![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Components of coagulation system |
(1) Vasculature (2) Platelets (3) Clotting pathway |
|
|
Role of platelets in hemostasis |
(1) Platelet adhesions to subendothelial connective tissue (2) Release of granules (ADP, Thromboxane) (3) Platelet Aggregation (4) Stabilization of hemostatic plug (5) Stimulation of limiting reactions |
|
|
Clotting cascade |
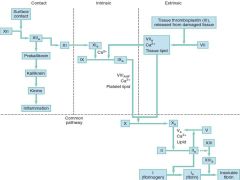
|
|
|
Thrombin sensitive factors |
I, V, VIII, XIII |
|
|
Vitamin K sensitive factors |
II, VII, IX, X |
|
|
Instrinsic Clotting Factors |
XII, XI, IX, VIII |
|
|
Extrinsic Clotting Factors |
VII |
|
|
Common Pathway Clotting Factors |
X, V, II (Thrombin), I (Fibrinogen) |
|
|
Activity of Protein C & S |
Inhibit cofactors Va and VIIIa |
|
|
Action of AntiThrombin |
inhibits the serine proteases (factors II, IX, X, XI, and XII);
its anticoagulant action is dramatically enhanced by heparin |
|
|
Control of excessive thrombis |
(1) Removal/dilution of activated clotting factors through blood flow (3) Removal of activated coagulation components by the reticuloendothelial system
(4) Regulation of the clotting cascade by antithrombin III, protein C, protein S, and tissue factor pathway inhibitor (5) Activation of the fibrinolytic system (plasmin degredation) |
|
|
Differential diagnosis of vascular disorders |
Inherited
|
|
|
Differential Diagnosis of Platelet Disorders |
Thrombocytopenia
Decreased production
Mechanical
Thrombocytopathy
Thrombocytosis |
|
|
Platelet lifespan |
7-10 Days |
|
|
4T's Score for HIT |
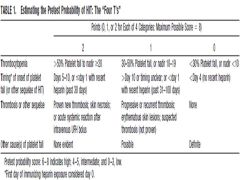
|
|
|
Treatment principles for HIT |
1. Discontinue and avoid all heparin. |
|
|
MOA of HIT |
IgG antibodies that bind to platelet factor 4/heparin complex activating platelets and triggering a pro-coagulant response |
|
|
Algorithim using 4 t's score |
0-3: Consider alternate Dx 4 or greater: D/C Heparin and W/U |
|
|
Rx of significant bleeding in patient with ITP |
Platelets IVIG Cortiosteroids |
|
|
Classic pentad of TTP |
(1) fever (2) hemolytic anemia (3) thrombocytopenia (4) renal impairment (5) neurologic manifestations |
|
|
Causes of TTP |
Idiopathic—most cases |
|
|
Pathophysiology of TTP |
MAHA + Thrombocytopenia without alternate explanation
Deficiency of ADAMTS-13, VWF cleaving protein, leads to platlet aggregation and occlusion of microvasculature |
|
|
TTP Management |
Plasma exchange Corticosteroids Rituximab in Consultation with hematology Platelet Transfusion |
|
|
HUS |
MAHA Thrombocytopenia Bloody Diarrhea Prominent Renal Failure
More common in children |
|
|
Medications implicated in ITP |
Acetaminophen |
|
|
DIC |
DIC is an acquired, systemic process of overstimulation of the coagulation pathway resulting in thrombosis, followed by consumption of platelets and coagulation factors, and ending in hemorrhage |
|
|
When to use heparin in DIC |
If evidence of thromboembolic disease, retained products of conception, or purpura fulminans (gangrene of digits and extremities) and requires a normal antithrombin level before initiation |
|
|
Effect of ASA on platelets |
Blocks enzyme cyclooxygenase, which participates in thromboxane A2 formation
Thereby decreases platelet aggregation |
|
|
Hemophilia A |
Deficient Factor VIII Activity X linked recessive |
|
|
Severity of Hemophillia A by level of factor activity |
<1% severe (Frequent atraumatic bleeds) 1-5% Moderate (Bleed after minor trauma) 5-10% Mild (Bleed after significant trauma) |
|
|
How much will unit/kg of factor VIII:C raise the circulating factory VIII level |
2% |
|
|
Recommended Factor VIII therapy for specific problems in hemophilia from Rosen's |
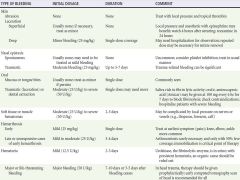
|
|
|
Monitoring response to therapy in Hemophilia |
Clinical Improvement PTT Factor VII coagulant activity |
|
|
Dosage guidelines for Factor VIII |
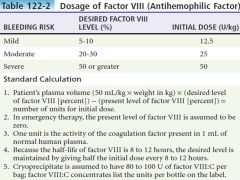
|
|
|
Hemophilia B (Christmas disease) |
Deficient Factor IX Activity
Treatment is similar to Hemophilia A |
|
|
Laboratory findings in keeping with DIC |
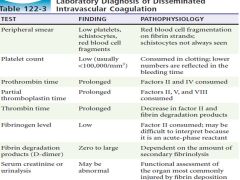
|
|
|
MOA of clopidogrel |
Inhibit ADP induced platelet aggregation |
|
|
Types of VWD |
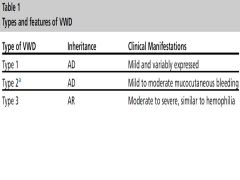
|
|
|
Lab Abnormalities in Congenital Bleeding Disorders |
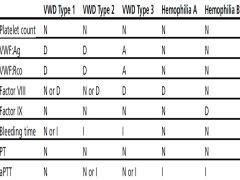
|
|
|
Simplified Factor Level recommendation for Hemophilia from EMNA |
Oral mucosa >30 |
|
|
Treatment of Von Willebrand
|
Type 1 - DDAVP
Type 2/3 - VWF Replacement |
|
|
Treatment in patients with Factor inhibitors (antibodies) |
aPCC (octoplex) rFVIIa |
|
|
Hemophiliac patients who are candidates for prophylactic admissions |
Deep lacerations Soft tissue in areas compromised by expanding hematomas - Eye - Airway - Spinal Column - Head trauma |

