![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is Phocomelia? |
a rare congenital deformity in which the hands or feet are attached close to the trunk, the limbs being grossly underdeveloped or absent. This condition was a side effect of the drug thalidomide taken during early pregnancy. |
|
|
|
What is symphalangism? |
Symphalangism is a rare congenital difference characterized by ankylosis of interphalangeal (IP) joints of the fingers and toes. no active or passive motion, absent skin creases
|
(no active or passive motion, absent skin creases), |
|
|
What is camptodactyly? Which digit is always affected? |
Camptodactyly is a medical condition that causes one or more fingers to be permanently bent. It involves fixed flexion deformity of the proximal interphalangeal joints. The fifth finger is always affected. |
|
|
|
What is clinodactyly? |
Clinodactyly /ˈklaɪnˌoʊdæktɪli/ (from the Ancient Greek κλίνειν klínein meaning "to bend" and δάκτυλος dáktulos meaning "digit") is a medical term describing the curvature of a digit (a finger or toe) in the plane of the palm, most commonly the fifth finger (the "little finger") towards the adjacent fourth finger |
|
|
|
What is the difference between complex and complicated syndactyly? |
Complex: Presence of bony fusion Complicated: In the presence of a syndrome |
|
|
|
What is arthrogryposis? |
arthrogryposis (multiple joint involvement, waxy skin, ulnar deviation) *congenital joint contractures in two or more areas of the body. It derives its name from Greek, literally meaning "curving of joints" (arthron, "joint"; grȳpōsis, late Latin form of late Greek grūpōsis, "hooking") |
|
|
|
What does the treatment physiolysis accomplish for clinodactyly? |
Physiolysis •Bracket resection of longitudinal physis with preservation of growth plate and fat graft •Works well when true delta phalanx is resected •Can be performed when child is 3-4 years old |
|
|
|
Which gene is implicated in polydactyly? Which ethnicity is at higher risk? |
HOX, African Americans 1:300 |
|
|
|
Difference in racial prevalence of pre vs postaxial polydactyly? |
RADIAL POLYDACTYLY (PREAXIAL) = white ULNAR-SIDED POLYDACTYLY (POSTAXIAL) = African |
|
|
|
Which type of polydactyly warrants further work up for syndromes? |
Type A postaxial Polydactyly has up to 29% syndromic association, which warrants workup. |
|
|
|
Most common Wassel thumb duplication? What does Type VII require? |
Type I is least common: 2%.1 ▀Type IV is most common: 43%.1 ▀Type VII is most complex and requires at least one triphalangeal thumb. |
|
|
|
When thumb duplications go to the OR at 6-18 months, which side is more important to preserve? |
In general, ulnar thumb preserved to save the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL), which provides MP joint stability for pinch. |
|
|
|
Which 2 diseases/syndromes are associated with macrodactyly? |
1.Neurofibromatosis 2. Klippel-Trénaunay-Weber syndrome (limb hypertrophy, hemangiomas, varicose veins) |
|
|
|
What type of work up should be done in a patient with absent radial structures? |
VACTERL: Vertebral, anal, cardiac, tracheoesophageal fistula, renal, radial, and lower extremity abnormalities. TIP: All patients with radial longitudinal deficiency should receive cardiac auscultation, echocardiography, renal ultrasound, CBC with differential, and a careful follow-up by the child's pediatrician. |
|
|
|
What causes trigger thumb? When does it typically develop? |
Thickening of FPL tendon (Notta's node), which catches on first annular pulley. Not present at birth, first 2 years. |
|
|
|
Treatment for trigger thumb? |
Easiest and most effective treatment is complete release of A1 pulley of thumb in controlled operating room environment. |
|
|
|
Hand Embryology: 1. Which days does digital separation occur? 2. When do limb buds appear? 3. When will the phalangeal Tips be ossified? |
The exact dates of digital separation vary by publication, but occur approximately between days 44 and 54. Limb buds appear by day 26, and a hand paddle by day 33. By day 56, the phalangeal tips are ossified. |
|
|
|
What is ectrodactyly? |
Ectrodactyly refers to a split-hand/split-foot malformation. |
|
|
|
Which signaling pathways are involved in limb development: 1. Proximal distal 2. Radial ulnar 3. Dorsal ventral |
1. apical ectodermal ridge (AER), a thickened layer of ectoderm over the limb bud. Fibroblast growth factors secreted within the AER signal the underlying mesoderm to differentiate. Disruption of the AER results in truncation of the limb. 2. zone of polarizing activity (ZPA). This is located in the posterior margin of the limb bud. The sonic hedgehog protein acts to signal development of the limb into radial and ulnar aspects. 3. Wnt signaling pathway, which produces a transcription factor, LMX1 that induces the development of dorsal structures. In the ventral portion of the limb, the EN1 gene product blocks the Wnt pathway, leading to ventralization. |
|
|
|
Surgical treatment of complete absence of the thumb? |
Index finger pollicization |
|
|
|
How many weeks does digital separation occur? |
8 weeks |
|
|
|
Most appropriate age to perform pollicization? |
1 year |
|
|
|
In the Blauth classification of the hypoplastic thumb, what is the cut off point for amputation with pollicization? |
The Blauth classification of the hypoplastic thumb, as modified by Manske, is a true working classification that can be used for planning treatment (see table). Type IIIB has an unstable CMC joint and is the €œcutoff point € for performing index finger pollicization and ablation of the hypoplastic thumb, versus attempting reconstruction of the original thumb |
|
|
|
During embryonic limb development, limb bud outgrowth is controlled by which of the following families of signaling proteins? A) Bone morphogenetic proteins B) Fibroblast growth factor C) Retinoic acid D) Sonic hedgehog (SHH) E) Wingless-type proteins
|
The correct response is Option B. Fibroblast... |
|
|
|
A 3-month-old male infant is evaluated for polydactyly and mirror hand. Which of the following is the most likely genetic anomaly in this patient? A) Engrailed-1 (EN1) B) Fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF2) C) LIM homeobox transcription factor 1-beta (LMX1B) D) Sonic hedgehog (SHH) E) Wingless type (WNT) |
D) Sonic hedgehog |
|
|
|
During which days of gestation does syndactyly occur? |
The exact dates of digital separation vary by publication, but occur approximately between days 44 and 54. Limb buds appear by day 26, and a hand paddle by day 33. By day 56, the phalangeal tips are ossified. |
|
|
|
Most limb abnormalities occur during the period of ___ to ___ weeks |
Most limb abnormalities occur during the period of 4 to 8 weeks |
|
|
|
Hypoplastic thumbs: What is needed for great toe to thumb transfer? |
The most appropriate reconstruction of Type V deformity is pollicization of the index finger. It is the only satisfactory method of a basal joint reconstruction. Pollicization refers to the neurovascular pedicle movement of a finger, often with its metacarpal, for thumb reconstruction. Great toe-to-thumb microsurgical reconstruction is appropriate when most of the first metacarpal is present. When the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint is absent or unstable, a great toe-to-thumb reconstruction will not reconstruct an adequate basilar joint. |
|
|
Which type of transfer is used to create functional opposition when it’s absent? |
Huber transfer is used to create functional opposition when absent. Type IIIA deformities can be reconstructed with the Huber transfer, which involves transfer of the hypothenar muscle to recreate the thenar musculature. |
|
|
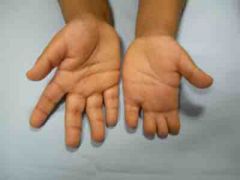
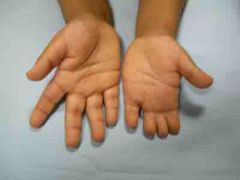
Possible syndrome? Name of deformity? |
Poland syndrome - Symbrachydactyly |
|
|
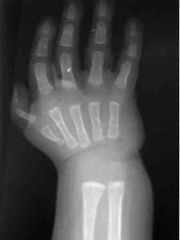
Treatment of this thumb? |
X-ray study is essentially diagnostic of the Blauth Type IIIB thumb. The most accepted treatment for this type of thumb is ablation/amputation of the existing thumb and replacement with the index finger in the thumb position (pollicization). |
|
|
|
A neonate is born with unilateral edema of the arm. During the ensuing day, there is worsening edema and bullae formation. What is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient? |
Fasciotomy- this is neonatal compartment syndrome. The sentinel lesion of neonatal compartment syndrome is bullous formation on the dorsum of the hand or arm. Etiology is often in utero and can be amniotic bands, umbilical cord loops, forceps extraction, oligohydramnios, preeclampsia, and excessive maternal weight. |
|
|
|
A 6-month-old boy is brought to the office with a Blauth type IV (pouce flottant) thumb deficiency. Reconstruction with pollicization is planned. What is the most appropriate new function of the first palmar interosseous muscle? |
The most appropriate new function of the first palmar interosseous muscle is the adductor pollicis.
|
|
|
|
What type (class) of Congenital Hand deformity is cleft hand? Another word for this? |
Typical cleft hand = ectrodactyly. This is classified as a Swanson type I (failure of formation) congenital difference of the upper extremity. This deformity is caused by a longitudinal growth deficiency of one or more central digits. This condition may have a genetic underpinning and is most commonly inherited in autosomal dominant fashion with approximately 70% penetrance. |
|
|
|
Which anatomic structure limits extent of separation in syndactyly? |
Artery |
|
|
|
A 12-month-old male infant is brought to the office for evaluation of a small right thumb. Physical examination shows instability of the metacarpophalangeal joint and hypoplasia of the first web space. The carpometacarpal joint is stable. The patient has difficulty moving the thumb. Which of the following is the next best step in management? A) Free toe transfer B) Metacarpal lengthening C) Opponensplasty D) Pollicization |
C) opponensplasty The correct response is Option C. This patient presents with a Blauth Grade 2 or 3A thumb hypoplasia. Surgical management is warranted and includes treatment of the absent or hypoplastic thenar musculature with opponensplasty; release of the first web space; and management of MCP instability.
Pollicization is reserved for Blauth Grade 3B or more severe deficiencies. The distinction between a Blauth 3A and 3b hypoplastic thumb is determined by the stability of the CMC joint. |
|
|
|
A 2-month-old infant is brought to the office for evaluation of bilateral complex syndactyly of the hands and feet. Which is the most likely gene involved? |
B) Fibroblast growth factor receptor-2 (FGFR2) |
|
|
|
Congenital constriction band syndrome is responsible for which of the following percentages of all congenital upper limb defects? A) 6% B) 12% C) 18% D) 24% E) 30% |
B) 12% |
|

