![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Aggressiveness |
verbal attacks that demean others' self-concept and inflict psychological pain
|
|
|
Ambiguous Response |
a response with more than one meaning, leaving the person unsure of the responder's position
|
|
|
Argumentativeness |
presenting and defending positions on issues while attacking positions taken by others |
|
|
Certainty |
dogmatically stating or implying that one's position is correct and others' ideas are not worth considering; likely to arouse defensiveness, according to Gibb
|
|
|
Communication Climate |
the emotional tone of a relationship between two or more individuals
|
|
|
Complaining |
a disagreeing message that directly or indirectly communicates dissatisfaction with another person
|
|
|
Confirming Communication |
a message that expresses caring or respect for another person; the person is valued by the speaker
|
|
|
Controlling Communication |
according to Gibb, messages that attempt to impose some sort of outcome on another person, resulting in a defensive response
|
|
|
Defensiveness |
the attempt to protect a presenting image a person believes is being attacked
|
|
|
Description |
messages that describe a speaker's position without evaluating others |
|
|
Disagreeing Message |
a message that essentially communicates to another person, "you're wrong" and includes argumentativeness, complaining, and aggressiveness |
|
|
Disconfirming Communication |
a message that expresses a lack of caring or respect for another person; the person is not valued by the speaker |
|
|
Empathy |
the ability to project oneself into another person's point of view in an attempt to experience the other's thoughts and feelings |
|
|
Equality |
a type of supportive communication described by Gibb, which suggests that the sender regards the receiver with respect |
|
|
Evaluation |
a message in which a sender judges a receiver in some way, usually resulting in a defensive response |
|
|
Face |
the image an individual wants to project to the world |
|
|
Face-Threatening Acts |
behavior by another that is perceived as attacking an individual's presenting image, or face |
|
|
Impersonal Response |
a disconfirming response that is superficial or trite |
|
|
Impervious Response |
a disconfirming response that ignores another person's attempt to communicate |
|
|
Incongruous Response |
a disconfirming response in which two messages, one of which is usually nonverbal, contradict each other |
|
|
Interrupting Response |
a disconfirming response in which one communicator interrupts another |
|
|
Invitational Response |
an approach that welcomes others to see your point of view and to freely share their own |
|
|
Irrelevant Response |
a disconfirming response in which one communicator's comments bear no relationship to the previous speaker's ideas |
|
|
Neutrality |
a defense-arousing behavior described by Gibb in which the sender expresses indifference toward a receiver |
|
|
Presenting Self |
the image a person presents to others; may be identical to or different from the perceived and desired selves |
|
|
Problem Orientation |
a supportive style of communication described by Gibb in which the communicators focus on working together to solve their problems instead of trying to impose their own solutions on one another |
|
|
communication is bi-dimensional: content and relational |
what is the grounding axiom of communication climate? |
|
|
Recognition Acknowledgement Endorsement |
what are the three types of confirming messages? |
|
|
Recognition |
the most shallow of the confirming message types; when you recognize someone, and we let them know that we are aware of their physical presence (eye contact, gesture, smile, "hi") |
|
|
Acknowledgement |
confirming message type; when you apply your interpersonal knowledge about a person rather than just recognizing their existence; rather than just seeing them as a human, you see them as a unique individual |
|
|
Endorsement |
most intense confirming message type; when you agree with someone about something, empathy is a big part of this; can result in giving the other person a compliment |
|
|
Disconfirming Messages |
messages that say "you're not important to me, I don't respect you" |
|
|
Impervious Message |
when you don’t respond to someone, you avert your gaze, etc.; when youdon’t acknowledge someone… intention doesn’t matter |
|
|
Interrupting Message |
when you talk over someone, implying that your perspective is more important than theirs. Sometimes, it’s well-intended and you’re trying to support their ideas by telling them you’re in agreement |
|
|
Irrelevant Messages |
in response to another person, but has nothingto do with what the other person is saying |
|
|
Tangential Messages |
variant of the irrelevant message, but instead of the other person just ignoring your comment and moving onto the next thing that is irrelevant, they will acknowledge your comment and THEN move on “oh that stinks, today I had to…” |
|
|
Impersonal Messages |
responding to someone you have an interpersonal relationship with a response that you would use with someone you just met“there are other fish in the sea” |
|
|
Incongruous Messages |
a message that is contradicting at the verbal and nonverbal levels;you’re saying one thing, but the way you’re saying it sounds very different |
|
|
Investment |
the process of putting something into something (money in the stock market, effort in a relationship, time into a project) |
|
|
Self-Disclosure |
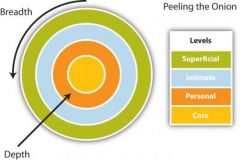
the process of sharing personal, meaningful, important information about ourselves with another person because we choose to do so, and with the knowledge that they cannot easily get that information elsewhere |
|
|
Petronio, 2002 |
who was the scholar that warns us that sometimes, people don't want to be disclosed, making them a "reluctant confidant"? |

