![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What arteries supply the anterior circulation of the brain?
|
The two internal carotid arteries.
|
|
|
What foramen does the internal carotid artery (ICA) enter the skull through?
|
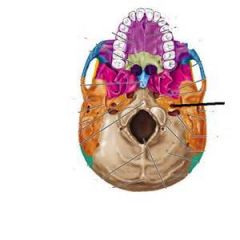
The carotid canal in the temporal bone
|
|
|
What arteries branch off the ICA?
|
1. ophthalmic artery
2. middle cerebral artery 3. anterior choroidal artery 4. anterior cerebral artery |
|
|
What does the ophthalmic artery supply?
|
The eye and orbital contents
|
|
|
What does the middle cerebral artery (MCA) supply?
|
Curves laterally to the sylvian fissure where it supplies the lateral surface of the brain (frontal, parietal and some of the temporal lobes)
|
|
|
What artery does the MCA give off before entering the sylvian fissure?
|
The lenticulostriate arteries which are small penetrating arteries that supply most of the internal capsule.
|
|
|
What do the lenticulostriate arteries supply?
|
Most of the internal capsule
|
|
|
What regions of the brain are supplied by the MCA?
|
1. primary motor cortex and sensory cortex for face and arm > leg
2. frontal eye fields 3. Broca's area 4. Wernicke's area 5. optic radiations 6. internal capsules (posterior limb and genu motor fibers) 7. much of basal ganglia |
|
|
Where does the anterior choroidal artery branch off the ICA?
|
A few mm above the posterior communicating artery.
|
|
|
What does the anterior choroidal artery supply?
|
part of the choroid plexus as well as the optic tract and posterior limb of the internal capsule.
|
|
|
Where is the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) located?
|
The ACA curves over the genu of the corpus callosum in the interhemispheric fissure to supply the medial surface of the frontal and parietal lobes.
|
|
|
What functions does the ACA supply?
|
1. primary motor and sensory cortex for the leg
2. motor and sensory cortex for the bladder |
|
|
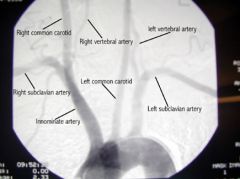
|
|
|
What is a stroke?
|
The sudden occlusion of an artery in the brain that can result in the death of the brain tissue in that vascular distribution.
|
|
|
What arteries supply the entire anterior circulation of the brain?
|
The internal carotid arteries
|
|
|
What supplies the posterior circulation of the brain?
|
Supplied entirely by the vertebral arteries which originate from the subclavian arteries.
|
|
|
Where do the vertebral arteries originate from?
|
The subclavian arteries
|
|
|
Where do the vertebral arteries join together?
|
At about the junction of the medulla and pons
|
|
|
What artery is formed by the union of the two vertebral arteries?
|
The basilar artery.
|
|
|
What branches do the vertebral arteries give off before joining to form the basilar artery?
|
1. A single anterior spinal artery, which is formed from a contribution from each vertebral artery.
2. The posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) |
|
|
What do the posterior spinal arteries arise from? anterior spinal artery?
|
The paired posterior spinal arteries arise either as a branch of the vertebral arteries or the PICA.
The single anterior spinal artery is formed by contributions from both vertebral arteries. |
|
|
What does the PICA ("posterior inferior cerebellar artery") supply?
|
The lateral medulla and the inferior surface of the cerebellum.
|
|
|
What artery is responsible for the "common stroke"?
|
Occlusion of the PICA.
|
|
|
Where is the basilar artery located?
|
On the surface of the pons and supplies it w/ multiple small penetrating branches.
|
|
|
What artery can be suddenly occluded to result in a devastating stroke that is often accompanied with a coma?
|
The basilar artery b/c it supplies much of the critical brain stem structures.
|
|
|
What artery is formed when the basilar artery divides? where does the division take place?
|
At the junction of the pons and midbrain the basilar artery divides into the two posterior cerebral arteries (PCA).
|
|
|
What do the posterior cerebral arteries (PCA) supply?
|
1. most of the temporal lobes
2. most of the occipital lobes 3. small penetrating branches that supply the thalamus. 4. ascending sensory fibers in the posterior limb of the internal capsule 5. part of the midbrain. |
|
|
What supplies most of the choroid plexus in the lateral and third ventricles?
|
A branch of the PCA the posterior choroidal artery
|
|
|
What arteries contribute to the circle of willis?
|
1. anterior communicating artery
2. anterior cerebral artery 3. internal carotid artery 4. posterior communicating artery 5. posterior cerebral artery |
|
|
What is the importance of the circle of willis?
|
Important in providing alternative routes of blood flow when there is cerebrovascular disease
|
|
|
What is the importance of the anastomosis b/e the posterior communicating artery? what does it attach together?
|
The posterior communicating artery links the ICA to the proximal portion of the posterior cerebral artery.
SO blood from the anterior circulation can supply some of the vasculature of the posterior circulation and vice versa. |
|
|
What nerve does the posterior communicating artery pass under? why is this important?
|
The oculomotor nerve (CNIII); this is important since aneurysms that arise from the posterior communicating artery result in third nerve palsy.
|
|
|
What does the anterior communicating artery link together? why is this important?
|
The anterior communicating artery links the two ACAs and allows one ACA to supply the other ACA if needed.
|
|
|
How can the external carotid supply the ICA vasculature if needed?
|
The ophthalmic artery may receive retrograde blood flow from the external carotid artery which allows the ECA to supply the ICA vasculature if needed.
|
|
|
What do the leptomeningeal anastomotic vessels do?
|
Allow communication b/e the distal portions of the ACA, MCA and posterior cerebral arteries.
|
|
|
B/e what layers are the venous sinuses located?
|
B/e the two layers of the dura matter
|
|
|
Where is the superior sagittal sinus located?
|
Along the attached border of the falx cerebri.
|
|
|
What does the SSS drain?
|
Drains the confluence of sinuses at the occipital protuberance.
|
|
|
What does the SSS drain into?
|
Drains into the transverse sinus
|
|
|
Where is the transverse sinus located?
|
In a groove on the occipital bone along the lateral margin of the tentorium cerebelli.
|
|
|
Where is the sigmoid sinus located?
|
Follows a curved course in the mastoid process of the petrous bone and eventually becomes continuous w/ the internal jugular vein at the jugular foramen.
|
|
|
What do the deep areas of the brain drain into?
|
Into the paired internal cerebral veins
|
|
|
What do the internal cerebral veins become?
|
They join to form the Great vein of Galen.
|
|
|
What does the Great vein of Galen become?
|
Joins w/ the inferior sagittal sinus to form the straight sinus which lies in the attachment of the falx cerebri to the tentorium cerebelli.
|
|
|
Where does the inferior sagittal sinus run?
|
Along the inferior edge of the falx cerebri.
|
|
|
What do the eyes drain into?
|
They drain via the cavernous sinuses
|
|
|
Where are the cavernous sinuses located?
|
On either side of the sphenoid bone.
|
|
|
What do the cavernous sinuses drain into?
|
The transverse sinus via the superior petrosal sinus AND directly into the internal jugular vein via the inferior petrosal sinus.
|
|
|
What does venous occlusion cause symptom-wise?
|
Results in increased intracranial pressure and ischemic and hemorrhagic infarctions.
|
|
|
What is the most common venous sinus involved in venous occlusion in the brain?
|
Superior sagittal sinus
|
|
|
What disorders commonly cause increased intracranial pressure as a result of venous occlusion?
|
Coagulopathies as a late complication of pregnancy.
|
|
|
What supplies the anterior spinal artery and the two posterior spinal arteries rostrally?
|
The vertebral arteries
|
|
|
What supplies the anterior/posterior spinal arteries distal to the upper cervical level?
|
The anterior and posterior radicular arteries
|
|
|
What are the anterior and posterior radicular arteries branches of?
|
They arise from the vertebral artery and thyrocervical trunk (from subclavian) as well as the intercostal and lumbar arteries (from the aorta)
|
|
|
What boosts the blood supply to the lower thoracic and upper lumbar spinal cord?
|
The artery of Adamkiewicz which is a large radicular artery.
|
|
|
What is the watershed artery of the spinal cord?
|
B/e the rostral radicular arteries and the artery of Adamkiewicz or roughly spinal cord levels T1-T4 because of the gap in a booster artery b/e the cervical and lower thoracic arteries.
|

