![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Connective Tissue |
Loose Connective Tissue 1. Areolar CT 2. Adipose Tissue 3. Reticular CT Dense Connective Tissue 1. Dense Regular CT 2. Dense Irregular CT 3. Elastic CT |
|
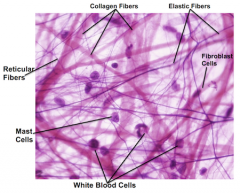
Loose (areolar) Connective Tissue |
Loose scatter of collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers binds tissue with each other (glue) diffusion of nutrients to epithelial cells Major tissue in the blood vessels Found everywhere in body |
|
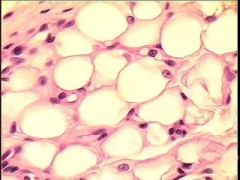
Adipose Tissue |
Support and Protection (padding) Energy (reserve) Insulation (reduce heat loss) consists of adipocytes (store triglycerides) subcutaneous layer of skin (part of hypodermis layer) around heart and kidneys |
|
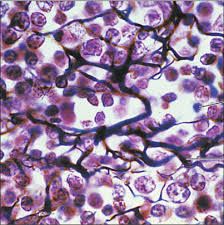
Reticular Tissue |
Made of reticular fibers and reticular cells Branching fibers form cell network and support system Spleen and lymph nodes (filtering system removes worn out blood, and microbes in LN) Red Bone Marrow (give rise to blood cells) |
|
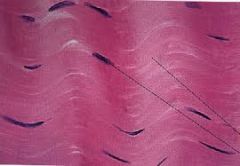
Dense Regular Connective Tissue |
parallel bundles of collagen fibers with fibroblasts in between Tensile strength (withstands pulling along the axis of the fibers) Hooks muscles or bones together (assist with movement in one direction) tendons (attach muscle to bone) ligaments (attach bone to bone) |
|
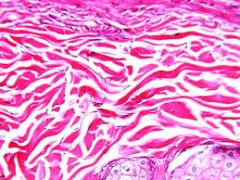
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue |
Collagen fibers are irregularly arranged and few fibroblasts Tensile strength found where pulling forces are exerted in all directions (won't stretch) Dermis layer of skin cow dermis makes leather |
|

Elastic Connective Tissue |
Dense network of elastin fibers with few fibroblasts Stretching and recoil Lung Tissue (recoils during exhale) Elastic Artieries - Aorta (expands to move blood and recoils so don't use energy, maintains blood flow) |
|
|
Mesenchymal Cell Fixed |
Stem cells that can differentiate into fibroblasts, adipose cells and other cells. |
|
|
Fibroblast and Fibrocyte Fixed |
Main cells of the connective tissue Produce the fiber of the extracellular matrix Cell shapes vary and found adhering to the fibers they produce and secrete |
|
|
Adipocyte Fixed |
Adipose cells that store triglycerides (energy reserve) |
|
|
Macrophage Fixed/Wandering |
Type of phagocyte (engulf bacteria or cellular debris and degrade with hydrolytic enzymes (phagocytosis)) Fixed macrophage - reside in particular tissue Wandering macrophage - can move throughout tissue, gathers at site of infection or inflammation for phagocytosis |
|
|
Mast Cell or Mastocyte Wandering |
detect foreign substances and initiate a local inflammatory response abundant along CT of blood vesses produce histamine that dilates blood vessels as part of the bodies reaction to infection or injury |
|
|
Lymphocyte Wandering |
Abundant in CT of respiratory and digestive tracts Type of white blood cell that initiates an immune response |
|
|
Plasma Cell or plasmocyte |
produce antibodies In CT of the GI and respiratory tract |
|
|
Extracellular Matrix |
CT composed of cells and ECM (stuff outside of cells) Fibers Ground Substance (nutritive environment) - Water 70% - Proteins and Polysaccharides |

