![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
102 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Who are the World Health Organization?
|
-an agency of the UN based Geneva Switzerland that MONITORS the health of the world and INITIATING responses
|
|
|
What are the 3 things truly involved in Public Health?
|
A) PREVENTING DISEASE
B) PROLONGING LIFE C) ORGANIZED COMMUNITY EFFORTS FOR THE SANITATION OF THE ENVIRONMENT, CONTROL OF COMMUNICABLE INFECTIONS, EDUCATION OF THE INDIVIDUAL IN PERSONAL HYGIENE |
|
|
What did the American public health association say about public health and what are the 3 importance of public health?
|
-They said that public health is preventing disease and policy development
-3 important things about public health were 1) public health saves MONEY and improves QUALITY of life 2)Improving public health helps CHILDREN THRIVE 3) public health prevention reduces HUMAN SUFFERING |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE-Injecting a patient for an ingrown toenail procedure is public health
|
FALSE-it's not public health because it's for the individual and not the whole
|
|
|
What was public health like in the 18th century?
|
-was carried out by local government
-focused more on preventing the introduction of diseases from the outside (travelers) so they had like PEST HOUSES where they threw people who had those diseases in |
|
|
What was public health like in the 19th century?
|
-This was the GREAT SANITARY AWAKENING and was the first time massachusetts set up the first board of health in the U.S
-was carried out by local governments and cities -main focus was sanitation and the social and environmental conditions |
|
|
What was public health like in the late 19th century to the early 20th century?
|
-Emphasis shifted to prevention of acute illnesses so there were more vaccinations/immunizations
-Mainly focused on INDIVIDUAL bacteria in INDIVIDUAL PEOPLE -mainly local government but this was when you started to see the states government getting involved |
|
|
What was public health like in the 20th century?
|
This was when the FEDERAL GOVERNMENT ACTIVITIES grew because they passed the sixteenth amendment that allowed them to get financial resources from NATIONAL INCOME TAXES, this was VERY IMPORTANT because it started to give more power to implement laws and regulations compared to the local and state government
|
|
|
what are two important things that happened in the 20th century?
|
-sixteenth amendment
-social security act which marked the first major effort by the federal government in creating the first nationwide system and solidified the federal-state partnership in public health while expanding the federal government role -the social security act gave grants to the states |
|
|
After WWII, it was perceived as necessary to have a cabinet level department in the federal government, what did they call it?
|
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH, EDUCATION, AND WEALTHFARE (HEW)
|
|
|
Department of Health and Human services is ALL FEDERAL
|
(Department of health and Human services)
(11 operating divisions) (10 regional offices) (8 U.S public health service) (3Human service Agenc) 1)CDC-center for disease control 2)FDA-food and drugs 3)HRSA-delivery of service to underserved 4)NIH-largest one for biomedical research 5 )IHS (indian health service) 6) SAMHSA (substance abuse and mental health services administration) 7) AHRQ (agency for healthcare research and quality) 8) ATSDR (agency for toxic substance and disease registry) |
|
|
What comprises the U.S public health service?
|
-office of public health and science
-regional health administrators (dept of agriculture, environmental protection agency, dept of defense, and dept of labor) -eight operating divisions |
|
|
The U.S public health service is run by who?
|
Surgeon General named Dr. Lushniak
|
|
|
is social securities administration a part of federal health agency?
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the 3 human service agencies?
|
MCC
1) centers for medicare and medicaid services 2) administration of children and families 3) administration of community living |
|
|
What are the 10 essential public health services?
|
MD in MD enforces LAER
1) MONITOR health status to identify community health problems 2)DIAGNOSE AND INVESTIGATE health problems and health hazards in the community 3)INFORM, EDUCATE, AND EMPOWER people about health problems 4)MOBILIZE community partnerships to identify and solve health problems 5) DEVELOP POLICIES AND PLANS that support individual and community health efforts 6) ENFORCE laws and regulations that protect health and ensure safety 7)LINK people ton needed personal health services and assure the provision of healthcare when otherwise unavailable 8) ASSURE a competent health and personal healthcare workforce 9) EVALUATE effectiveness, accessibility, and quality of personal and popuation-based health services 10) RESEARCH for new insights and innovative solutions to health problems |
|
|
What are the four concepts that have helped frame the NPHPSP (National Public Health Performance Standards Program)
|
1) Revolves around the 10 essential public health services
2) focus on Overall public health system 3) decries the optimal level of performance rather than provide the minimum expectations 4) intended to support process of quality improvement |
|
|
What is HEALTHY PEOPLE 2020?
|
10 year agenda for improving the nation's health that the U.S department of health and human services release each decade as a result of a multiyear process that reflects input from the diverse group of individuals and organizations
|
|
|
What are the four foundation health measures?
|
HD GD
1) General Health status 2 )Health-related quality of life and well being 3) Determinants of health 4) Disparities (age and gender) |
|
|
What are the overarching goals of Healthy people 2020?
|
Quality, equality, good environment, and good behavior, remember treatment is NOT involved!
|
|
|
What is the Health Belief Model?
|
It's a good used to try and predict health behaviors based on a theory that a person's willingness to change their behavior is based on 4 things:
-perceived suscptibility -perceived severity -perceived benefits -perceived barriers |
|
|
Transtheoretical Model
|
based on a individuals behavior change to gain something positive or change a bad behavior
it's based on the model of STAGES OF CHANGE 1. PRECONTEMPLATION (not ready to take action) 2. CONTEMPLATION (getting ready) 3. PREPARATION (ready) 4. ACTION (overt change) 5. MAINTENANCE (sustained change) 6. TERMINATION (no risk of relapse) |
|
|
5 stages of DIFFUSION OF INNOVATION by everett rodgers
|
KNOWLEDGE PERSUASION DECISION
IMPLEMENTATION CONFIRMATION |
|
|
what is the point of diffusion of innovation?
|
-to help explain how, why, and what rate new ideas and technology spread through a culture
|
|
|
3 aspects of healthcare
|
1) Personal Healthcare
2) Community healthcare- pure drinking water, sanitary disposal, pollution 3) Combined services=TB or mass immunizations |
|
|
Medical Care
|
Generally thought of as care provided by a physician restricted in scope, focusing on pathophysiological and social problems, and containing a strong element of “caring”
|
|
|
3 most important things in growing interest in the social and organizational structure of health - 1940’s
|
HMN
-Hill Burton Act (Hospital Survey and Construction Act of 1946) -help plan for and construct hospitals and other health facilities by providing federal grants -Medicare - Title 18 of the Social Security Act of 1965. It is a federally sponsored and supervised health insurance plan for the elderly 65 and over. -National Institute of Health (NIH) - Provided large research budgets. NIH contributed to medical technology assessment by sponsoring clinical trails and by conducting consensus development conferences on specific medical practice issues. |
|
|
Medicare
|
-federal program that covers individuals aged 65, some disabled individuals and end-stage renal disease
-A single-payer program administered by the government (there is only one entity (the government) performing the insurance function of reimbursement -financed by federal income taxes, a payroll tax shared by employers and employees, and individual enrollee premiums (parts B and D). |
|
|
Parts A-D of Medicare
|
Part A covers HOSPITAL services,
Part B covers PHYSICIAN services Part D offers a PRESCRIPTION drug benefit. Part C refers to MEDICARE Advantage Programs (HMO’s that administer Medicare benefits). |
|
|
Bad parts of medicare
|
Gaps in Medicare coverage
-incomplete coverage for skilled nursing facilities, -incomplete preventive care coverage -no coverage for dental, hearing, or vision care. Deductibles and Co-insurances The majority of enrollees obtain supplemental insurance. Seniors pay about 22% of their income for health care costs despite their Medicare coverage. |
|
|
Medicaid
|
-A program for the low-income and disabled.
federal law states - must cover very poor pregnant women, children, elderly, disabled, and parents. -Childless adults are not covered, -many poor individuals make too much to qualify for Medicaid. -States have the option of expanding eligibility by increasing income eligibility levels. |
|
|
How does medicaid work?
|
Financed jointly by the states and federal government through taxes.
-Administered by the states and the District of Columbia - fifty-one different Medicaid programs in the country. -Every dollar that a state spends on Medicaid is matched by the federal government at least 100% -In poorer states, the federal government matches each dollar more than 100%. -Overall, the federal government pays for 57% of Medicaid costs. |
|
|
Predominant health problem in 1850-1900
|
-Epidemics of ACUTE INFECTIOUS DISEASES were the most critical health problem for the majority of Americans.
-of particular importance were diseases related to impure food, contaminated water supply, and inadequate sewage disposal, and the general poor condition of urban housing. |
|
|
Predominant health problems in 1900's (early)
|
-The predominate health problems plaguing the health services system were those ACUTE EVENTS, whether infectious or traumatic, that affected individuals one by one and required individualized attention.
-Pneumonia, influenza, and tuberculosis were the primary causes of death, with heart disease, nephritis, and accidents close behind. |
|
|
Predominant health problems in 1950's to now
|
-Acute infections are no longer ending lives>>People are living longer>>they began to manifest long term CHRONIC DISEASES
-Heart disease, cancer and stroke account for approximately 2/3rds of all deaths. Then comes personal injury and chronic obstructive bowel disease. |
|
|
Top 4 leading causes of death
|
1. Heart Disease 2. Cancer
3. Lung Diseases 4. Stroke |
|
|
leading cause of disability and decreased function
|
arthritis
|
|
|
Endemic
|
“WITHIN PEOPLE” and denotes a condition that persists within a geographical area
|
|
|
Epidemic
|
Epidemic: “AROUND PEOPLE” - denotes a condition from a common cause that has affected a large number of people (ex: a communitywide or statewide outbreak of a disease)
|
|
|
Pandemic
|
Pandemic: “ALL PEOPLE” - denotes spread of a disease over considerable areas (ex: nationwide, continentwide, worldwide)
|
|
|
6 subsystems of American Healthcare
|
Employed VPMMM
Employer Sponsored health Veteran Affairs Private insurance Medicare Medicaid Military Medical care |
|
|
Illness vs. disease
|
ILLNESS - The individual’s perception of
loss of functional capacity DISEASE - The professionals definition of a pathologic process |
|
|
PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC PROCESSES INVOLVED IN DISEASE PRODUCTION
|
VINT MD
VASCULAR INFLAMMATORY NEOPLASTIC TOXIC METABOLIC DEGENERATIVE |
|
|
Indicators of Health service utilization
|
PURPOSE: Reason care is being sought
-Primary Prevention - Health maintenance in the ABSENCE of symptoms -Secondary Prevention - Diagnosis and treatment of illness in the interest of a PREVIOUS STATE of well being -Tertiary Prevention - Rehabilitation or maintenance in the case of a LONG TERM health problem -Maintenance or Custodial Care - For MEDICALLY FRAGILE or dependent adults or children she's gonna ask which form of prevention is it in a scenario |
|
|
SUCHMANN and KOSA & ROBERTSON MODELS
COST SUCKS |
These two models are NOT health belief models because they are psychological and social
|
|
|
3 variables in CHARACTERISTICS OF THE POPULATION
|
predisposing variable-age, sex, race, ethnicity
Enabling variables- Income (people with higher incomes use medical support more) and residence (people who live in the city use it more) Need variables- Perceived need (people with poorer health need it more) and Evaluated need (severity of condition increases so does the utilization) |
|
|
What is the largest service industry in country?
|
healthcare industry
|
|
|
What are the contributing factors in health care spending?
|
GET LTR
government financing, elderly growth, technological advancement, lack of competitive forces, third party reimbursements, rising expectations |
|
|
Moral hazard
|
-an economic principal that states if you are insured for a service you will use more of it.
-Example- Failing business>fire>collect insurance -Health Insurance usage is highly discretionary. Doctors and patients can conspire (intentionally or not) to use the insurance. Example - privately insured patient being kept in hospital an extra day when the services of the institution are no longer needed. |
|
|
What are the consequences of moral hazard?
|
BF Comes In
Benefit structure-health insurance pays less than the total cost so you have to pay out of pocket Fee-for-service-you have to pay a deductible, which is something you have to pay before the insurance policy become active Copayment Insurance plans-reimburses on a percentage basis, so a coinsurance where the insurance only pays for a certain percentage of the fee |
|
|
Premium Determination basis
|
on two things:
Experience rating-used by most health insurance and fee for service plans, required to pay DIFFERENT PRICES because based on past experiences Community rating-used by most HMO's based on geographic area and they are required to all pay the SAME price |
|
|
A company of young healthy 35 year old with low risks, want to determine premium based on what?
|
experience ratings because you know they were healthy prior years
|
|
|
A company of woman want to determine premium based on what?
|
community rating because woman cost more because cost associated with child bearing
|
|
|
3 categories of U.S Health insurance
|
Voluntary=Blue cross/blue shield, HMO, Private
Public=from government, public assistance (Medicaid), welfare Social= Worker's compensation, Medicare |
|
|
non-financial resources for health services
|
DEVELOP I.D
-Innovation - advances in medical technology -Development - biomedical research and development funded by the federal government and private sector -Diffusion - The spread of technology into society once it is developed is known as diffusion, It includes entry, adoption, widespread use, and final obsolescence of an innovation -- The Life Cycle of Technology. |
|
|
Prospective payment system define it
|
a method of reimbursement in which payment is made based on a predetermine, fixed amount. The
payment amount for a particular service is derived based on the classification of that service. -For example, DRGs for inpatient hospital services. |
|
|
Diagnosis Related Groups define (DRG)
|
-DRG (Diagnosis Related Groups)- a system used since 1983 to classify hospital cases into one of approximately 500 groups, also referred to as DRGs, developed for Medicare as part of the prospective payment system.
-DRGs are assigned by a “grouper” program based on ICD diagnoses, procedures, age, sex, and the presence of complications or co-morbidities. -DRGs are used to determine how much Medicare pays the hospital, since patients within each category are similar clinically and are expected to use the same level of hospital resources. |
|
|
Professional Review Organization (PRO)
|
Uses utilization review and other techniques to guard against, unnecessary admissions, expensive outliers, early or premature discharge, medical record miscoding, and validation of DRGs
|
|
|
Professional standards review organization (PSRO)
|
Group that monitors government health insurance programs. Authorized by the 1972 amendment to the Social Security Act, PSROs were set up to cut costs and minimize abuses by checking on the need of applicants for care and the cost and quality of care.
|
|
|
What are the 4 market interventions for regulating and monitoring the healthcare system
|
RESQ
Rate Controls=fee, commission, reimbursement Entry Restrictions=licensure Subsidy Intervention=grants and tax Quality Controls=reviews, admissions, certifications |
|
|
Assessment vs. Assurance
|
Quality Assessment=measurement of the quality of care includes structure (facilities), process (patient/doctor interaction), and outcomes (results)
Quality Assurance=The process of institutionalizing, or conducting, on an ongoing basis, quality measurement activities and combining these with FEEDBACK MECHANISMS aimed at continual quality improvement |
|
|
Describe and interpret a receiver-operator characteristic (ROC) curve.
|
a
|
|
|
Sensitivity
|
measure how sensitive a test is at detecting a disease
-WITH disease =TP/total -to find false negative rate= 1-sensitivity |
|
|
specificity
|
measures the ability of a test to detect the absence of a disease
-WITHOUT disease =TN/total -to find false positive rate= 1-specfiicity |
|
|
positive predictive value
|
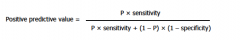
is defined as the likelihood that a positive test result represents a true positive result
p=prevalence |
|
|
negative predictive value
|
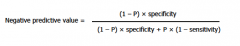
defined as the likelihood that a negative test result represents a true negative result
|
|
|
prevalence
|
Is the number of affected persons present in the population at a specific time divided by the number of persons in the population at that time
|
|
|
incidence
|
Is the number of new cases of the disease during a specified period of time in a population at risk for developing the disease. incidence is a measure or RISK
|
|
|
Discuss the relationship between data obtained during the history and positive predictive value of subsequent lab tests.
|
a
|
|
|
Define SPIN and SNOUT
|
SnOUT-if sensitivity is high, a negative test will rule the disorder OUT
SpIN-if Specificity is high, a positive test will rule the disorder IN |
|
|
Describe how moving the cutoff point within the area of overlap between two distribution curves affects the following: sensitivity, specificity, false negatives, and false positives.
|
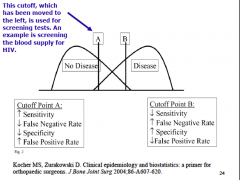
a
|
|
|
Describe and interpret a 2 x 2 table as it relates to a novel test.
|
a
|
|
|
What are the two required elements of proof in a medical malpractice case?
|
1) A deviation or departure from accepted practice
2) evidence that such departure was a proximate cause of injury or damage |
|
|
Define Malpractice
|
-IT IS A DEVIATION OR DEPARTURE FROM ACCEPTED PRACTICE
-Is negligence, which is a failure to use reasonable care under the circumstances, doing something that a reasonably prudent doctor would not do under the circumstances, or failing to do something that a reasonably prudent doctor would do under the circumstances |
|
|
When are doctors not liable?
|
not from a complication, not from a bade results, and no in an error of judgement
|
|
|
theories of malpractice
|
Negligently performed surgery
Failing to diagnose a medical condition (for example, an infection) Failing to refer a patient to a medical specialist Performing unnecessary surgery Performing the wrong surgery Failing to give the patient appropriate post-operative instructions Failing to properly monitor and treat a diabetic ulcer Failing to attempt conservative therapy prior to surgery Negligently prescribing or administering medications |
|
|
4 common defenses to medical malpractice claims
|
1. Defendant did not depart from the standard of care
2. It would not have made a difference 3. Not Defendant’s responsibility 4. Patient Negligence |
|
|
Does a plaintiff need an expert witness to prove a podiatric malpractice case?
|
Yes, expert medical testimony is necessary because jurors are idiots, but the expert doesn't have to be a specialist in that field
|
|
|
True or False?
McGlamry’s Comprehensive Textbook of Foot and Ankle Surgery is always recognized as the standard of care. |
False
|
|
|
Which of the following is a defense to a claim of lack of informed consent?
a)The patient could not give informed consent because of a language barrier between the patient and podiatrist. b)The patient had a lot of pain and wanted to have surgery. c)The treatment was indicated according to the judgment of the podiatrist. d)The risks of treatment were so obvious. |
a
|
|
|
What is in the informed consent?
|
(1) the patient's existing physical condition; (2) the purposes and advantages of the operation, procedure or medication; (3) the reasonably foreseeable risks to the patient's health or life which the operation, procedure or medication may impose; (4) the risks involved to the patient if there is no operation, procedure or use of medication; and (5) the available alternatives and the risks and advantages of those alternatives.
|
|
|
treated at hospital by private physician, is it the hospital or the physicians responsibility to get the informed consent?
|
private physician
|
|
|
when is disclosure not required in informed consent?
|
(a) the risk not disclosed is too commonly known to warrant disclosure
(b) the patient assured the doctor that he or she would undergo the treatment or procedure regardless of the risk involved c) that he or she did not want to be informed of the matters to which the patient would be entitled to be informed d) consent by or on behalf of the patient was not reasonably possible. |
|
|
2 circumstances of battery?
|
1)operating without consent
2)performing surgery beyond the scope of consent |
|
|
What is the National Practitioner’s Data Bank?
|
NPDB is an information clearinghouse to collect and release information related to the professional competence and conduct of physicians, and other health care practitioners.
|
|
|
3 elements of lack of informed consent
|
Elements
1. Did Defendant before obtaining plaintiff’s consent to the procedure provide appropriate information? 2. Would a reasonably prudent person in plaintiff’s position at the time consent was given have given such consent if given appropriate information? 3. Was the procedure a substantial factor in causing the injury to plaintiff? |
|
|
If a podiatrist is negligent, what type of damages will the patient not be entitled to recover?
a)The income lost while the patient was recovering from the negligent treatment b)The cost of the medical care the patient will need in the future c)The reasonable value of their pain and suffering d)The reasonable value of the pain caused by any pre-existing medical problem |
D
|
|
|
main reason Why Doctors Are Sued
|
Breakdown in communication between patient and the doctor
|
|
|
What is the purpose of medical records? Legal implications of inadequate medical records
|
Requirement that doctors maintain a medical record
-Document all findings? SOAP -Document patient complaints, instructions, informed consent discussion, non-compliance -Inadequate records lose lawsuits and may prevent a doctor from being paid |
|
|
Likelihood ratio
|
combines sensitivity and specificity
-true posiive/false positive |
|
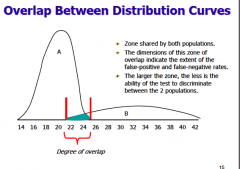
|
-overlap tells you how much you can't distinguish between A and B, A is positive test and B is negative test
-small overlap=high discriminant value= GOOD TEST -big overlap=low discriminant value=BAD TEST |
|
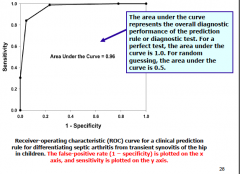
|
Area under the curve tells you how good the diagnostic test is
this is a reciever operating characteristic curve! ROC curve |
|
|
p-value
|
probability value, tells you how confident you can be that the difference between two groups are statistically significant and not due to random error
-you want it to be <.05 |
|
|
what does parameter describe?
|
population
|
|
|
what does statistic describe?
|
sample
|
|
|
confidence level (u)
|
tells you how confident you are that something will be between two intervals
- |
|
|
Type I error
|
rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true
-alpha |
|
|
Type II error
|
failing to reject a null hypothesis when it is false
-Beta |
|
|
univariable analysis
|
is one DV and no IV
-mean and median |
|
|
bivariable anyalysis
|
1 DV and 1 IV
|
|
|
chi square
|
is a tool used to anyalze the freques or proportions
-use "Goodness of fit" line to compare actual vs theoretical frequencies |
|
|
multivariable analysis
|
one DV and two or more IV
|

