![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Know the three mechanisms for demyelinating disorders and examples of each.
|
1. Destruction of normal myelin
-Example: multiple sclerosis 2. Production of abnormal myelin -Example: leukodystrophy 3. Destruction of oligodendrocytes -Examples: multiple sclerosis, slow virus infections |
|
|
Epidemiology of multiple sclerosis
|
1) Most common demyelinating disease
2) Female predominance -Occurs in women 20-40 years old. 3) Most common demyelinating disease |
|
|
Pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis.
|
(1)CD8 T cell destruction of myelin sheaths and/or oligodendrocytes.
(2) Antibodies directed against myelin basic protein in oligodendrocytes |
|
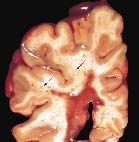
Gross findings (be able to identify)of multiple sclerosis.
|
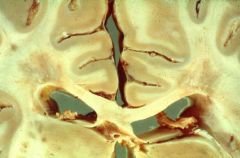
Demyelinating plaques occur in white matter of brain/spinal cord (Slide 35, 36)
|
|
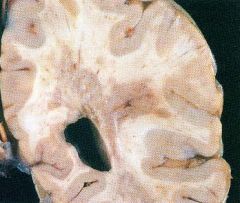
Clinical findings of multiple sclerosis.
|
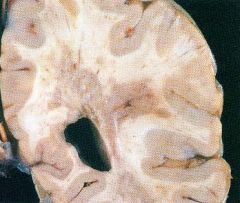
(1) Episodic course punctuated by acute relapses and remissions
(2) Sensory and motor dysfunction •Paresthesias, muscle weakness (3) Optic neuritis (a)Inflammation of the optic nerve (b)Blurry vision or sudden loss of vision (4) Cerebellar ataxia (5) Scanning speech (sound drunk) (6) Intention tremor, nystagmus (7) Bilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia (see schematic next page) • Demyelination of medial longitudinal fasciculus |
|
Regarding multiple sclerosis, laboratory findings.
|
(1) Increased CSF leukocyte count
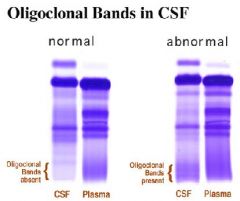
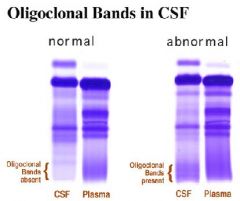
•Primarily T lymphocytes (2) Increased CSF protein •Primarily an increase in γ-globulins (3) Increased CSF myelin basic protein •Indicates active disease (4) Normal CSF glucose (5) High resolution electrophoresis shows oligoclonal bands (a) Discrete bands of protein in the γ-globulin region (b) Sign of demyelination |
|
|
MS:
|
autoimmune destruction of myelin sheath and oligodendrocytes
|
|
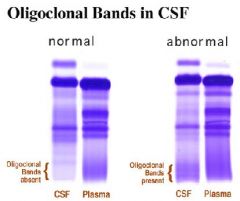
Oligoclonal bands in CSF electrophoresis:
|
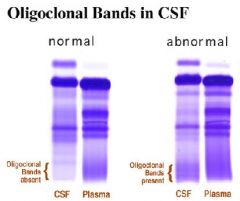
sign of demyelination
|
|
|
Epidemiology of central pontine myelinolysis.
|
Most often occurs in alcoholics who have hyponatremia
|
|
|
pathogenesis of central pontine myelinolysis
|
Rapid intravenous correction causes demyelination in the basis pontis.
|
|

What is this?
|

Gross findings of central pontine myelinolysis
|
|
|
Central pontine myelinolysis:
|
due to rapid intravenous correction of hyponatremia
|
|
|
State examples of viral infections that infect oligodendrocytes causing demyelination.
|
-subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
-progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy |
|
|
Mendelian inheritance of Adrenoleukodystrophy
|
X-linked recessive disorder
|
|
|
Enzyme deficiency of
Adrenoleukodystrophy |
Enzyme deficiency in β-oxidation of fatty acids in peroxisomes.
|
|
|
Accumulation products of Adrenoleukodystrophy
|
Results in accumulation of long-chain fatty acids
|
|
|
Clinical findings and gross findings of Adrenoleukodystrophy
|
Causes generalized loss of myelin in the brain and adrenal insufficiency
|
|
|
Mendelian Inheritance of Metachromatic leukodystrophy
|
Autosomal recessive disorder
|
|
|
Enzyme deficiency of Metachromatic leukodystrophy
|
Deficiency of arylsulfatase A
|
|
|
Accumulation Products of Metachromatic leukodystrophy
|
Results in accumulation of sulfatides
|
|
|
Clinical and Gross Findings of Metachromatic leukodystrophy
|
Lysosomal storage disease
|
|
|
Mendelian inheritance of Krabbe’s disease
|
Autosomal recessive disorder
|
|
|
Enzyme Deficiency of Krabbe's disease
|
Galactocerebroside β-galactocerebrosidase deficiency
|
|
|
Accumulation product of Krabbe’s disease
|
galactocerebroside
|
|
|
Clinical and Gross Findings of Krabbe’s disease
|
Brain shows large, multinucleated, histiocytic cells (globoid cells)
|

