![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Avoidance
|
A technique of risk control based on stopping or starting an activity, thereby eliminating the possibility of future loss from the activity.
|
|
|
************************************
Business Continuity Management ************************************ |
************************************
A 6-step method for identifying threats to a business and then managing them in a systematic way so that business will not be interrupted. ************************************ |
|
|
Disaster Recovery Plan
|
A post-loss plan to ensure key resources and backup plans are available to support continued operation of the business in case of emergency.
|
|
|
Diversification
|
A risk control method that spreads loss exposures across several markets, products, projects, or regions.
|
|
|
Duplication
|
A risk control method that keeps backups or copies of an organization's crucial information or property in reserve.
|
|
|
Life Safety
|
The aspect of fire safety that deals with the minimum building construction, design, maintenance, and operation requirements needed to give building occupants a safe exit during a fire.
|
|
|
Loss Prevention
|
A technique of risk control that reduces the frequency of a particular loss.
|
|
|
Loss reduction
|
A technique of risk control that reduces the severity of a particular loss.
|
|
|
Risk control
|
A conscious decision not to act in order to reduce the frequency, severity, or unpredictability of losses.
|
|
|
Separation
|
A technique of risk control that disperses a particular asset or operation over several locations while regularly relying on that asset or activity as part of the organization's resources.
|
|
|
A given risk control measure is risk control only with respect to _____________.
Give an example |
One or more SPECIFIED exposures.
Example: Installing fire-supression sprinklers may control a fire but will not control embezzlement |
|
|
Action that is a good risk control for one exposure may _____________________.
Give an example |
Increase the frequency or severity of losses from another exposure
Example: Equipping employees with portable oxygen tanks increases the chances for fire associated with storing oxygen under pressure. |
|
|
************************************
What are the 6 main techniques of Risk control? ************************************ |
************************************
1. Avoidance 2. Loss prevention (frequency) 3. Loss reduction (severity) 4. Separation 5. Duplication 6. Diversification ************************************ |
|
|
What is the only complete risk management technique that requires no further risk control or risk financing measures?
|
Avoidance
|
|
|
Applications of which risk management technique are limited, and why?
|
Avoidance
*Just being an organization creates loss exposures that can't be avoided (ex: you avoid property loss only by avoiding property ownersip) *Certain narrow exposures can be avoided, but avoiding one loss exposure can create another |
|
|
You should consider avoidance as a risk control method only when...
|
the expected value of the losses from an activity outweigh the expected benefits.
|
|
|
Loss prevention may not affect ____________.
|
Loss severity
|
|
|
What is the basis of current risk control theory?
|
Heinrich's domino theory. It states that workplace accidents are the result of a chain of factors, and removing one factor can prevent injury
|
|
|
What are the 5 factors (dominoes) of Henrich's theory?
|
1. Ancestry and social environment
2. Personal fault 3. Unsafe act/hazard 4. Accident 5. Injury resulting from accident |
|
|
What are the 2 categories of Loss reduction?
|
1. Pre-loss measures - applied before loss, reduces the amount of property affected by an event. Can also reduce loss frequency (example: driving an ambulance at a lower speed in nonemergencies)
2. Post-loss measures - after loss, stops spread of loss. Focus on emergency procedure, legal defense and rehab activities (ex: fire detection system). Disaster Recovery plans come into play here. |
|
|
Which risk control method: Separation or Duplication, is more practical in terms of cost? Why?
|
Separation is more practical in terms of cost because units are kept in daily use, not on standby
|
|
|
Unlike other risk control techniques that deal with hazard risks, _____________ deals mainly with business risk.
|
Diversification
|
|
|
4 key risk control goals
|
Memory Aid: ICEE
1. Implement effective, efficient risk control methods 2. Comply with legal requirements 3. Encourage life safety 4. Ensure business continuity |
|
|
How do we decide which risk control methods are efficient?
|
Efficient measures are those that cost the least and are still effective.
|
|
|
List the disadvantages of using cash flow analysis when selecting risk control measures
|
1. It's hard to estimate future cash flows
2. Assumptions made are sometimes weak 3. Non-$$ related goals might not be considered |
|
|
Business continuity management should meet what 2 primary risk management program post-loss goals?
|
1. Survival
2. Continuity of operations |
|
|
************************************
Discuss externality ************************************ |
************************************
A risk control measure that controls one type of loss exposure may affect the frequency and severity of other loss exposures. This is called externality. ************************************ |
|
|
Applying Risk control techniques to specific loss exposures (table)
|
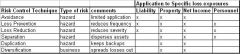
|
|
|
Any risk control technique that controls any loss exposure will also indirectly affect ____________.
|
Net income loss exposure
|
|
|
What are some loss prevention methods that can be applied to control personnel loss exposures?
|
Education
Training Safety |
|
|
Positive externality
|
When a risk control measure for one loss exposure reduces the severity or frequency of another loss exposure (ex: random drug testing to reduce frequency of employee injury may also reduce workplace theft)
|
|
|
Negative externality
|
When a risk control measure for one loss exposure increases the severity or frequency for another loss exposure (ex: installing a sprinkler system can reduce fire loss but increase water dmg losses if they leak)
|
|
|
What types of risk control measures can apply to property loss exposures?
|
All...because there are so many different type s of property.
|
|
|
What are the 4 main types of loss exposures?
|
1. Property (tangible/intangible)
2. Personnel 3. Liability 4. Net income |
|
|
In commercial properties, what method is used to analyze property loss exposures?
|
COPE method:
*Construction *Occupancy *Protection *Environment |
|
|
What types of risk control measures can apply to net income loss exposures?
|
*Separation and duplication will directly reduce severity of net income losses
*Because net income loss exposures are an indirect result of other types of loss exposures, the use of any risk control measures will indirectly reduce net income loss exposures |
|
|
************************************
What are the 6 steps of Business Continuity management? ************************************ |
************************************
*Count The Enemy Dead, Do More!* 1. ID Critical functions 2. ID Threats to these functions 3. Evaluate the effect of the threats on the functions 4. Develop a business continuity strategy 5. Develop a business continuity plan 6. Monitor the process and revise it as necessary ************************************ |
|
|
************************************
What are the key attributes of a good business continuity plan? ************************************ |
************************************
*Clear and easy to understand *Copies of plan given to all necessary personnel *Training and drills shoudl be conducted ************************************ |
|
|
Business continuity plans typically include these 6 areas
|
1. Strategy to manage the crisis
2. Rules and duties of key personnel 3. Steps to prevent further damage 4. Emergency plan to deal with life and safety issues 5. Business recovery plan to deal with property, process and product loss 6. Access to counseling |
|
|
************************************
What are the risk control techniquest for liability losses? ************************************ |
************************************
************ALL******************* 1. Avoid the activity that creates the loss exposure 2. Loss Prevention - decrease likelihood of loss occurring 3. Loss reduction - minimize effects. ************************************ |
|
|
************************************
Positive Externality ************************************ |
************************************
When a risk control measure implemented for one loss exposure reduces the frequency or severity related to another loss exposure ************************************ |
|
|
************************************
Negative Externality ************************************ |
***********************************
When a risk control measure implemented for one loss exposure increases the frequency or severity related to another loss exposure ************************************ |

