![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
describe in detail the lifecycle of toxoplasma gondii in the FH
|
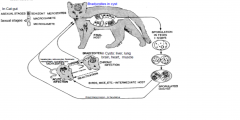
FH- CAT - can be infected in any way self infection with oocysts/ extra intestinal infection/tachyzoites in IH - but usually infected via ingestion of IH which has bradyzoite cysts in tissue./ cysts wall digested and then bradyzoites invade gut epi cells where they undergo shizogony ( schizonts-merozoites ) then gametogony ( merozoites - macro and micro gametocytes which fuse to make a zygote then a oocyyst which is shed in the faeces.)
oocyst takes 1-5 days to sporulate and is unique as it has 2 sporocysts and 4 sporozoites. note the oocysts are only shed for 1-2 weeks then the cat becomes immune. Cats may also have extra-intestinal phase where it generates tachzoites and bradyzoites. |
|
|
describe in detail the lifecycle of toxoplasma gondii in the IMH
|
IH ( all mammals- esp sheep and humans)- usually infected via ingestion of oocyst ( can also be infected by ingestion of another IMH or crossing the placenta in immunocompromised). the sporozoites invade intestinal cells and form tachyzoites. The tachyzoites devide quickly and rupture the epi cell.
EXTRA-INTESTINAL PHASE- they then spread via the blood and lymph and invade any nucleated cell. When the immune system begins to control the tachyzoites then they will form bradyzoite cysts usually in ( brain/ liver/lung/muscle) they may convrt back to tachyzoites if the animal becomes immunocompromised. |
|
|
what shape are tachyzoites
|

cresent shaped
|
|
|
describe the epi of toxocara in sheep.
(do cats shed toxocara gondii oocysts their whole life and roughly how many do they shed and do the oocysts survive in the environment. why is Toxoplasma Gondii such a problem is sheep) |
the cat only sheds oocysts for 1-2 weeks until its immunity prevents shedding. however they may shed millions of oocysts. the oocysts are very resistant and can survive for up to 2 years.
it causes abortion and perinatal mortality. mice act as a reservoir for cat as cats eat mice. Then cats contaminate sheep feed with their faeces containing the toxocara oocyst. Sheep are at risk from Toxoplasma gondii if they ingest the oocysts less than 3 weeks before tupping or during pregnancy. |
|
|
what pathology does the toxoplasma gondii cause in sheep and in cats
|
SHEEP-mainly caused by the extra-intestinal phase.
acute- replication of tachyzoites causes necrosis of vital organs. In a helathy host ( any mammal esp sheep or human ) there may be no clinical signs. there may by pyrexia and lymph N enlargement. The bradyzoites do not cause symptoms. The tachyzoites may come back if the host becomes immunocompromised. CATS- rare to see clinical disease. ( fever, enteritis, pneumonia, ocular lesions) rare to see congenital form ( severe and fatal - hypothermia, anorexia, and sudden death) |
|
|
How does being infected with toxiplasma gondii at different stages of pregnancy in sheep affect the clinical signs?
note (sheep are at risk of abortion if they are infected with toxoplasma gondii 3 weeks before tuping or during pregnancy.) |

infection 0-55 days of gestation ( small foetus expelled or reabsorbed and the farmer will notice it as a barren ewe)
50 - 120 days ( premature birth of weak lambs or stillborn a few days before term. Also if twins there will be 1 chocolate brown mummified foetus) 120 -145 days ( infected but normal lambs) |
|
|
how do you diagnose infection with toxoplasma gondii in sheep
|

1. clinical signs ( barren ewe ( 0-55 days) / weak lamb or still born ( 50-120 days)/ 120-145 ( normal lamb but infected) and lesions on the placenta ( small white foci of necrosis on the cotyledons- focal placentitis )
2 .Ab test for toxoplasma gondii in foetal fluids or pre colostral lamb serum. take paired samples. IgM??? 3 .Inoculate mice with test tissue ( but takes 3 weeks). 4. Immunohistochem. to detect parasite. 5. PCR of placental tissue. |
|
|
how can toxoplasma gondii infection be controlled
|
PREVENT INFECTION OF CATS- incinerate any material which has been infected with cat faeces/ do not feed raw meat to cats and cook well if you do/ decrease new cats ( who will be infected and shed) by having a neutered tom.
PREVENT INFECTION OF SHEEP- cover feed and prevent access of cats/ retail sheep which have been infected as they will be immune / give the coccidistat decoquinate in feed during pregnancy esp for replacement stock./ Vaccine ( attenuated tachyzoites ) IM > 6 weeks before tupping. protects for 18-24 months. note women and sheep are immune and wont pass it to their foetus unless they are immunocompromised eg in AIDS |
|
|
can humans get toxoplasia from eating undercooked pork
|
yea
|

