![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Overview: Step I + II |
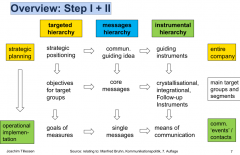
|
|
|
«Betty Bossi»-Recipe: 10 Steps of IMC |
1. SWOT-analysis / challenge/objectives of communication 2. Strategic positioning 3. Primary and secondary target groups 4. Objectives for target groups (goals of communication) 5. Core idea, core and single messages 6. Guiding instrument, supporting tools, principles of design 7. Goals of the measures and means of communication 8. Communication budget 9. Organisational rules for implementation 10. IMC Controlling |
|
|
Step 1 SWOT-Analysis |
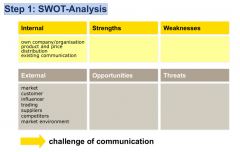
|
|
|
Step 1: internal factors > marketing mix |
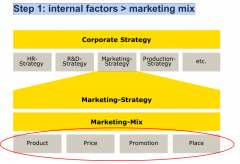
|
|
|
Step 1: External factors > market system |
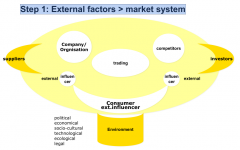
|
|
|
Step 2: Definition of Strategic Positioning |
The strategic positioning describes the main target of the overallcommunication. It is therefore basis for the formulation and integrationresp. hierarchisation of all communication targets. It describes how acompany/organisation resp. the communication object itself would liketo be experienced by the core target groups in a short to long periodin comparision with its competitors. |
|
|
Step 2: Strategic Positioning –characteristics |
► describes experience of the market performance (company,products, brands, services) by all target groups ► bases on a strategic competitive advantage and describes a brandpromise ► gives answer to the question: «What’s in it for me?» ► has a mid to long focal period ► bases pm the corporate strategy ► is effective as an integrative link for the overall communication ► will be applied to all further communication decisions |
|
|
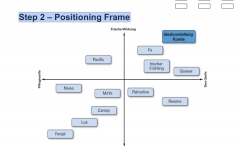
Step 2: Strategic Positioning –perception |
Axes titling within the positioning system/frame |
|
|
Step 2 – Positioning Frame |
|
|
|
Step 2: Strategic Positioning –Positioning Statement |
possible content: • rational part: – USP (Unique Selling Proposition) – Product Benefit • emotional part – UCP (Unique Communications Proposition) – Consumer Benefit |
|
|
Step 2: Strategic positioning –Positioning Statement |
possible structure (according to Y&R-group): • for what > target group (perspective) • is > what context (brand competence) • which > promise (rather emotional) • because > argumentation/reason why (rather rational) |
|
|
Step 2: Strategic Positioning –requirements |
• relevance from a customer’s point of view • focus only on key characteristics (single-minded) • discrimination ability: unique! • future orientated: targeted image • flexibility in case of changing environmental conditions • continuity in core positioning • operational ability: practicable, workable! |
|
|
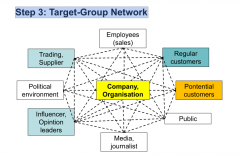
Step 3: Target-Group Network |
|
|
|
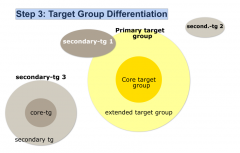
Step 3: Target Group Differentiation |
|
|
|
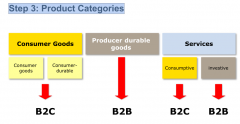
Step 3: Product Categories |
|
|
|
Step 3: Target Groups in Consumer Markets (summarized) |
socio-demografic psychological/-graphical 209 |
|
|
socio-demographic |
• gender • age • residence • size of household • income • profession • education • family status • type of settlementeconomical area |
|
|
psychological/-graphical |
• attitude/motivation• consumption behaviour• communicationbehaviour |
|
|
step 4: definition of target groupscommunikation goals |
Objectives for target groups (communication goals) provide acontribution to reach a strategic position (main target). They aremedium-term orientated and differently formulated for individualtarget groups. |
|
|
step 4: objectives target groups- (communication goals) –AIDA-formula |
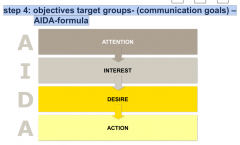
|
|
|
step 4: objectives target groups- (communication goals) –categories |
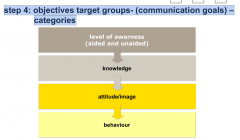
|
|
|
step 4: objectives target groups –pyramid of brand awarness |
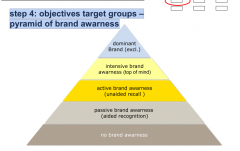
|
|
|
step 4: objectives target groups (communication goals) –definition of goals |
• content (What should be achieved) • dimension / degree (to what degree) • segments (at which target group) • geographical region/area (In which region/area) • time period (And in which time period) |
|
|
step 5a: def. of communicative core idea |
The communicative core idea is a basic message about the firm, resp.about the object of communication (e. g. product, service) whichconcerns the essential characteristics of its positioning It is therefore a simply to communicate guiding principle (leitmotiv)which depends not on a specific target group and serves as key signal(internal and external) |
|
|
step 5a: communicative core idea – ex. claim/slogan – ex. logo/symbol – ex. leading figure – ex. key visual |
• Raiffeisen – Wir machen den Weg frei • Audi – Vorsprung durch Technik • Mc Donald‘s – i‘m lovin‘ it • Nike – just do it • Toyota – Today. Tomorrow. Toyota. • Coop – Für mich und dich • Migros – Ein besser • etc. |
|
|
step 5b/c: definition core- and single-messages |
Core messages concertize the communicative core idea of a firm,resp of the object of communication. They build up a system of mainmessages, structured accordingly to the target groups. Single messages are proofs resp evidences for the core messages ofa firm resp of the object of communication.They form a system of cardinal patterns of argumentation,structured accordingly to the main target groups. |
|
|
Step 5b/c: Core- and single messages –possible content |
• core messages as a rational promise of performance – USP (Unique Selling Proposition) – Product Benefit • core messages as a emotional promise of performance – UCP (Unique Communications Proposition) – Consumer Benefit • single messages = Reason why (proof of promises) – facts, examples, stories, events etc. – recommendation Bruhn: 10–20 per core message! |
|
|
step 6a: guiding instrument – definition |
Guiding instruments are cardinal communication instruments andare defined on the level of the overall communication of a firm, respobject of communication.They are of specific strategic importance and best able to„transporte“ the communicative core idea. Therefore they overtake aleading function for the other communication instruments (highpotential of influence). |
|
|
step 6a/b: choice of communication instruments |
• (media-)advertising • personal sales (communication) • promotion • direct marketing • sponsoring (incl. product placement) • event marketing • fairs/exhibitions • (product) public relations • internal communication • social media-communication |
|
|
step 6a/b: instrument categorising –analysis of cross-Impact |
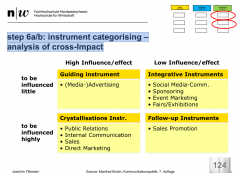
|
|
|
step 6c: design principles= Corporate Design |
• name• logo/signet• elements of design• colour system• typo system• visual language• layout principles• jingles• dress codes• etc. |
|
|
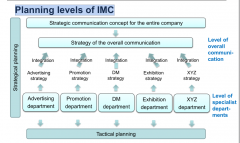
Planning levels of IMC |
|
|
|
Step 7a: Objectives of Measures – Definition |
Objectives of measures are short term orientated and definedaccording to „communication contacts“ with the target groups.They provide a contribution to reach target group goals and are relatatedto the concrete application of the communication instruments(highly operational). |
|
|
Step 7a: Objectives of Measures – Possible Content |
Basic communication goals, regarding instruments • same content as objectives for target groups:level of awareness, knowledge, attitude/image, behavior Additional goals: • e.g. sales promotion: sales targets, turn-over etc. • e.g. public relations: confidence, motivation, credibility etc.(media-PR: number of clippings etc.) • e.g. direct marketing: response, return rates etc. • e.g. event marketing: number of participants |
|
|
Step 7b: Definition Means of Communication |
Means of communication are real, sense perceivable forms (inappearance) of communication messages. They replace the original communication between people and allowreproduction |
|
|
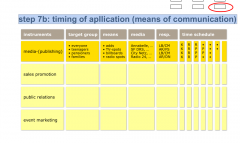
step 7b: timing of application (means of communication) |
|
|
|
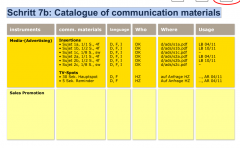
Step 7b: Catalogue of communication materials |
|
|
|
Step 8: Definition of Communication Budget |
4 methods of budgeting • percentage of turnover, previous year etc. • profit targeting («all you can afford») • orientation at competitors • objective-measures calculation |
|
|
Step 8: Communication Budget – Allocation |
Functionality in terms of time allocation • communication instruments • products • target / consumer groups • distribution channels • etc. notice:Never forget costs for research and externalpartners / consultants! |
|
|
Step 8: Communication Budget – Planning of breakdown to single instruments and measures |
Detail calculation on the level of single communication instruments andmeasures e. g. (media) publishing:• concept/creation• realisation• production• media and distribution costs• reserve• fees• total |
|
|
Step 8: Communication Budget – Overview |

|
|
|
step 9: organizational rules – rules of cooperation |
structuring and formalisation of • organizational structure(responsibility and competences) • organizational processes • cooperation between centralized and decentralizedcommunication departments |
|
|
Step 10: Controlling of IMC |
4 types of controlling • Process controlling – check of integration degree – check of successful reduction of barriers • Performance controlling – controlling of target group and measured goals (research!) – controlling of reached consistency (messages, CD etc.) • Efficiency controlling – cost-benefit comparison: economic approachof controlling the communication budget • Premise controlling – check whether the premises at the start were ok |

