![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Fixed costs
|
Are those costs that do not vary with changes in output
|
Are also known as indirect costs or overheads
|
|
|
Examples of fixed costs
|
rent insurance premiums, interest on loans and depreciation
|
|
|
|
Depreciation
|
Is rhe fall in value of the existing stock of capital through wear and tear
|
|
|
|
Variable costs
|
Are incurred by a firm when it purchases the factors such as land, labor and raw materials
|
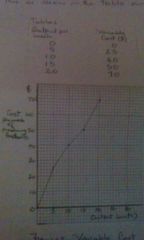
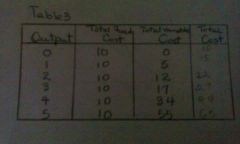
Total variable costs
|
|
|
Variable costs are zero when output is zero and rises when output rises
|
|
|
|
Examples of things that are both fixed and variable costs
|
Electricity, gas, water and the telephone
|
|
|
|
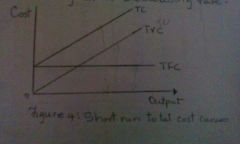
Total costs
|
The sum of fixed and variable costs at each level of output
TC=TFC+TVC |
|
|

|
|
|
|
Total costs
|
I have nothing to say
|
|
|
|
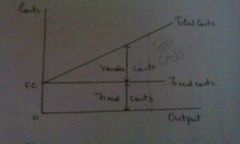
The difference between variable and fixed costs
|
Variable costs vary with the level of output, fixed costs don't
|
|
|
|
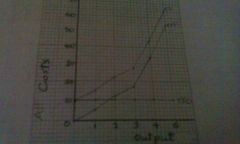
|
|
|
|
Average cost
|
AC=total cost / number of units produced
|
Average total cost (ATC)
|
|
|
The average cost curve is usually u shaped. Why
|
Average fixed cost is falling as output levels increase and average variable costs falls initially as the firm is able to produce more efficiently. However inefficiencies may arise later in the production process
|
|
|
|
The optimum point
|
The lowest point on the acc and shows the point at which the business is combining its resources most efficiently
|
|
|
|
Marginal cost
|
Is the cost of producing an additional unit of output.
It marginal cost =change in tc/change in quantity |
|
|
|
Production
|
Is the transformation of land, labor, capital and enterprise into good and services
|
|
|
|
Long run
|
The period of time when all factors of production in the production process are available
|
|
|
|
Short run
|
The period of time when it isn't possible to vary the quantity of all the factors of production used in the production process
|
|
|
|
Determinant of supply
|
The price of the good itself, the price of factors of production, taxes And subsidies
|
|

