![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Articles of Confederation |
Plan for national government ratied in 1781 |

|
|
|
ratification |
act of official confirmation |

|
|
|
levy |
impose or raise a tax |

|
|
|
Founders (or Framers) |
people who helped create the U.S. constitution |

|
|
|
Virginia Plan |
Proposal for a two-house legislature with representation according to each state's population or wealth |

|
|
|
New Jersey Plan |
Proposal for a legilature in which each state would have one vote
|

|
|
|
Great Compromise |
agreement to establish a two house legislature, with all states having equal representationin one house and each state having representation based on its population in the other house |

|
|
|
Three-Fifths Compromise |
agreement that three-fifths of a states slave population would be counted for representation and taxation |

|
|
|
Executive Branch |
Branch of government that enforces laws |

|
|
|
Judicial Branch |
government branch that interprets laws |

|
|
|
Legislative Branch |
government department that makes laws
|

|
|
|
Checks & Balances |
The ability to every branch of government to exercise checks, or controls, over the other branches |

|
|
|
Antifederalists |
People who opposed ratification of the constitution |

|
|
|
Federalists |
people who supported ratification of the government |

|
|
|
Federalism |
system of government in which power is shared between the national(or federal) government and states |

|
|
|
majority rule |
System of government in which more than one half of the power to make decisions binding the entire group |

|
|
|
amendment |
addition to a document |

|
|
|
Bill of Rights |
First ten amendments to the us constitution |

|
|
|
House of Representatives |
the lower legislative branch in many national and state bicameral governing bodies, as in the United States, Mexico, and Japan. |

|
|
|
Senate |
an assembly or council of citizens having the highest deliberative functions in a government, especially a legislative assembly of a state or nation. |

|
|
|
Congress |
the national legislative body of the U.S., consisting of the Senate, or upper house, and the House of Representatives, or lower house, as a continuous institution. |

|
|
|
Popular Sovereignty |
the doctrine that sovereign power is vested in the people and that those chosen to govern, as trustees of such power, must exercise it in conformity with the general will. |

|
|
|
Republicanism |
the principles or policy of the Republican Party. |

|
|
|
separation of powers |
the principle or system of vesting in separate branches the executive, legislative, and judicial powers of a government.
|

|
|
|
limited government |
Government. restricted with reference to governing powers by limitations prescribed in laws and in a constitution |

|
|
|
bicameralism |
having two branches, chambers, or houses, as a legislative body. |

|
|
|
judicial review |
the power of a court to adjudicate the constitutionality of the laws of a government or the acts of a government official.
|

|
|
|
impeachment |
the presentation of formal charges against a public official by the lower house, trial to be before the upper house. |

|
|
|
quorum |
the number of members of a group or organization required to be present to transact business legally, usually a majority. |

|
|
|
revenue |
the income of a government from taxation, excise duties, customs, or other sources, appropriated to the payment of the public expenses. |

|
|
|
veto |
To prevent from becooming a law |

|
|
|
naturalization |
to introduce into a region and cause them to flourish |

|
|
|
elastic clause |
a statement in the U.S. Constitution (Article I, Section 8) granting Congress the power to pass all laws necessary and proper for carrying out the enumerated list of powers. |

|
|
|
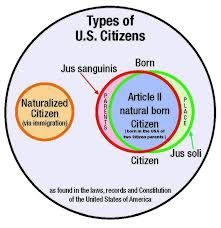
natural born citizen |
A phrase denoting one of the requirements for becoming President or Vice-President of the United States. |
|
|
|
electoral college |
a body of electors chosen by the voters in each state to elect the president and vice president of the U.S. |
|
|
|
Supreme Court |
the highest court of the U.S. |

|
|
|
suffrage |
The right to vote |
|
|
|
due process of law |
the regular administration of the law, according to which no citizen may be denied his or her legal rights and all laws must conform to fundamental, accepted legal principles, as the right of the accused to confront his or her accusers. |

|
|
|
bail |
property or money given as surety that a person released from custody will return at an appointed time. |

|
|
|
Constitution |
the system of fundamental principles according to which a nation, state, corporation, or the like, is governed.
|

|

