![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a cell?
|
- Smallest structural & functional unit of an organism- Basic unit of life- usually too small to be seen without light microscope
|
|
|
Prokaryotic cells
|
- 'before nucleus'- DNA not organised into Chromosomes
|
|
|
Eukaryotic cells
|
- 'true nucleus'~ 10x size of prokaryotic cell- membrane bound compartments (e.g. mitochondria)
|
|
|
3 main prokayotic (bacterium) shapes
|
1. Spirilli (spiral)2. Bacilli (rod)3. Cocci (sphere)(Also Stella, star-shaped, and Haloarcula, rectangular)
|
|
|
Consists of ________, a polymer consisting of ___ and ___ and short chains of __________.
|
peptidoglycan, NAG, NAM, amino acids.
|
|
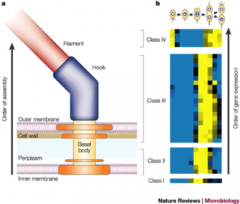
This shows?
|
Flagellum assembly
|
|
|
What are the two main types of eukaryotic cells?
|
Animal cells and plant cells
|
|
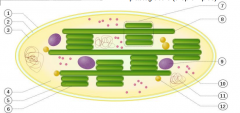
what are the long green tubes in this mitochondria?
|
A thylakoid is a disc in the chloroplast with the granum being the name of a stack of thylakoids
|
|
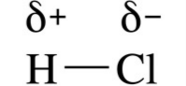
what does this show?
|
A permanent dipole (stronger than Van der waals' forces)
|
|
|
Ketones have ________ dipole- dipole interactions and __________ points
|
lower, boiling
|
|
|
The atomic number equals...
|
the number of electrons
|
|
|
Electrophile
|
Reagent attracted to electrons (electron loving)
|
|
|
Nucleophiles
|
Nuclear loving, donates a pair of electrons in order to form a chemical bond
|
|

what is happening here?
|
Nucleophilic addition
|
|
|
Elements are made up of
|
different atoms
|
|
|
Number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus is the
|
Mass number
|
|
|
Removing electrons from an atom creates a positive or negative ion?
|
Positive
|
|
|
Adding electrons to an atom creates a positive or negative ion?
|
Negative
|
|
|
Acids and bases are described as a __________ pair
|
conjugate (conjugate refers to an acid and base that differ from each other by a proton- is reversible)
|
|
|
A conjugate acid _______ H+
|
donates
|
|
|
A conjugate base ________ H+
|
accepts (it contributes a lone pair of electrons to the dative covalent bond with the proton)
|
|
|
Most reactions of acids...
|
take place in water
|
|
|
(Water is) amphoteric
|
Can act like an acid or a base
|
|
|
Concentration of an acid is
|
the amount (moles) dissolved in 1dm-3 of solution
|
|
|
Redox reductions
|
involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another (spontaneous generally exothermic)
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
loss of electrons
|
|
|
Reduction
|
gain of electrons
|
|
|
Redox reaction
|
Where electrons are transferred from one atom to another
|
|
|
Oxidising agent
|
a reagent which increases the oxidation number of an element of a given element. These reagents are called oxidants
|
|
|
Reducing agent
|
a reagent that lowers the oxidation number of a given element. These reagents are also called reductants
|
|
|
Fe2+ (iron) transports _________
|
oxygen
|
|
|
Mg2+ (Magnesium) for _________ & _________ function
|
muscle & nerve
|
|
|
K+ (Potassium) transmission of _______ _________ & _________ __________
|
nerve impulses & muscle function
|
|
|
Ca2+ (Calcium) formation of _________ and _______
|
bone and teeth
|
|
|
Na+ (Sodium) for ________ __________
|
Nerve transmission
|
|
|
3 forms of water
|
1. Solid- ice2. Liquid- water3. Gas- steam
|
|
|
3 Special properties of water
|
1. Solvent2. Cohesion3. Stabilises temperature
|
|
|
Hydrolysis reaction
|
- Water split - Water used to break bond
|
|
|
Condensation/ Dehydration reaction
|
- Combining of 2 or more molecules with the loss of water- water is released
|
|
|
Covalent bonds need...
|
a lot of energy to be broken
|
|
|
Hydrocarbons are long chains of...
|
carbon and hydrogen
|
|
|
Hydrocarbons are ________ in water
|
insoluble
|
|
|
Isomers have the same ________ _________ but different _________ formula
|
molecular formula, structural
|
|
|
The two types of isomerism:
|
1. Structural isomerism2. Stereoisomerism
|
|
|
Structural isomerism
|
Same molecular formula but different structural formula
|
|
|
Stereoisomerism
|
Same molecular formula but atoms occupy different positions in space
|
|
|
Three types of structural isomerism:
|
1. Chain isomerism2. Position isomerism3. Functional group isomerism
|
|
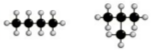
what is being shown here?
|
Chain isomerism
|
|

what is being shown here?
|
Position isomerism
|
|

what is being shown here?
|
Functional group isomerism
|
|
|
Two types of stereoisomerism
|
1. Geometrical isomerism
2. Optical isomerism |
|
|
Geometrical isomerism occurs due to...
|
restricted rotation of c=c double bonds
|
|
|
Optical isomerism occurs due to...
|
molecules having a chiral centre
|
|
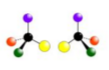
what is being shown here?
|
Optical isomerism
|
|
|
Science
|
derived from a latin term 'scientia' meaning knowledge
|
|
|
Taxonomy
|
Science of organising organisms into groups (also known as systematics)
|
|
|
Classification order:(King prawn curry, or fat greasy sausage?)
|
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
|
|
|
Chordata characteristics
|
stiff rod/ notochord running along the body
|
|
|
Vertebrata characteristics
|
Notochord is replaced by a true backbone
|
|
|
Notochord
|
Cartilaginous skeletal rod
|
|
|
Mammalia characteristics
|
Possesses fur/hair, female produces milk
|
|
|
Carnivora characteristics
|
Predators with teeth developed with a meat diet (Mainly canines)
|
|
|
Canidae characteristics
|
(Dogs) Non-retractile claws and 'long' skulls
|
|
|
Canis
|
Wolves and dogs
|
|
|
Canis familiaris
|
all domestic dogs
|
|
|
Darwin vs Creationism (3 lines of evidence)
|
1. The Earth is ancient and has experienced long-term climate change. 2. ‘Life’ is ancient and also shows evidence of long-term change. 3. These changes to ‘Life’ are coincident with those to climate and very slow.
|
|
|
Darwin & evolutionary changes
|
1. are inherited via sexual reproduction2. have an immediate (‘adaptive’) advantage3. are random as opposed to ‘driven’ or ‘directed’.
|
|
|
adaptive
|
an organism with a natural advantage
|
|
|
character
|
single structural/ behavioural feature of an organism
|
|
|
Creationism
|
belief that the universe is a product of Divine purpose
|
|
|
Deleterious
|
a natural disadvantage of an organism
|
|
|
(Bio) diversity
|
Range of species present in a location or globally
|
|
|
Extant
|
Alive today (but may also be represented in a fossil record)
|
|
|
Extinct
|
No longer alive but evidence present in a fossil record
|
|
|
Immutable
|
unchanged throughout the passage of time
|
|
|
Modern synthesis
|
development of Darwinian evolution
|
|
|
Speciation
|
Evolution of a new species
|
|
|
Transitional fossil
|
Fossil possessing characters typical of two major modern taxa
|
|
|
Taxa (sing. taxon)
|
Group of organisms sharing a set of diagnostic characteristics
|

