![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
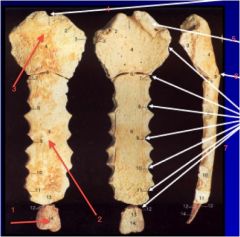
Label parts and also explain what the sternum can clinically be used for...
|
Used for bone marrow biopsy because it has hemapoietic marrow, also split during surgery to access lungs
1. Manubrium 2. Body 3. Xiphoid process 4. Suprasternal notch 5. Clavicular notch 6. Sternal angle (angle of Louis) 7. Costal Notches |
|
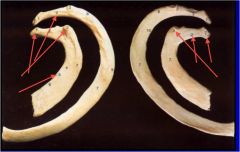
a. Label parts with arrows...
b. Which ribs are they? c. Which ribs are most likely to be fractured? What could the broken ends of the ribs cause? |
1. Head- articulates with corresponding vertebral bodies
2. Neck 3. Tubercle- 5. Scalene tubercle and ridge b. 1st and 2nd c. middle ribs, could causepneumothorax and lung or spleen injury |
|
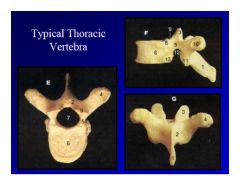
|
1. Spinous process
2. Lamina 3. Superior articular facet 4. Transverse process 5. Pedicle 6. Body 7. Vertebral canal 8. Superior costal facet 9. Superior vertebral notch 10. Costal facet on transverse process 11. Inferior articular facet 12. Inferior vertebral notch 13. Inferior costal facet |
|
|
What could supernumerary ribs cause problems with and what specific problems could occur?
|
1. Extra cervical- neural and circulatory problems due to closeness to brachial plexus and subclavian A.- als cause thoracic outlet syndrom
2. Extra lumbar- confusion during radiograph readiings |
|
|
Describe the primary and secondary cartilagenous joints.
Describe the the two main joints of the sternum... |
Primary- synchondrosis (bone-cartilage-bone)- usually temporary like between diaphysis and epiphysis
Secondary- strong moveable joints united by fribrocartilage 1. Manubriosternal (2ndary cartilagenous joint)- (at sternal angle) 2. xiphoisternal (primary cartilagenous joint)- articulates with sternal body |
|
|
What are the joints between the
1. ribs and the sternum, 2. ribs and vertebra, 3. tubercle or neck of rib to transverse process of vertebra, 4. ribs and costal cartilages? |
1. 1-7 (synchondrosis "primary") between sternum and 7 costal cartilages
2. Costovertebral- (synovial planar) head of rib to vertebral body 3. costotranverse- (synovial planar)- i. lateral costotransverse- tubercle to transverse process ii. superior costotransverse- neck to transverse process (one vertebral segment above it) |
|
|
Where does the head of each rib articulate with? Specifically if you had rib 2 which vertebral spots would you see it attach to?
|
- head of each rib articulates with inferior costal demifacet of superior numeric thoracic vertebral segment and the superior demifacet of the same numbered thoracic vertebra
- second rib head articulates with inferior demi facet of T1 and body of T2 and superior demi facet of T2 |
|
|
What types of movement occur at the costovertebral joint?
What do they function to do? |
Two forms of movement to increase thoracic volume and decrease pressure
1. Bucket handle- elevation of lateral part of rib, increases transverse diameter of thorax 2. pump handle- elevation of sternal part of rib to increase post/ant diameter 2. Pump handle |
|
|
Where do dislocations and separations of the ribs occurs?
What are the interchondral joints? |
1. Dislocation- sternocostal joint
2. separation - costochondral joint Joints between ribs 6/7 7/8 8/9 and 9/10 as they join a common costal cartilage all but 9/10 are planar synovial, 9/10 is fibrous |
|
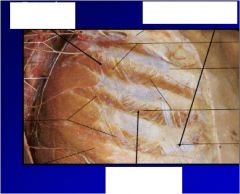
|
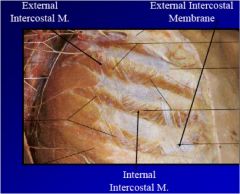
|
|
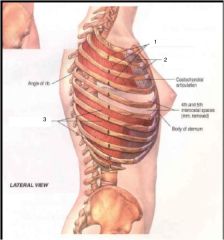
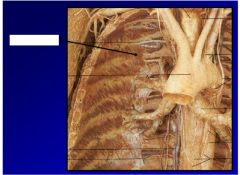
Label... parts
what is action and innervation |
1. external intercostal muscles- intercostal nerve, elevates rib in inspiration
2.external intercostal membrane 3. internal intercostal muscles- intercostal nerve- depress ribs, except intercondral part elevates ribs |
|
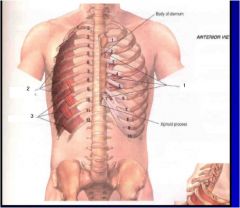
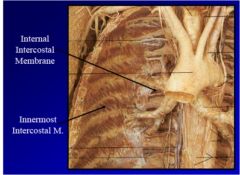
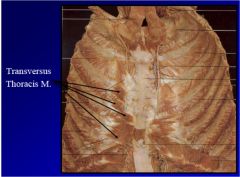
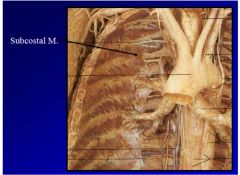
What the muscles and say innervation and actions
|
1. transverse thoracic muscles- intercostal nerve depresses ribs
2. innermost intercostal muscle- intercostal nerve, elevates ribs 3. subcostal muscle- intercostal nerve, elevates ribs, travels more than one rib space |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|

