![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cytoplasm |
Interior content of all cells. |
The substance which holds all organelles in a cell. |
|
|
Phospholipids |
Two fatty acid tails with one phosphate head. |
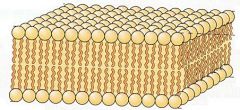
Major lipid in all cell membranes. |
|
|
Phospholipid bilayer |
Organization of phospholipids. |
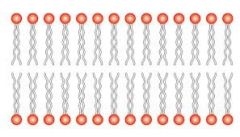
Structure within the cell membrane; universal component. |
|
|
Polar |
A molecule with a partial positive charge and a complementary negative charge. |
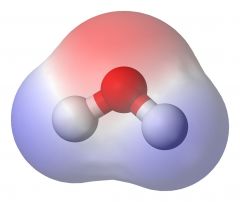
H2O is one of these. |
|
|
Nonpolar |
These molecules have equal sharing of electrons, and the charges are equal. |
CO2 is one of these types of molecules. |
|
|
Transport Proteins |
Proteins used to pass necessary polar molecules and ions through the membrane. |
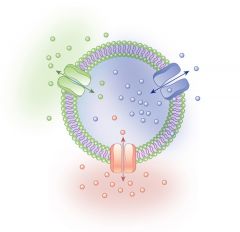
Within the bilayer, these are important in delivering nutrients to the cell. |
|
|
Selective permeability |
A type of membrane that allows certain materials by active or passive transport. |
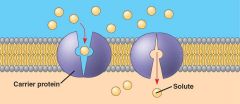
Also referred to as "semi". |
|
|
Glycoproteins |
A Receptor protein; protein + sugar |
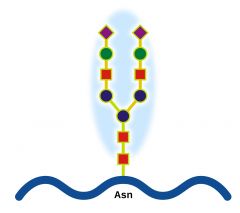
A protein that monitors the cell membrane and reacts with hormones. |
|
|
Glycolipids |
A receptor lipid; lipid + sugar |
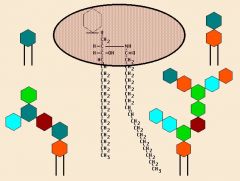
Lipids that provide energy; cellular recognition as markers. |
|
|
Fluid Mosaic Model |
Flexible structure of the cell membrane. |
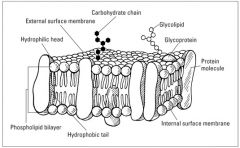
Phospholipid bilayer, transport proteins, receptors. |
|
|
Diffusion |
The process of molecules intermingling. |
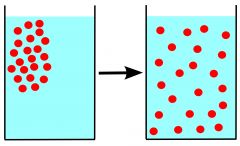
A mixing of certain materials. |
|
|
Concentration gradient |
A difference in the concentration of particles across an area. |

Imbalance in amount, across an area. |
|
|
Osmosis |
The movement of particles through a semi-permeable membrane. |
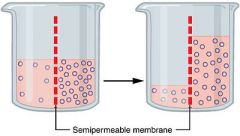
Passing of molecules in order to equalize both sides. |
|
|
Turgor |
The state of tension within the cell |

Pressure on the cell caused by osmosis. |
|
|
Isotonic |
Movement of water in and out of a cell is equal. |
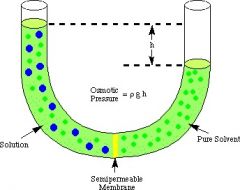
"Equilibrium" of water movement; even number in and out. |
|
|
Hypotonic |
A cell in a hypotonic solution has less water flow outward, but more on the uptake. |
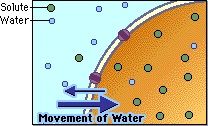
Cell bloating. |
|
|
Hypertonic |
A hypertonic solution has a higher flow outward and less on the uptake. |

Cell dehydration. |
|
|
Passive Transport |
The movement of molecules across the cell membrane without the use of energy. |
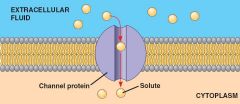
Small polar and nonpolar molecules use this to get in the cell. |
|
|
Active Transport |
The passage of molecules through the membrane using transport proteins. |
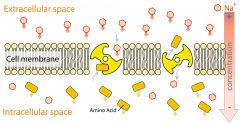
Larger polar molecules and ions use this to cross into the cell. |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
A type of transport that uses no energy to pass larger molecules and ions across the membrane. |
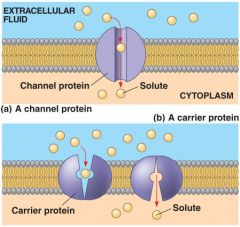
Spontaneous transport. |
|
|
Endocytosis |
Form of active transport where the cell transports molecules into itself by engulfing it. |
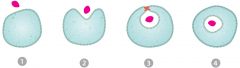
An energy using process; IN |
|
|
Exocytosis |
Exocytosis is an active transport in which a cell pushes molecules out using energy. |
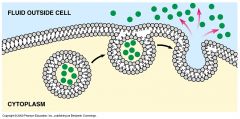
Excretion of molecules by the cell; OUT |

