![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an Articulation? |
They are formed when 2 or more bones are connected by fibrous, elastic, or cartilaginous. |
|
|
What are the three types of joints? |
-Synovial Joint
-Fibrous Joint or Suture
-Cartilaginous or Vertebral Joint |
|
|
What is a Synovial Joint? |
-A true joint.
-Most important and permit a fair amount of mobility.
-Most commonly involved in dislocations and arthritis.
EX: Shoulder and Stifle. |
|
|
What is a Fibrous Joint or Suture? |
No mobility.
EX: Skull joint or Splint bones in horses. |
|
|
What is a Cartilaginous or Vertebral Joint? |
Limited mobility.
EX:Mandible, or Symphyses in pelvis. |
|
|
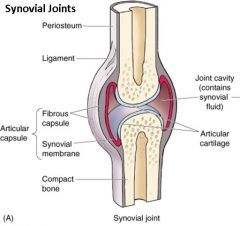
Anatomy of a Synovial Joint? |
|
|
|
What is the Joint Cavity in a Synovial Joint? |
-Space between the bones (Contains Synovial Fluid) |
|
|
What is the Joint Capsule in a Synovial Joint? |
-Encloses the joint cavity
-Connective tissue that surround the joint |
|
|
What is the Fibrous Membrane in a Synovial Joint? |
-Outer layer, Heavy fibrous CT |
|
|
What is the Synovial Membrane in a Synovial Joint? |
-Inner layer of the Joint Capsule
-Delicate, Vascular CT
-Secretes Synovial Fluid
-Covers everything except Articular Cartilage |
|
|
What is Synovial Fluid? |
-Lubricant
-Carries nutrients to Articular Cartilage
-Sample is collected during Joint Tap.
-Transparent and Viscous |
|
|
What is Articular Cartilage? |
-Hyaline Cartilage
-Smooth glass like, covers the articular surface of bones. |
|
|
What are the 4 types of Synovial Joints? |
-Hinged
-Ball and Socket
-Pivot
-Gliding |
|
|
What is the Hinged Joint? |
Flexion and Extension only
EX: Elbow |
|
|
What is the Ball and Socket Joint? |
Allows most movement. Flexion, Extension, Adduction, and Abduction, Rotation, Circumduction.
EX: Hip and Shoulder |
|
|
What is the Pivot Joint? |
Rotation and Circumduction.
EX: The skull and atlas and axis |
|
|
What is the Gliding Joint? |
Flexion and Extension, limited Abduction and Adduction.
EX: Joints that are flat (Carpus) |
|
|
What is a Bursa? |
A Synovial sac located between 2 structures which tend to rub. |
|
|
What is a Synovial Sheath or Tendon Sheath? |
Protects Tendons that travel a long distance over bone. |
|
|
What is the Stifle Joint? |
The largest and most complex joint. |
|
|
How many Ligaments does the Stifle contain? |
5 |
|
|
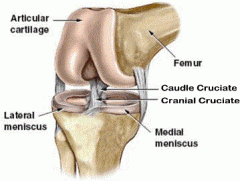
Where are the five ligaments located? |
|
|
|
What are the 5 ligaments in the Stifle? |
-Cranial cruciate (ACL)
-Caudal cruciate (PCL)
-Lateral collateral
-Medial collateral
-Patellar ligament |
|
|
What is the Meniscus? |
Forms a cushion of support between the bones. |
|
|
What is the most commonly ruptured ligament in the Stifle? |
The Cranial Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tester with Drawer Test. |
|
|
What is a Tendon? |
Muscle to bone. |
|
|
What is a Ligament? |
Bone to bone. |
|
|
What is an Origin? |
Beginning of a muscle. |
|
|
What is the Belly? |
Main portion of a muscle. |
|
|
What is the Insertion? |
End of a muscle. |
|
|
What is a Sphincter? |
A circular band of muscle around an opening. Some are voluntary some are involuntary (Smooth). |
|
|
What is Striated? |

EX: Cardiac and Skeletal |
|
|
How many types of Muscle are there? |
4 |
|
|
What are the 4 types of muscle? |
-Smooth
-Skeletal
-Cardiac
-Cutaneous |
|
|
What is Smooth Muscle? |
Involuntary EX:Uterus, bladder, stomach, intestines |
|
|
What is Skeletal Muscle? |
Voluntary, Striated, Moves bones of the body, source of red meat |
|
|
What is Cardiac Muscle? |
Involuntary (Adopts the rate), Striated muscles |
|
|
What is Cutaneous Muscle? |
Located in CT under skin, little to no attachment to bone, twitches the skin (Horses and Cats) |
|
|
What is the Longissimus Lumborum Muscle? |
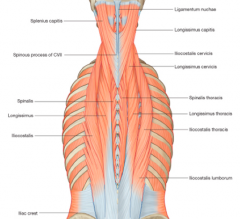
One of the lumbar epaxial muscles. The boundaries are the last rib, to iliac crest and dorsal spinal processes to lateral tip of transverse process. |
|
|
How many layers of muscles are there to the abdominal wall? |
Four |
|
|
What is the Linea Alba (White line) ? |
The CT that surrounds the muscles, often used for ventral midline abdominal incisions for less bleeding. |
|
|
What is the Diaphragm? |
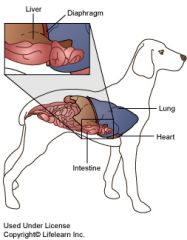
Divides the Thoracic and Abdominal cavities. |
|
|
What are the Thoracic Limb Muscles? |
-Biceps Brachii
-Triceps Brachii
-Digital extensors and flexors |
|
|
What is the Biceps Brachii and Triceps Brachii? |
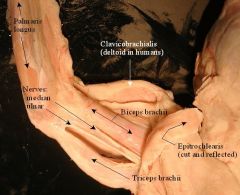
Biceps: Elbow Flexor, Cranial, Medial. Triceps: 4 heads that join that inserts into the O-le-cra-non. Extensor for Elbow, Flexor for Shoulder. Caudal, Lateral. In the forerms. |
|
|
What are the five pelvic limb muscles? |
-Gluteal Muscles
-Quadriceps (Femoris)
-Biceps Femoris
-Semitendinosis -Semimembranosus |
|
|
What is the Gluteal Muscles? |
- 3 diffrent muscle, Superficial, Middle and Deep.
-Often used for injections. |
|
|
What is the Quadriceps Femoris? |
- Large muscle cranial to femur
- Extends the knee
-Injections for small animals/ pocket pets |
|
|
What is the Biceps femoris? |
-Wraps around the lateral thigh, long and superficial
-Extends 3 joints (Hip, Stifle, and Hock)
-Insertion - middle of tibia |
|
|
What is the Semitendinosus? |
-Caudal aspect of thigh
-It acts as a Flexor |
|
|
What is the Semimembranosus? |
-Medial to the Semitendinosus and deeper
-Stifle flexor, Hip extensor
-Sciatic Nerve |
|
|
What is the most common muscle for injections in dog and cat? |
Longissimus lumborum and Semimembranosus/Semitendinosus (Hamstring) |
|
|
What muscles are used for injections in Equine and Bovine? |
Pectoral, neck and hamstring. |
|
|
What is the Nuchal Ligaments in Equine and Bovine? |
A dense connective tissue extending from the cranial Thoracic spines to the skull which allows the animal to lift its head. (Rubber band) |
|
|
What is the largest muscle in Avian? |
Pectoralis Major which controls the wings in flight. |

