![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Personal computer |
A computer designed for use by an individual, usually incorporating a graphics display, a keyboard, and a mouse. |
|
|
Server |
A computer used for running larger programs for multiple users, often simultaneously, and typically accessed only via a network. |
|
|
Super computer |
A class of computer with the highest performance and cost; they are configured as servers and typically cost tens to hundreds of millions of dollars. |
|
|
Terabyte |
10^ 12 bytes |
|
|
Megabyte |
10^6 |
|
|
Gigabyte |
10^9 bytes |
|
|
Kilobyte |
10^3 |
|
|
Petabyte |
10^15 |
|
|
Exabyte |
10^18 |
|
|
Zettabyte |
10^18 |
|
|
Yottabyte |
10^24 |
|
|
Embedded computer |
A computer inside another device used for running one predetermined application or collection of software. |
|
|
Personal mobile devices |
Small wireless devices that connect to the internet; they reply on batteries for power, and software is installed by downloading apps. Conventional examples are smart phones and tablets. |
|
|
Cloud computing |
Large collections of servers that provide services over the Internet; some providers rent dynamically varying numbers of servers as a utility. |
|
|
Moore's Law |
Integrated circuit resources double every 18-24 months. |
|
|
Compiler |
A program that translates high-level language statements into assembly language statements. |
|
|
Instruction |
A command that computer hardware understands and obeys. |
|
|
Assembler |
A program that translates that translates a symbolic version of instructions into the binary version. |
|
|
How to translate source code |

High level code goes through a compiler then converted into assembly and goes through the assembler to become machine code |
|
|
Dynamic random access memory |
Memory built as an integrated circuit; It provides random access to any location. Access times are 50 nanoseconds and cost per gigabyte in 2012 was 5 to 10 dollars |
|
|
Cache memory |
A small,fast memory that acts as a buffer for a slower, larger memory. Like DRAM |
|
|
Static random access memory |
Memory built as an integrated circuit,but faster and less dense than DRAM. |
|
|
Instruction set architecture |
An abstract interface between the hardware and the lowest level software that encompasses all the information necessary to write a machine language program that will run correctly,including instructions, registers,memory access,I/O,and so ob |
|
|
Application binary interface |
The user portion of the old instruction set plus the operating system interfaces used by application programmers. It defines a standard for binary portabilty across computers. |
|
|
Volatile memory |
Storage, such as DRAM, that retains data only if it revives power. |
|
|
Nonvolatile memory |
A form of memory that retains data even in the absence of a power source and that is used to store programs between runs. |
|
|
Main memory/ primary memory |
Memory used to hold programs while they are running typically consists of dram in today's computers |
|
|
Secondary memory |
Nonvolatile memory used to store programs and data between runs; typically consists of flash memory in PMDs and magnetic disks in servers. |
|
|
Magnetic disk/ hard disk |
A form of non volatile secondary memory composed of rotating platters coated with magnetic recording material. Because they are rotating mechanical devices, access times are about 5 to 20 milliseconds and cost per gigabyte .05 to .10 dollars |
|
|
Flash memory |
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory. It is cheaper and slower than DRAM but more expensive per bit and faster than magnetic disks. Access times are about 5 to 50 microseconds and cost per gigabyte in 2013 was .75 to 1.00 dollars. |
|
|
Advantages of networked computers |
Communication: information is exchanged between computers at high speeds.
Resource sharing: Rather than each computer having its own I/o device, computers on the network cab share I/O. Non local access: By connecting computers over long distances, users need not be near the computer they are using. |
|
|
Local area network |
A network designed to carry data within a geographically confined area, typically within a single building. |
|
|
Wide area network |
A network extended over hundreds if kilometers that can span a continent. |
|
|
Chip manufacturing process |
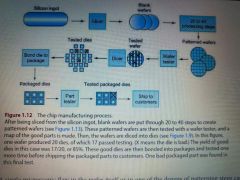
|
|
|
Cost of an integrated circut |
Cost per die = cost per wafer / dies per wafer x yield Dies per wafer = wafer area / die area Yield = 1/(1+ (defects per area x die area / 2))^2 |
|
|
Operating system |
Interface between a users program and a compiler. - handles basic input and output -allocating storage and memory -providing for protected sharing of the computer among multiple applications using it simultaneously |

