging gardens of Babylon - attacked and burned Jerusalem sending thousands of Jews to Babylonia as slaves |
|
|
|
ziggurat
|
- largest building constructed by ancient Sumerians
- huge, pyramid-shaped, mud-brick temple - at the top was a shrine to the city's special god |
|
|
|
Enlil
|
- main god of ancient Sumerians
- controlled the wind, storms, and rain |
|
|
|
Ea
|
- second most important god of ancient Sumerians
- controlled the waters - god of wisdom |
|
|
|
inventions of ancient Sumerians
|
- writing (cuneiform - wedge shaped symbols written onto wet clay tablets)
- irrigation - wheel - sailboats - measurement: iku (land unit corresponding to our acre), quart, hour and minute - concept of place value |
|
|
|
class in Sumer
|
- upper: king, priests, other important people
- middle (largest): artisans and merchants - low: slaves b/c of war or as a form of punishment |
|
|
|
Code of Hammurabi
|
- laws created by Hammurabi that covered all areas of conduct
- Hammurabi united lower Mesopotamia into Babylonia in 1760 B.C., ruled Mesopotamia as one large empire - part of Babylonian empire |
|
|
|
Sargon of Akkad
|
- said to be the son of sheepherders who spoke Akkadian
- founded the city of Akkad and conquered northern Mesopotamia and other lands - said to have created the world's first empire (around 2500 B.C.) |
|

